|
Amyloid Angiopathy
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) is a form of angiopathy in which amyloid beta peptide deposits in the walls of small to medium blood vessels of the central nervous system and meninges. The term ''congophilic'' is sometimes used because the presence of the abnormal aggregations of amyloid can be demonstrated by microscopic examination of brain tissue after staining with Congo red. The amyloid material is only found in the brain and as such the disease is not related to other forms of amyloidosis. Signs and symptoms CAA is associated with brain hemorrhages, particularly microhemorrhages. Since CAA can be caused by the same amyloid protein that is associated with Alzheimer's dementia, brain bleeds are more common in people who have a diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. However, they can also occur in those who have no history of dementia. The bleeding within the brain is usually confined to a particular lobe and this is slightly different compared to brain bleeds which occur as a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congo Red
Congo red is an organic compound, the sodium salt of 3,3′-( ,1′-biphenyl4,4′-diyl)bis(4-aminonaphthalene-1-sulfonic acid). It is an azo dye. Congo red is water-soluble, yielding a red colloidal solution; its solubility is greater in organic solvents. However, the use of Congo red has long been abandoned, primarily because of its carcinogenic properties.Klaus Hunger, Peter Mischke, Wolfgang Rieper, Roderich Raue, Klaus Kunde, Aloys Engel: "Azo Dyes" in ''Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.. History Congo red was first synthesized in 1883 by Paul Böttiger, who had been employed at Friedrich Bayer Company in Elberfeld, Germany. He was looking for textile dyes that did not require a mordant step. The company which had a right of first refusal to his inventions was not interested in this bright red color, so he filed the patent under his own name and sold it to the AGFA company of Berlin. AGFA marketed the dye under the name "Congo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. Endocytosis includes pinocytosis (cell drinking) and phagocytosis (cell eating). It is a form of active transport. History The term was proposed by De Duve in 1963. Phagocytosis was discovered by Élie Metchnikoff in 1882. Pathways Endocytosis pathways can be subdivided into four categories: namely, receptor-mediated endocytosis (also known as clathrin-mediated endocytosis), caveolae, pinocytosis, and phagocytosis. * Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is mediated by the production of small (approx. 100 nm in diameter) vesicles that have a morphologically characteristic coat made up of the cytosolic protein clathrin. Clathrin-coated vesicles (CCVs) are found in virtually all cells and form domains of the plasma membrane terme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
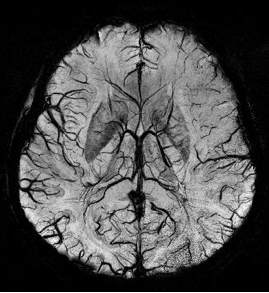
Susceptibility Weighted Imaging
Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI), originally called BOLD venographic imaging, is an MRI sequence that is exquisitely sensitive to venous blood, hemorrhage and iron storage. SWI uses a fully flow compensated, long echo, gradient recalled echo (GRE) pulse sequence to acquire images. This method exploits the susceptibility differences between tissues and uses the phase image to detect these differences. The magnitude and phase data are combined to produce an enhanced contrast magnitude image. The imaging of venous blood with SWI is a blood-oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) technique which is why it was (and is sometimes still) referred to as BOLD venography. Due to its sensitivity to venous blood SWI is commonly used in traumatic brain injuries (TBI) and for high resolution brain venographies but has many other clinical applications. SWI is offered as a clinical package by Philips and Siemens but can be run on any manufacturer’s machine at field strengths of 1.0 T, 1.5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy. Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous or inflammatory conditions. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autopsy
An autopsy (post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death or to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present for research or educational purposes. (The term "necropsy" is generally reserved for non-human animals). Autopsies are usually performed by a specialized medical doctor called a pathologist. In most cases, a medical examiner or coroner can determine the cause of death. However, only a small portion of deaths require an autopsy to be performed, under certain circumstances. Purposes of performance Autopsies are performed for either legal or medical purposes. Autopsies can be performed when any of the following information is desired: * Determine if death was natural or unnatural * Injury source and extent on the corpse * Manner of death must be determined * Post mortem interval * Determining the decea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compare SWI And GRE CAA
Comparison or comparing is the act of evaluating two or more things by determining the relevant, comparable characteristics of each thing, and then determining which characteristics of each are similar to the other, which are different, and to what degree. Where characteristics are different, the differences may then be evaluated to determine which thing is best suited for a particular purpose. The description of similarities and differences found between the two things is also called a comparison. Comparison can take many distinct forms, varying by field: To compare things, they must have characteristics that are similar enough in relevant ways to merit comparison. If two things are too different to compare in a useful way, an attempt to compare them is colloquially referred to in English as "comparing apples and oranges." Comparison is widely used in society, in science and in the arts. General usage Comparison is a natural activity, which even animals engage in when dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITM2B
Integral membrane protein 2B (ITM2B or BRI2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ITM2B'' gene. ''ITM2B'' or ''BRI2'' is a gene located on chromosome 13. The gene is connected to familial Danish dementia and familial British dementia causing amyloid and pre-filbrillar effects similar to those seen in Alzheimer's Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-13-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystatin C
Cystatin C or cystatin 3 (formerly gamma trace, post-gamma-globulin, or neuroendocrine basic polypeptide), a protein encoded by the CST3 gene, is mainly used as a biomarker of kidney function. Recently, it has been studied for its role in predicting new-onset or deteriorating cardiovascular disease. It also seems to play a role in brain disorders involving amyloid (a specific type of protein deposition), such as Alzheimer's disease. In humans, all cells with a nucleus (cell core containing the DNA) produce cystatin C as a chain of 120 amino acids. It is found in virtually all tissues and body fluids. It is a potent inhibitor of lysosomal proteinases (enzymes from a special subunit of the cell that break down proteins) and probably one of the most important extracellular inhibitors of cysteine proteases (it prevents the breakdown of proteins outside the cell by a specific type of protein degrading enzymes). Cystatin C belongs to the type 2 cystatin gene family. Role in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presenilin
Presenilins are a family of related multi-pass transmembrane proteins which constitute the catalytic subunits of the gamma-secretase intramembrane protease protein complex. They were first identified in screens for mutations causing early onset forms of familial Alzheimer's disease by Peter St George-Hyslop. Vertebrates have two presenilin genes, called ''PSEN1'' (located on chromosome 14 in humans) that codes for presenilin 1 (PS-1) and '' PSEN2'' (on chromosome 1 in humans) that codes for presenilin 2 (PS-2). Both genes show conservation between species, with little difference between rat and human presenilins. The nematode worm ''C. elegans'' has two genes that resemble the presenilins and appear to be functionally similar, sel-12 and hop-1. Presenilins undergo cleavage in an alpha helical region of one of the cytoplasmic loops to produce a large N-terminal and a smaller C-terminal fragment that together form part of the functional protein. Cleavage of presenilin 1 can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyloid Precursor Protein
Amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP) is an integral membrane protein expressed in many biological tissue, tissues and concentrated in the synapses of neurons. It functions as a cell surface receptor and has been implicated as a regulator of synapse formation, neural plasticity, antimicrobial activity, and iron export. It is coded for by the gene ''APP'' and regulated by substrate presentation. APP is best known as the precursor molecule whose proteolysis generates amyloid beta (Aβ), a polypeptide containing 37 to 49 amino acid residues, whose Amyloid#Structure, amyloid fibrillar form is the primary component of amyloid plaques found in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients. Genetics Amyloid-beta precursor protein is an ancient and highly Conserved sequence, conserved protein. In humans, the gene ''APP'' is located on chromosome 21 and contains 18 exons spanning 290 kilobases. Several alternative splicing isoforms of APP have been observed in humans, ranging in len ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood–brain Barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable border of endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from ''non-selectively'' crossing into the extracellular fluid of the central nervous system where neurons reside. The blood–brain barrier is formed by endothelial cells of the capillary wall, astrocyte end-feet ensheathing the capillary, and pericytes embedded in the capillary basement membrane. This system allows the passage of some small molecules by passive diffusion, as well as the selective and active transport of various nutrients, ions, organic anions, and macromolecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function. The blood–brain barrier restricts the passage of pathogens, the diffusion of solutes in the blood, and large or hydrophilic molecules into the cerebrospinal fluid, while allowing the diffusion of hydrophobic molecules (O2, CO2, hormones) and small non-polar molecules. Cells of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin Degrading Enzyme
Insulin-degrading enzyme, also known as IDE, is an enzyme. Known alternatively as insulysin or insulin protease, IDE is a large zinc-binding protease of the M16 metalloprotease family known to cleave multiple short polypeptides that vary considerably in sequence. Other members of this family include the mitochondrial processing peptidase and presequence protease. Structure Gene The gene ''IDE'' encodes protein Insulin-degrading enzyme. The human gene ''IDE'' has 28 exons and is located at chromosome band 10q23-q25. Protein Due to alternative splicing, The human protein Insulin-degrading Enzyme has two isoforms. Isoform1 is ~118 kDa in size and composed of 1019 amino acids while the isoform 2 is ~54.2 kDa size and composed of 464 amino acids (missing 1-555 amino acids). The calculated theoretical pI of this protein isoform is 6.26. Structural studies of IDE by Shen et al. have provided insight into the functional mechanisms of the protease. Reminiscent of the previously dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |