|
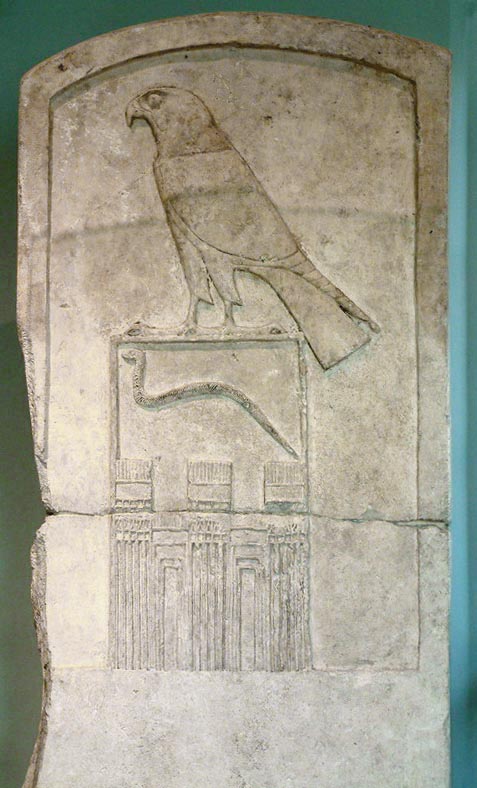
Amyrtaios
Amyrtaeus ( , a Hellenization of the original Egyptian name Amenirdisu) of Sais, is the only pharaoh of the Twenty-eighth Dynasty of EgyptCimmino 2003, p. 385. and is thought to be related to the royal family of the Twenty-sixth Dynasty (664–525 BC). He ended the first Persian occupation of Egypt (i.e. the Twenty-seventh Dynasty: 525–404 BC) and reigned from 404 BC to 399 BC.Clayton 1999, p. 202. Amyrtaeus' successful insurrection inaugurated Egypt's last significant phase of independence under native sovereigns, which lasted for about 60 years until the Persians conquered the country again. Biography Sources and identity Sextus Julius Africanus (''Chronographiai'') calls him "Amyrteos", while Eusebius of Caesarea (''Chronicon'') calls him "Amirtaios" — both of them recording that he reigned for 6 years. An ancient Egyptian prophetic text, the ''Demotic Chronicle'' (3rd/2nd century BC), states: Amyrtaeus was probably the grandson of the Amyrtaeus of Sais who, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inaros II
Inaros (II), also known as Inarus, (fl. ca. 460 BC) was an Egyptian rebel ruler who was the son of an Egyptian prince named Psamtik, presumably of the old Saite line, and grandson of Psamtik III. In 460 BC, he revolted against the Persians with the help of his Athenian allies under Admiral Charitimides, and defeated the Persian army commanded by satrap Achaemenes. The Persians retreated to Memphis, but the Athenians were finally defeated in 454 BC by the Persian army led by Megabyzus, satrap of Syria, and Artabazus, satrap of Phrygia, after a two-year siege. Inaros was captured and carried away to Susa where he was reportedly crucified in 454 BC. Revolt and aftermath He held a kingship over the Libyans from Mareia (above Pharos) and the part of the Nile Delta around Sais. With help from Amyrtaeus, also from Sais, who took the northern marshes, Inarus drove out the tax-collectors while collecting mercenaries. These actions started a revolt in Egypt at the beginning of the rei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in the ancient region of Syria. For over three thousand years, It is a sub-group of the Semitic languages. Aramaic varieties served as a language of public life and administration of ancient kingdoms and empires and also as a language of divine worship and religious study. Several modern varieties, namely the Neo-Aramaic languages, are still spoken in the present-day. The Aramaic languages belong to the Northwest group of the Semitic language family, which also includes the Canaanite languages such as Hebrew, Edomite, Moabite, and Phoenician, as well as Amorite and Ugaritic. Aramaic languages are written in the Aramaic alphabet, a descendant of the Phoenician alphabet, and the most prominent alphabet variant is the Syriac alphabet. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demotic Chronicle
The ''Demotic Chronicle'' is an ancient Egyptian prophetic text. The work is intended to provide a chronicle of the 28th, 29th and 30th dynastiesBresciani, op. cit., p. 551 – thus the independence interval between the two Persian dominations. Rather than providing historical events occurred during the reigns of the pharaohs of the aforementioned period, the ''Demotic Chronicle'' judges these rulers on the basis of their behaviour, explaining the length and prosperity of their reigns as an expression of divine will. The ''Chronicle'' also emphasizes the misrule of the "Medes" (i.e. the Achaemenids) and of the Ptolemies, and prophesies the coming of a native hero who will ascend to the throne and restore an era of order and justice upon Egypt.Toby Wilkinson, ''The Rise and Fall of Ancient Egypt'', Bloomsbury, London, 2010, p. 481 The anti-Achaemenid themes within the Demotic Chronicle especially focus on Cambyses II, Xerxes I and Artaxerxes III. The manuscript consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
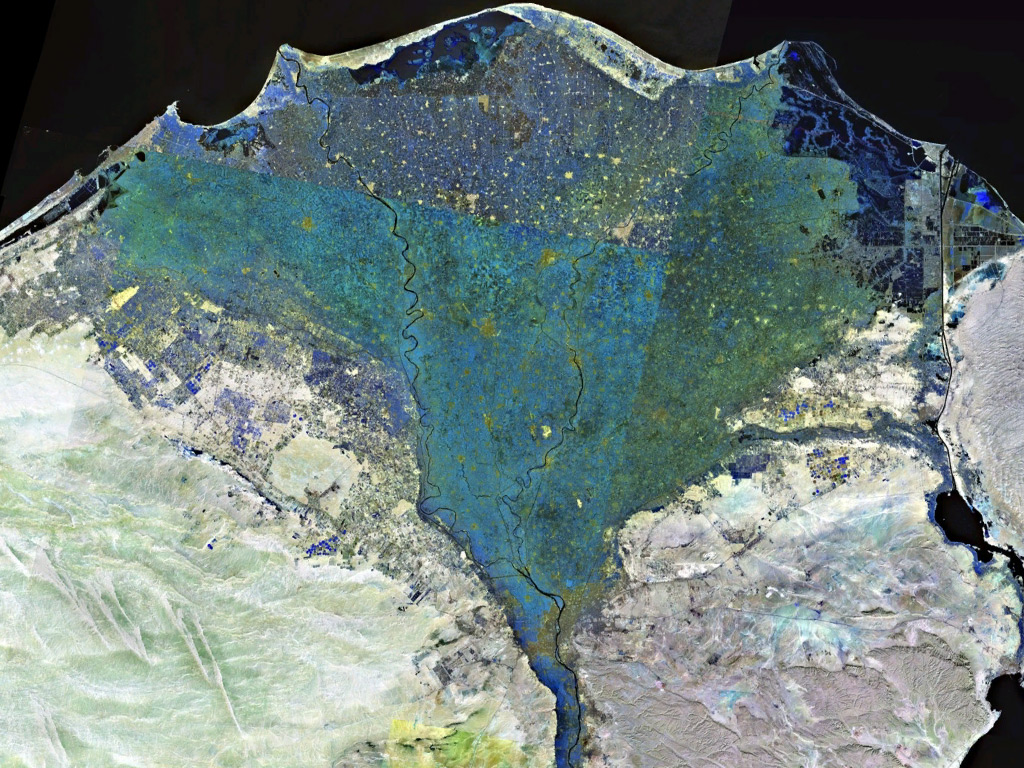
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east, it covers of Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same name. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta and enters the coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darius II
Darius II ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ), also known by his given name Ochus ( ), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 423 BC to 405 or 404 BC. Artaxerxes I, who died in 424 BC, was followed by his son Xerxes II. After a month and half Xerxes II was murdered by his brother Sogdianus. His illegitimate brother, Ochus, satrap of Hyrcania, rebelled against Sogdianus, and after a short fight killed him, and suppressed by treachery the attempt of his own brother Arsites to imitate his example. Ochus adopted the name Darius (Greek sources often call him Darius ''Nothos'', "Bastard"). Neither the names Xerxes II nor Sogdianus occur in the dates of the numerous Babylonian tablets from Nippur; here effectively the reign of Darius II follows immediately after that of Artaxerxes I. Historians know little about Darius II's reign. A rebellion by the Medes in 409 BC is mentioned by Xenophon. It does seem that Darius II was quite dependent on hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronation Of The Pharaoh
A coronation was an extremely important ritual in early and ancient Egyptian history, concerning the change of power and rulership between two succeeding pharaohs. The accession to the throne was celebrated in several ceremonies, rites and feasts. Origins The coronation feast was not one event but rather a long lasting process including several festivals, rites and ceremonies lasting up to a full year. For this reason, Egyptologists today describe the year that a new pharaoh accessed to power as the "year of the coronation".Toby A. H. Wilkinson: ''Early Dynastic Egypt: Strategies, Society and Security''. Routledge, London 2001, , p. 209 - 213.Siegfried Schott: ''Altägyptische Festdaten'' (= ''Akademie der Wissenschaften und der Literatur. Abhandlungen der Geistes- und Sozialwissenschaftlichen Klasse.'' Bd. 10, 1950, ). Verlag der Akademie der Wissenschaften und der Literatur, Mainz u. a. 1950.Margaret Bunson: ''Encyclopedia of Ancient Egypt''. Infobase Publishing, 2009, , p. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Daric 330-300 Obverse CdM Paris
A double is a look-alike or doppelgänger; one person or being that resembles another. Double, The Double or Dubble may also refer to: Film and television * Double (filmmaking), someone who substitutes for the credited actor of a character * ''The Double'' (1934 film), a German crime comedy film * ''The Double'' (1971 film), an Italian film * ''The Double'' (2011 film), a spy thriller film * ''The Double'' (2013 film), a film based on the Dostoevsky novella * '' Kamen Rider Double'', a 2009–10 Japanese television series ** Kamen Rider Double (character), the protagonist in a Japanese television series of the same name Food and drink * Doppio, a double shot of espresso * Dubbel, a strong Belgian Trappist beer or, more generally, a strong brown ale * A drink order of two shots of hard liquor in one glass * A "double decker", a hamburger with two patties in a single bun Games * Double, action in games whereby a competitor raises the stakes ** , in contract bridge ** Doublin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Royal Titulary
The royal titulary or royal protocol is the standard naming convention taken by the pharaohs of ancient Egypt. It symbolised worldly power and holy might, also acting as a sort of mission statement for the duration of a monarch's reign (although sometimes it even changed during the reign). The full titulary, consisting of five names, did not come into standard usage until the Middle Kingdom but remained in use as late as the Roman Empire. Origins In order that the pharaoh, who held divine office, could be linked to the people and the gods, special epithets were created for them at their accession to the throne. These titles also served to demonstrate one's qualities and link them to the terrestrial realm. The five names were developed over the centuries beginning with the Horus name. This name identified the figure as a representative of the god Horus. The Nebty name was the second part of the royal titular of Upper and Lower Egypt. This name placed the king under the protectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Hieroglyphs
Egyptian hieroglyphs (, ) were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt, used for writing the Egyptian language. Hieroglyphs combined logographic, syllabic and alphabetic elements, with some 1,000 distinct characters.There were about 1,000 graphemes in the Old Kingdom period, reduced to around 750 to 850 in the classical language of the Middle Kingdom, but inflated to the order of some 5,000 signs in the Ptolemaic period. Antonio Loprieno, ''Ancient Egyptian: A Linguistic Introduction'' (Cambridge: Cambridge UP, 1995), p. 12. Cursive hieroglyphs were used for religious literature on papyrus and wood. The later hieratic and demotic Egyptian scripts were derived from hieroglyphic writing, as was the Proto-Sinaitic script that later evolved into the Phoenician alphabet. Through the Phoenician alphabet's major child systems (the Greek and Aramaic scripts), the Egyptian hieroglyphic script is ancestral to the majority of scripts in modern use, most prominently the Latin and Cyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demotic (Egyptian)
Demotic (from grc, δημοτικός ''dēmotikós'', 'popular') is the ancient Egyptian script derived from northern forms of hieratic used in the Nile Delta, and the stage of the Egyptian language written in this script, following Late Egyptian and preceding Coptic. The term was first used by the Greek historian Herodotus to distinguish it from hieratic and hieroglyphic scripts. By convention, the word "Demotic" is capitalized in order to distinguish it from demotic Greek. Script The Demotic script was referred to by the Egyptians as ', "document writing," which the second-century scholar Clement of Alexandria called , "letter-writing," while early Western scholars, notably Thomas Young, formerly referred to it as "Enchorial Egyptian." The script was used for more than a thousand years, and during that time a number of developmental stages occurred. It is written and read from right to left, while earlier hieroglyphs could be written from top to bottom, left to right, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Language
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramaic Language
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in the ancient region of Syria. For over three thousand years, It is a sub-group of the Semitic languages. Aramaic varieties served as a language of public life and administration of ancient kingdoms and empires and also as a language of divine worship and religious study. Several modern varieties, namely the Neo-Aramaic languages, are still spoken in the present-day. The Aramaic languages belong to the Northwest group of the Semitic language family, which also includes the Canaanite languages such as Hebrew, Edomite, Moabite, and Phoenician, as well as Amorite and Ugaritic. Aramaic languages are written in the Aramaic alphabet, a descendant of the Phoenician alphabet, and the most prominent alphabet variant is the Syriac alphabet. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |