|
Amvrosii Metlynsky
Amvrosy Metlinsky (russian: Амвросий Метлинский, uk, Амвросій Метлинський, romanized: ''Amvrosii Metlynskyi''; 1814 in Sary, Poltava Governorate, Russian Empire – 29 July 1870 in Yalta, Taurida Governorate, Russian Empire) was a Ukrainian poet, ethnographer, folklorist and panslavist. Professor at the Imperial University of Kharkov. Metlinsky was a professor of Russian Literature at Kharkov University from 1843–49, and again from 1854–58. From 1849–54 he was a professor at Kiev University. During the 1830s, the city of Kharkov became the center of Ukrainian Romanticism. Metlinsky and other authors such as Izmail Sreznevsky and Nikolay Kostomarov published ethnographic materials, native interpretations of Ukrainian history, and collections of folk legends and Cossack chronicles.''Ukrainian literature.'' (2009). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 8 July 2009, from Encyclopædia Britannica Onlin/ref> In 1839, he pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
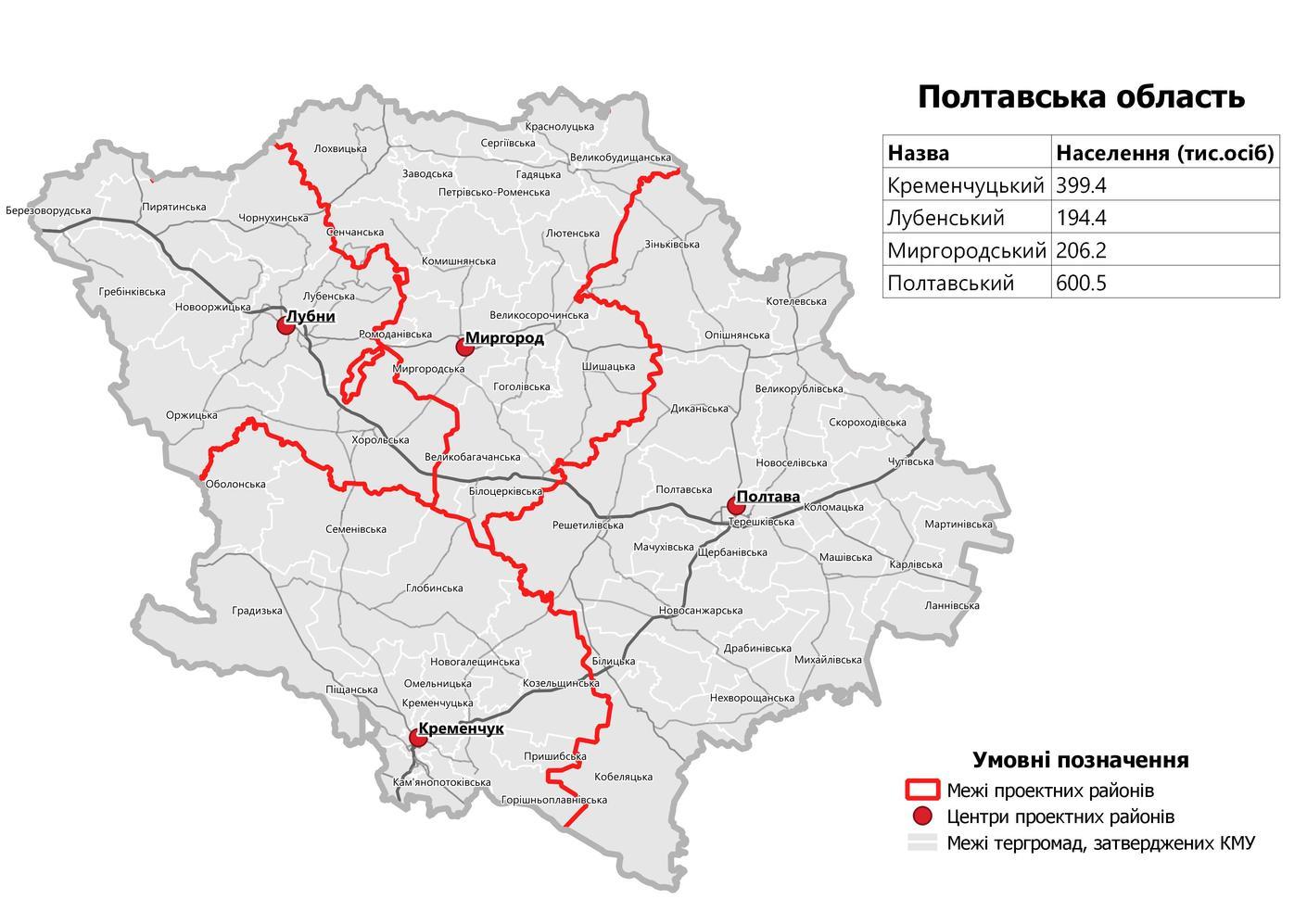
Poltava Region
Poltava Oblast ( uk, Полта́вська о́бласть, translit=Poltavska oblast; also referred to as Poltavshchyna – uk, Полта́вщина, literally 'Poltava Country') is an oblast (province) of central Ukraine. The administrative center of the oblast is the city of Poltava. Most of its territory is part of the historic Cossack Hetmanate (its southern regions: Poltava, Myrhorod, Lubny, and Hadiach). Population: Two other important cities there are Horishni Plavni and Kremenchuk. History During the 2022 Russian Invasion of Ukraine, the town of Myrhorod was bombed. However as of April 2022, there has been no ground fighting and the province remains completely under Ukrainian control. Geography Poltava Oblast is situated in the central part of Ukraine. Located on the left bank of Dnieper, Poltava region was part of the Cossack Hetmanate. It has an area of 28,800 km2. The oblast borders upon Chernihiv, Sumy, Kharkiv, Dnipropetrovsk, Kirovohrad, Cherkasy and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Of Ukraine
The ''Encyclopedia of Ukraine'' ( uk, Енциклопедія українознавства, translit=Entsyklopediia ukrainoznavstva), published from 1984 to 2001, is a fundamental work of Ukrainian Studies. Development The work was created under the auspices of the Shevchenko Scientific Society in Europe (Sarcelles, near Paris). As the ''Encyclopedia of Ukrainian Studies'' it conditionally consists of two parts, the first being a general part that consists of a three volume reference work divided in to subjects or themes. The second part is a 10 volume encyclopedia with entries arranged alphabetically. The editor-in-chief of Volumes I and II (published in 1984 and 1988 respectively) was Volodymyr Kubijovyč. The concluding three volumes, with Danylo Husar Struk as editor-in-chief, appeared in 1993. The encyclopedia set came with a 30-page ''Map & Gazetteer of Ukraine'' compiled by Kubijovyč and Arkadii Zhukovsky. It contained a detailed fold-out map (scale 1:2,000,000). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Folk Songs
Ukrainian folk music includes a number of varieties of traditional, folkloric, folk-inspired popular music, and folk-inspired European classical music traditions. In the 20th century numerous ethnographic and folkloric musical ensembles were established in Ukraine and gained popularity. During the Soviet era, music was a controlled commodity and was used as a tool for the indoctrination of the population. As a result, the repertoire of Ukrainian folk music performers and ensembles was controlled and restricted. Vocal music Authentic folk singing Ukrainians, particularly in Eastern Ukraine have fostered a peculiar style of singing – The White voice ( uk, Білий голос). This type of singing primarily exploits the chest register and is akin to controlled yelling or shouting. The vocal range is restrictive and in a lower tessitura. In recent times vocal courses have been established to study this particular form of singing. Among the most popular exponents of tradi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and shares Borders of Russia, land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than List of countries and territories by land borders, any other country but China. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's ninth-most populous country and List of European countries by population, Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city is Moscow, the List of European cities by population within city limits, largest city entirely within E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan-Slavism
Pan-Slavism, a movement which crystallized in the mid-19th century, is the political ideology concerned with the advancement of integrity and unity for the Slavic people. Its main impact occurred in the Balkans, where non-Slavic empires had ruled the South Slavs for centuries. These were mainly the Byzantine Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Venice. Origins Extensive pan-Slavism began much like Pan-Germanism - both these movements flourished from the sense of unity and nationalism experienced within ethnic groups after the French Revolution and the consequent Napoleonic Wars against traditional European monarchies. As in other Romantic nationalist movements, Slavic intellectuals and scholars in the developing fields of history, philology, and folklore actively encouraged Slavs' interest in their shared identity and ancestry. Pan-Slavism co-existed with the Southern Slavic drive towards independence. Commonly used symbols of the Pan-Slavic movement were the Pan- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Toronto Press
The University of Toronto Press is a Canadian university press founded in 1901. Although it was founded in 1901, the press did not actually publish any books until 1911. The press originally printed only examination books and the university calendar. Its first scholarly book was a work by a classics professor at University College, Toronto. The press took control of the university bookstore in 1933. It employed a novel typesetting method to print issues of the ''Canadian Journal of Mathematics'', founded in 1949. Sidney Earle Smith, president of the University of Toronto in the late 1940s and 1950s, instituted a new governance arrangement for the press modelled on the governing structure of the university as a whole (on the standard Canadian university governance model defined by the Flavelle commission). Henceforth, the press's business affairs and editorial decision-making would be governed by separate committees, the latter by academic faculty. A committee composed of Vincent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandurist
A banduryst ( uk, бандури́ст) is a person who plays the Ukrainian plucked string instrument known as the bandura. Types of performers There are a number of different types of bandurist who differ in their particular choice of instrument, the specific repertoire they play and manner in which they approach their vocation. *Kobzari, who play authentic ethnographic instruments or copies. This group can also be further categorized into ''authentic'', ''reproduction'', and ''stage'' performers. *Academic players, playing more sophisticated contemporary concert banduras. These performers have a tertiary education majoring in bandura performance and typically perform works by Western classical composers in addition to, or instead of, Ukrainian folk music. This category can be further divided into instrumentalists (who only perform instrumental works) and vocalists (who primarily use the bandura to accompany their voice). The most common academic bandurists play in the Kiev acad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nostalgia
Nostalgia is a sentimentality for the past, typically for a period or place with happy personal associations. The word ''nostalgia'' is a learned formation of a Greek language, Greek compound, consisting of (''nóstos''), meaning "homecoming", a Homeric word, and (''álgos''), meaning "sorrow" or "despair", and was coined by a 17th-century medical student to describe the anxieties displayed by Swiss mercenaries fighting away from home. Described as a medical condition—a form of Depression (mood), melancholy—in the Early Modern period, it became an important Trope (literature), trope in Romanticism. Nostalgia is associated with a longing for the past, its personalities, possibilities, and events, especially the "Good old days, good ol' days" or a "warm childhood". There is a predisposition, caused by cognitive biases such as rosy retrospection, for people to view the past more favourably and future more negatively. When applied to one's beliefs about a society or institutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various times through the centuries. The encyclopaedia is maintained by about 100 full-time editors and more than 4,000 contributors. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, which spans 32 volumes and 32,640 pages, was the last printed edition. Since 2016, it has been published exclusively as an online encyclopaedia. Printed for 244 years, the ''Britannica'' was the longest running in-print encyclopaedia in the English language. It was first published between 1768 and 1771 in the Scottish capital of Edinburgh, as three volumes. The encyclopaedia grew in size: the second edition was 10 volumes, and by its fourth edition (1801–1810) it had expanded to 20 volumes. Its rising stature as a scholarly work helped recruit eminent con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicle
A chronicle ( la, chronica, from Greek ''chroniká'', from , ''chrónos'' – "time") is a historical account of events arranged in chronological order, as in a timeline. Typically, equal weight is given for historically important events and local events, the purpose being the recording of events that occurred, seen from the perspective of the chronicler. A chronicle which traces world history is a universal chronicle. This is in contrast to a narrative or history, in which an author chooses events to interpret and analyze and excludes those the author does not consider important or relevant. The information sources for chronicles vary. Some are written from the chronicler's direct knowledge, others from witnesses or participants in events, still others are accounts passed down from generation to generation by oral tradition.Elisabeth M. C. Van Houts, ''Memory and Gender in Medieval Europe: 900–1200'' (Toronto; Buffalo : University of Toronto Press, 1999), pp. 19–20. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cossack
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or , sk, kozáci , uk, козаки́ are a predominantly East Slavic Orthodox Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of Ukraine and southern Russia. Historically, they were a semi-nomadic and semi-militarized people, who, while under the nominal suzerainty of various Eastern European states at the time, were allowed a great degree of self-governance in exchange for military service. Although numerous linguistic and religious groups came together to form the Cossacks, most of them coalesced and became East Slavic-speaking Orthodox Christians. The Cossacks were particularly noted for holding democratic traditions. The rulers of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russian Empire endowed Cossacks with certain spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Folklore
Ukrainian folklore is the folk tradition which has developed in Ukraine and among ethnic Ukrainians. The earliest examples of folklore found in Ukraine is the layer of pan-Slavic folklore that dates back to the ancient Slavic mythology of the Eastern Slavs. Gradually, Ukrainians developed a layer of their own distinct folk culture. Folklore has been an important tool in defining and retaining a cultural distinctiveness in Ukraine in the face of strong assimilatory pressures from neighboring lands. Distinctiveness Ukrainian folk customs have numerous layers defined by the period in which that aspect developed and the area in which it was exploited. The lowest and oldest level is the pan-Slavic layer of folk culture which has many elements that are common to the Slavic people in general. Above that are elements common to the Eastern Slavs, and above that are elements found only in Ukraine itself. The layer above this contains cultural and folkloric elements that define the various m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
