|
Analogue Robot
An analog robot is a type of robot which uses analog circuitry to go toward a simple goal such as finding more light or responding to sound. The first real analog robot was invented in the 1940s by William Grey Walter. The name of these robots were ELSIE and ELMER (Electro Mechanical Robot). The original circuitry was developed using two vacuum tubes and a photocell to search and follow a light. Recently a kind of analog robots was developed by Mark Tilden. Some modern analog robots are BEAM robots. Braitenberg Vehicles A Braitenberg vehicle is a concept conceived in a thought experiment by the Italian-Austrian cyberneticist Valentino Braitenberg. The book models the animal world in a minimalistic and constructive way, from simple reactive behaviours (like photota ... (described by Valentino Braitenberg) also are frequently analog, consisting of the output of sensors connected to motors without any form of signal processing. See Also * Analog computer External links BEAM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robot
A robot is a machine—especially one programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the control may be embedded within. Robots may be constructed to evoke human form, but most robots are task-performing machines, designed with an emphasis on stark functionality, rather than expressive aesthetics. Robots can be autonomous or semi-autonomous and range from humanoids such as Honda's ''Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility'' ( ASIMO) and TOSY's ''TOSY Ping Pong Playing Robot'' ( TOPIO) to industrial robots, medical operating robots, patient assist robots, dog therapy robots, collectively programmed ''swarm'' robots, UAV drones such as General Atomics MQ-1 Predator, and even microscopic nano robots. By mimicking a lifelike appearance or automating movements, a robot may convey a sense of intelligence or thought of its own. Autonomous things are expected to proliferat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Circuit
Analogue electronics ( en-US, analog electronics) are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal. The word analogue is derived from the el, word ανάλογος (analogos) meaning "proportional". Analogue signals An analogue signal uses some attribute of the medium to convey the signal's information. For example, an aneroid barometer uses the angular position of a needle as the signal to convey the information of changes in atmospheric pressure. Electrical signals may represent information by changing their voltage, current, frequency, or total charge. Information is converted from some other physical form (such as sound, light, temperature, pressure, position) to an electrical signal by a transducer which converts one type of energy into another (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Grey Walter
William Grey Walter (February 19, 1910 – May 6, 1977) was an American-born British neurophysiologist, cybernetician and robotician. Early life and education Walter was born in Kansas City, Missouri, United States, on 19 February 1910, the only child of Minerva Lucrezia (Margaret) Hardy (1879–1953), an American journalist and Karl Wilhelm Walter (1880–1965), a British journalist who was working on the Kansas City ''Star'' at the time. His parents had met and married in Italy, and during the First World War the family moved from to Britain. Walter's ancestry was German/British on his father's side, and American/British on his mother's side. He was brought to England in 1915, and educated at Westminster School with an interest in classics and science, and entered King's College, Cambridge, in 1928. He achieved a third class in part one (1930) and a first class in physiology in part two of the natural sciences tripos (1931). He failed to obtain a research fellowship in Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elsie (robot)
William Grey Walter (February 19, 1910 – May 6, 1977) was an American-born British neurophysiologist, cybernetician and robotician. Early life and education Walter was born in Kansas City, Missouri, United States, on 19 February 1910, the only child of Minerva Lucrezia (Margaret) Hardy (1879–1953), an American journalist and Karl Wilhelm Walter (1880–1965), a British journalist who was working on the Kansas City ''Star'' at the time. His parents had met and married in Italy, and during the First World War the family moved from to Britain. Walter's ancestry was German/British on his father's side, and American/British on his mother's side. He was brought to England in 1915, and educated at Westminster School with an interest in classics and science, and entered King's College, Cambridge, in 1928. He achieved a third class in part one (1930) and a first class in physiology in part two of the natural sciences tripos (1931). He failed to obtain a research fellowship in Cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elmer (robot)
William Grey Walter (February 19, 1910 – May 6, 1977) was an American-born British neurophysiologist, cybernetician and robotician. Early life and education Walter was born in Kansas City, Missouri, United States, on 19 February 1910, the only child of Minerva Lucrezia (Margaret) Hardy (1879–1953), an American journalist and Karl Wilhelm Walter (1880–1965), a British journalist who was working on the Kansas City ''Star'' at the time. His parents had met and married in Italy, and during the First World War the family moved from to Britain. Walter's ancestry was German/British on his father's side, and American/British on his mother's side. He was brought to England in 1915, and educated at Westminster School with an interest in classics and science, and entered King's College, Cambridge, in 1928. He achieved a third class in part one (1930) and a first class in physiology in part two of the natural sciences tripos (1931). He failed to obtain a research fellowship i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Tilden
Mark W. Tilden is a robotics physicist who produces complex robotic movements from simple analog logic circuits, often with discrete electronic components, and usually without a microprocessor. He is controversial because of his libertarian Tilden's Laws of Robotics, and is known for his invention of BEAM robotics and the WowWee Robosapien humanoid robot. Early career Born in the UK in 1961, raised in Canada, Tilden started at the University of Waterloo then moved on to the Los Alamos National Laboratory where he developed simple robots such as the SATbot which instinctively aligned itself to the magnetic field of the earth, de-mining insectoids, "Nervous Network" theory and applications, interplanetary explorers, and behavioral research into many solar-powered "Living Machines" of his own design. Tilden later referred to his early robots as "wimpy" for the results of their programming using Isaac Asimov's Three Rules of Robotics. He accordingly promulgated another set of thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BEAM Robotics
BEAM robotics (from biology, electronics, aesthetics and mechanics) is a style of robotics that primarily uses simple analogue circuits, such as comparators, instead of a microprocessor in order to produce an unusually simple design. While not as flexible as microprocessor based robotics, BEAM robotics can be robust and efficient in performing the task for which it was designed. BEAM robots may use a set of the analog circuits, mimicking biological neurons, to facilitate the robot's response to its working environment. Mechanisms and principles The basic BEAM principles focus on a stimulus-response based ability within a machine. The underlying mechanism was invented by Mark W. Tilden where the circuit (or a Nv net of Nv neurons) is used to simulate biological neuron behaviours. Some similar research was previously done by Ed Rietman in 'Experiments In Artificial Neural Networks'. Tilden's circuit is often compared to a shift register, but with several important features makin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
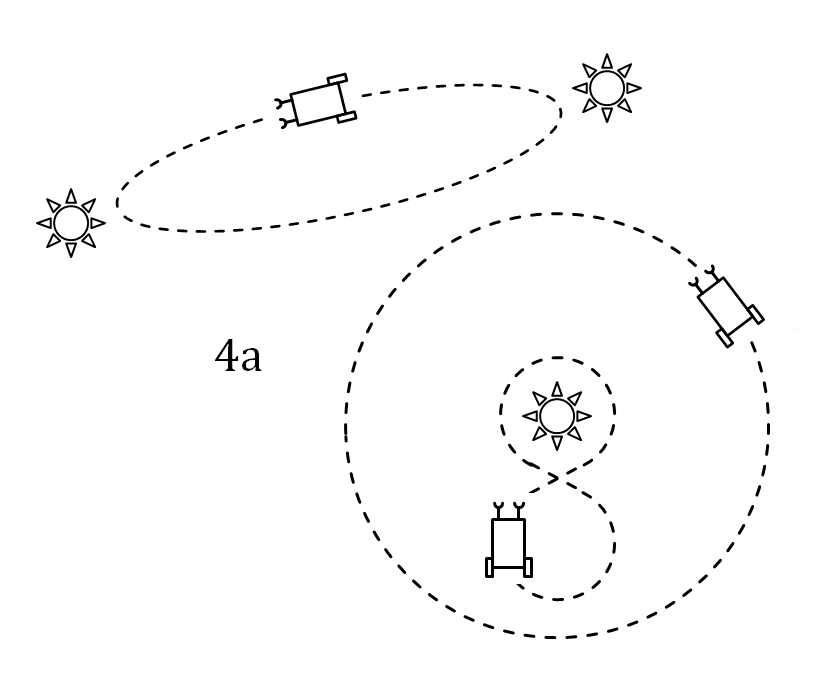
Braitenberg Vehicles
A Braitenberg vehicle is a concept conceived in a thought experiment by the Italian-Austrian cyberneticist Valentino Braitenberg. The book models the animal world in a minimalistic and constructive way, from simple reactive behaviours (like phototaxis) through the simplest vehicles, to the formation of concepts, spatial behaviour, and generation of ideas. For the simplest vehicles, the motion of the vehicle is directly controlled by some sensors (for example photo cells). Yet the resulting behaviour may appear complex or even intelligent. Mechanism A Braitenberg vehicle is an agent that can autonomously move around based on its sensor inputs. It has primitive sensors that measure some stimulus at a point, and wheels (each driven by its own motor) that function as actuators or effectors. In the simplest configuration, a sensor is directly connected to an effector, so that a sensed signal immediately produces a movement of the wheel. Depending on how sensors and wheels are con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valentino Braitenberg
Valentino Braitenberg (or ''Valentin von Braitenberg''; 18 June 1926 – 9 September 2011) was an Italian neuroscientist and cyberneticist. He was former director at the Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics in Tübingen, Germany. His book '' Vehicles: Experiments in Synthetic Psychology'' became famous in Robotics and among Psychologists, in which he described how hypothetical analog vehicles (a combination of sensors, actuators and their interconnections), though simple in design, can exhibit behaviors akin to aggression, love, foresight, and optimism. These have come to be known as Braitenberg vehicles. His pioneering scientific work was concerned with the relation between structures and functions of the brain. Life Valentino Braitenberg grew up in the province of South Tyrol. Braitenberg's father was Senator , a member of the South Tyrolean nobility. Since the age of 6, Braitenberg grew up bilingual in the two languages Italian and German. German was spoken at hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Computer
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities (''analog signals'') to model the problem being solved. In contrast, digital computers represent varying quantities symbolically and by discrete values of both time and amplitude ( digital signals). Analog computers can have a very wide range of complexity. Slide rules and nomograms are the simplest, while naval gunfire control computers and large hybrid digital/analog computers were among the most complicated. Complex mechanisms for process control and protective relays used analog computation to perform control and protective functions. Analog computers were widely used in scientific and industrial applications even after the advent of digital computers, because at the time they were typically much faster, but they started to become obsolete as early as the 1950s and 1960s, although they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robots
"\n\n\n\n\nThe robots exclusion standard, also known as the robots exclusion protocol or simply robots.txt, is a standard used by websites to indicate to visiting web crawlers and other web robots which portions of the site they are allowed to visit.\n\nThis relies on voluntary compliance. Not all robots comply with the standard; email harvesters, spambots, malware and robots that scan for security vulnerabilities may even start with the portions of the website where they have been told to stay out.\n\nThe \"robots.txt\" file can be used in conjunction with sitemaps, another robot inclusion standard for websites.\n History\nThe standard was proposed by Martijn Koster, when working for Nexor in February 1994\n on the ''www-talk'' mailing list, the main communication channel for WWW-related activities at the time. Charles Stross claims to have provoked Koster to suggest robots.txt, after he wrote a badly-behaved web crawler that inadvertently caused a denial-of-service attack on Kos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |