|
Aminophenols
Aminophenol may refer to any of three isomeric chemical compounds: * 2-Aminophenol * 3-Aminophenol * 4-Aminophenol They are simultaneously an aniline and a phenol Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it .... {{Chemistry index Aminophenols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-Aminophenol
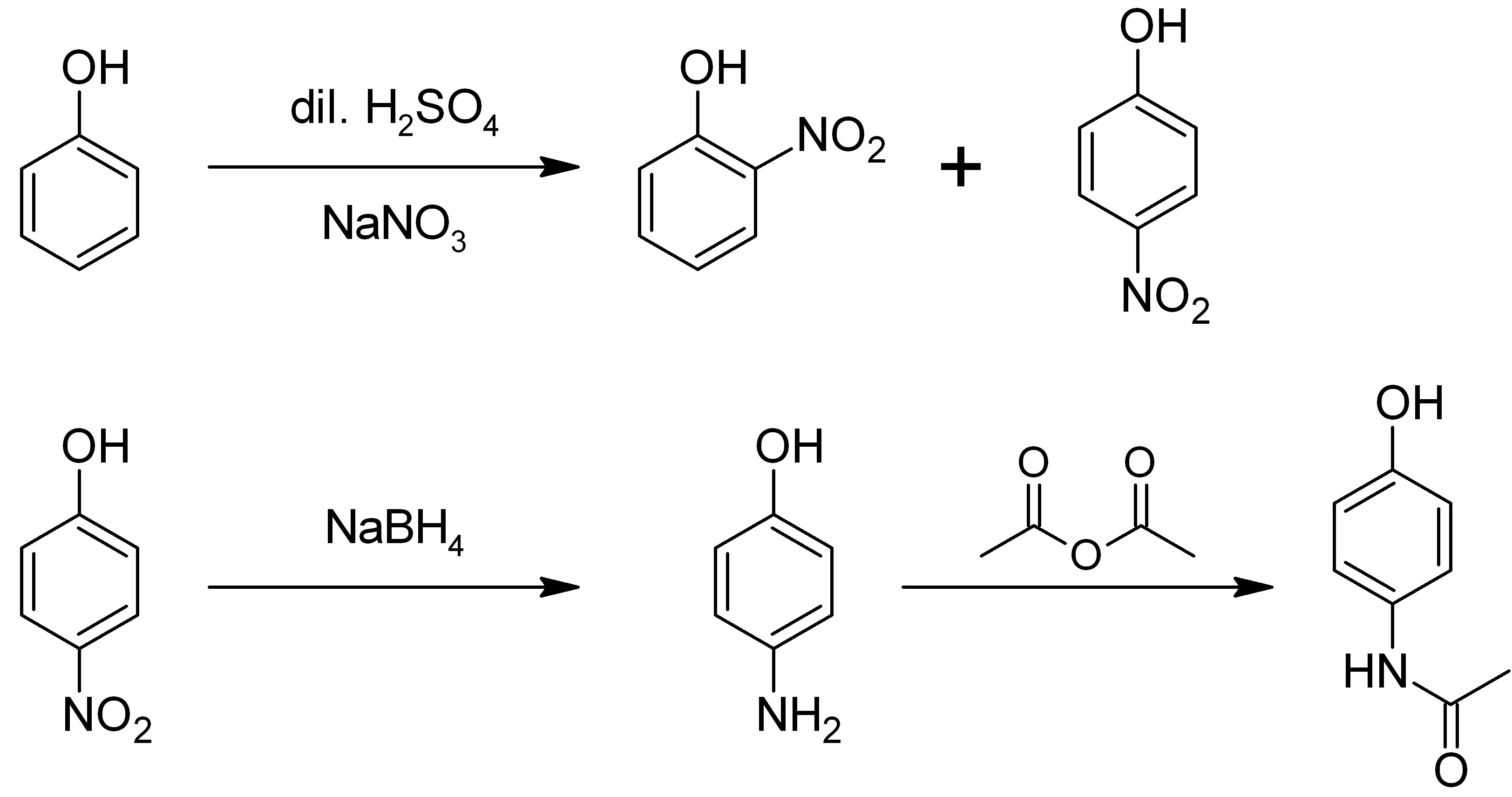
4-Aminophenol (or ''para''-aminophenol or ''p''-aminophenol) is an organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4OH. Typically available as a white powder, it is commonly used as a developer for black-and-white film, marketed under the name Rodinal. Reflecting its slightly hydrophilic character, the white powder is moderately soluble in alcohols and can be recrystallized from hot water. In the presence of a base, it oxidizes readily. The methylated derivatives ''N''-methylaminophenol and ''N'',''N''-dimethylaminophenol are of commercial value. The compound is one of three isomeric aminophenols, the other two being 2-aminophenol and 3-aminophenol. __TOC__ Preparation From phenol It is produced from phenol by nitration followed by reduction with iron. Alternatively, the partial hydrogenation of nitrobenzene affords phenylhydroxylamine, which rearranges primarily to 4-aminophenol ( Bamberger rearrangement). :C6H5NO2 + 2 H2 → C6H5NHOH + H2O :C6H5NHOH → HOC6H4NH2 From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-Aminophenol
2-Aminophenol is an organic compound with the formula C6H7NO. Along with its isomer 4-aminophenol, it is an amphoteric molecule and a reducing agent. It is a useful reagent for the synthesis of dyes and heterocyclic compounds.Mitchell, S.C. & Waring, R.H. "Aminophenols." In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; 2002 Wiley-VCH, . Reflecting its slight hydrophilic character, white powder is moderately soluble in alcohols and can be recrystallized from hot water. Synthesis and structure 2-Aminophenol (and its isomer, 4-aminophenol) is industrially synthesized by reducing the corresponding nitrophenol by hydrogen in the presence of various catalysts. The nitrophenols can also be reduced with iron. The compound exhibits intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonding involving the neighbouring amine and hydroxyl groups. As a result, 2-aminophenol has a relatively high melting point (174 °C) compared to other compounds with a similar molecular mass; for example, 2-m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomers Of Aminophenol
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulae – that is, same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers. Isomers do not necessarily share similar chemical or physical properties. Two main forms of isomerism are structural or constitutional isomerism, in which ''bonds'' between the atoms differ; and stereoisomerism or spatial isomerism, in which the bonds are the same but the ''relative positions'' of the atoms differ. Isomeric relationships form a hierarchy. Two chemicals might be the same constitutional isomer, but upon deeper analysis be stereoisomers of each other. Two molecules that are the same stereoisomer as each other might be in different conformational forms or be different isotopologues. The depth of analysis depends on the field of study or the chemical and physical properties of interest. The English word "isomer" () is a back-fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulae – that is, same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers. Isomers do not necessarily share similar chemical or physical properties. Two main forms of isomerism are structural or constitutional isomerism, in which ''bonds'' between the atoms differ; and stereoisomerism or spatial isomerism, in which the bonds are the same but the ''relative positions'' of the atoms differ. Isomeric relationships form a hierarchy. Two chemicals might be the same constitutional isomer, but upon deeper analysis be stereoisomers of each other. Two molecules that are the same stereoisomer as each other might be in different conformational forms or be different isotopologues. The depth of analysis depends on the field of study or the chemical and physical properties of interest. The English word "isomer" () is a back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aniline
Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds. It is toxic to humans. Relative to benzene, it is electron-rich. It thus participates more rapidly in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Likewise, it is also prone to oxidation: while freshly purified aniline is an almost colorless oil, exposure to air results in gradual darkening to yellow or red, due to the formation of strongly colored, oxidized impurities. Aniline can be diazotized to give a diazonium salt, which can then undergo var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 billion kg/year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs. Properties Phenol is an organic compound appreciably soluble in water, with about 84.2 g dissolving in 1000 mL (0.895 M). Homogeneous mixtures of phenol and water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |