|
Amenhotep-Huy
Amenhotep-Huy was a Vizier of Ancient Egypt during the reign of Amenhotep III. Besides being Amenhotep III's Vizier, Amenhotep-Huy was also director of Upper and Lower Egypt and overseer of all the works of the King in Upper and Lower Egypt.O'Connor and Cline, Amenhotep III: Perspectives on His Reign,University of Michigan Press, 2001 Life and career There were two Viziers at this time and Amenhotep-Huy served alongside another vizier Ramose. It is not entirely clear who served as Vizier of northern Egypt and who served as Vizier of southern Egypt. Amenhotep-Huy is attested in both the north and the south. He is attested in inscriptions from Gebel el Silsila where he oversaw work in the sandstone quarry. Tomb and Burial Amenhotep-Huy owned a tomb, k028, in the Theban necropolis. This tomb was located by Dieter Eigner and identified by Andrew Gordon in 1978 in El-Assasif, Thebes. A multi-national team led by the ''Instituto de Estudios del Antiguo Egipto de Madrid'' and Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akhenaten
Akhenaten (pronounced ), also spelled Echnaton, Akhenaton, ( egy, ꜣḫ-n-jtn ''ʾŪḫə-nə-yātəy'', , meaning "Effective for the Aten"), was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth Dynasty. Before the fifth year of his reign, he was known as Amenhotep IV ( egy, jmn-ḥtp, links=no, meaning "Amun is satisfied", Hellenized as ''Amenophis IV''). As a pharaoh, Akhenaten is noted for abandoning Egypt's traditional polytheism and introducing Atenism, or worship centered around Aten. The views of Egyptologists differ as to whether the religious policy was absolutely monotheistic, or whether it was monolatry, syncretistic, or henotheistic. This culture shift away from traditional religion was reversed after his death. Akhenaten's monuments were dismantled and hidden, his statues were destroyed, and his name excluded from lists of rulers compiled by later pharaohs. Traditional religious practice was gradually restored, not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenhotep III
Amenhotep III ( egy, jmn-ḥtp(.w), ''Amānəḥūtpū'' , "Amun is Satisfied"; Hellenized as Amenophis III), also known as Amenhotep the Magnificent or Amenhotep the Great, was the ninth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty. According to different authors, he ruled Egypt from June 1386 to 1349 BC, or from June 1388 BC to December 1351 BC/1350 BC, after his father Thutmose IV died. Amenhotep was Thutmose's son by a minor wife, Mutemwiya. His reign was a period of unprecedented prosperity and splendour, when Egypt reached the peak of its artistic and international power. When he died in the 38th or 39th year of his reign he was succeeded by his son Amenhotep IV, who later changed his name to Akhenaten. Family and early life Amenhotep was the son of Thutmose IV and his minor wife Mutemwiya. He was born probably around 1401 BC. Later in his life, Amenhotep commissioned the depiction of his divine birth to be displayed at Luxor Temple. Amenhotep claimed that his true father was the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El-Assasif
El-Assasif ( ar, العساسيف) is a necropolis near Luxor on the West Bank at Thebes, Egypt, Upper Egypt. It is located in the dry bay that leads up to Deir el-Bahari and south of the necropolis of Dra' Abu el-Naga'. El-Assasif contains burials from the 18th, 22nd, 25th and 26th dynasties of ancient Egypt, covering the period c. 1550 to 525 BC across all three dynasties. Archaeology In November 2018, France's University of Strasbourg announced the discovery of two sarcophagi thought to be more than 3,500 years old with two perfectly preserved mummies and approximately 1,000 funerary statues in the Assasif valley near Luxor. One of the tombs with paintings where the female body found, was opened to the public in front of the international media, but the other one was previously opened by Egyptian antiquities officials. In October 2019, 30 coffins (3.000 year-old) were uncovered and presented, dating back to the Twenty-second Dynasty by the Egyptian archaeological mission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vizier (Ancient Egypt)
The vizier () was the highest official in ancient Egypt to serve the pharaoh (king) during the Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms. Vizier is the generally accepted rendering of ancient Egyptian , etc., among Egyptologists. The ''Instruction of Rekhmire'' (''Installation of the Vizier''), a New Kingdom text, defines many of the duties of the , and lays down codes of behavior. The viziers were often appointed by the pharaoh. During the 4th Dynasty and early 5th Dynasty, viziers were exclusively drawn from the royal family; from the period around the reign of Neferirkare Kakai onwards, they were chosen according to loyalty and talent or inherited the position from their fathers. Responsibilities The viziers were appointed by the pharaohs and often belonged to a pharaoh's family. The vizier's paramount duty was to supervise the running of the country, much like a prime minister. At times this included small details such as sampling the city's water supply. All other lesser supervis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramose (TT55)
The Ancient Egyptian noble, Ramose was Vizier under both Amenhotep III and Akhenaten. He was in office in the last decade of Amenhotep's III reign and at the beginning of the reign of the latter king. Ramose appears on jar labels found in the palace of king Amenhotep III at Malkata. Here appears also the vizier Amenhotep-Huy. Both viziers are also shown side by side in the temple of Soleb. In the New Kingdom the office of the vizier was divided in a northern vizier and a southern one. It is not entirely clear whether Ramose was the southern or northern one. Ramose was born into an influential family. His father was the mayor of Memphis Heby, in office at the beginning of Amenhotep's III reign. The brother of Ramose was the high steward of Memphis Amenhotep (Huy). Tomb His tomb TT55 is located in the Sheikh Abd el-Qurna – part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor, and is notable for the high quality decorations in both the traditiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebes, Egypt
, image = Decorated pillars of the temple at Karnac, Thebes, Egypt. Co Wellcome V0049316.jpg , alt = , caption = Pillars of the Great Hypostyle Hall, in ''The Holy Land, Syria, Idumea, Arabia, Egypt, and Nubia'' , map_type = Egypt , map_alt = , map_size = , relief = yes , coordinates = , location = Luxor, Luxor Governorate, Egypt , region = Upper Egypt , type = Settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , height = , builder = , material = , built = , abandoned = , epochs = , cultures = , dependency_of = , occupants = , event = , excavations = , archaeologists = , condition = , ownership = , management = , public_access = , website = , notes = , designation1 = WHS , designation1_offname = Ancient Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ar, صعيد مصر ', shortened to , , locally: ; ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the lands on both sides of the Nile that extend upriver from Lower Egypt in the north to Nubia in the south. In ancient Egypt, Upper Egypt was known as ''tꜣ šmꜣw'', literally "the Land of Reeds" or "the Sedgeland". It is believed to have been united by the rulers of the supposed Thinite Confederacy who absorbed their rival city states during the Naqada III period (c. 3200–3000 BC), and its subsequent unification with Lower Egypt ushered in the Early Dynastic period. Upper and Lower Egypt became intertwined in the symbolism of pharaonic sovereignty such as the Pschent double crown. Upper Egypt remained as a historical region even after the classical period. Geography Upper Egypt is between the Cataracts of the Nile beyond modern-day Aswan, downriver (northward) to the area of El-Ayait, which places modern-day Cairo in Lower Egypt. The northern (d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Egypt
Lower Egypt ( ar, مصر السفلى '; ) is the northernmost region of Egypt, which consists of the fertile Nile Delta between Upper Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea, from El Aiyat, south of modern-day Cairo, and Dahshur. Historically, the Nile River split into seven branches of the delta in Lower Egypt. Lower Egypt was divided into nomes and began to advance as a civilization after 3600 BC. Today, it contains two major channels that flow through the delta of the Nile River – Mahmoudiyah Canal (ancient Agathos Daimon) and Muways Canal (, "waterway of Moses"). Name In Ancient Egyptian, Lower Egypt was as ''mḥw'' and means ''"north"''. Later on, during Antiquity and the Middle Ages, Greeks and Romans called it ''Κάτω Αἴγυπτος'' or ''Aegyptus Inferior'' both meaning "Lower Egypt", but Copts carried on using the old name related to the north – ''Tsakhet'' () or ''Psanemhit'' () meaning the "Northern part". It was further divided into number of regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gebel El-Silsila
Gebel el-Silsila or Gebel Silsileh ( ar, جبل السلسلة - Jabal al-Silsila or Ǧabal as-Silsila – "Chain of Mountains" or "Series of Mountains"; Egyptian: ẖny, Khenyt,Kitchen (1983). Kheny or Khenu – "The Place of Rowing"; German: Dschabal as-Silsila – "Ruderort", or "Ort des Ruderns" – "Place of Rowing"; Italian: Gebel Silsila – "Monte della Catena" – "Upstream Mountain Chain") is north of Aswan in Upper Egypt, where the cliffs on both sides close to the narrowest point along the length of the entire Nile. The location is between Edfu in the north towards Lower Egypt and Kom Ombo in the south towards Upper Egypt. The name ''Kheny'' (or sometimes ''Khenu'') means "The Place of Rowing". It was used as a major quarry site on both sides of the Nile from at least the 18th Dynasty to Greco-Roman times. Silsila is famous for its New Kingdom stelai and cenotaphs. Sandstone quarry During the 18th Dynasty the Egyptians switched from limestone to sandstone. At thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
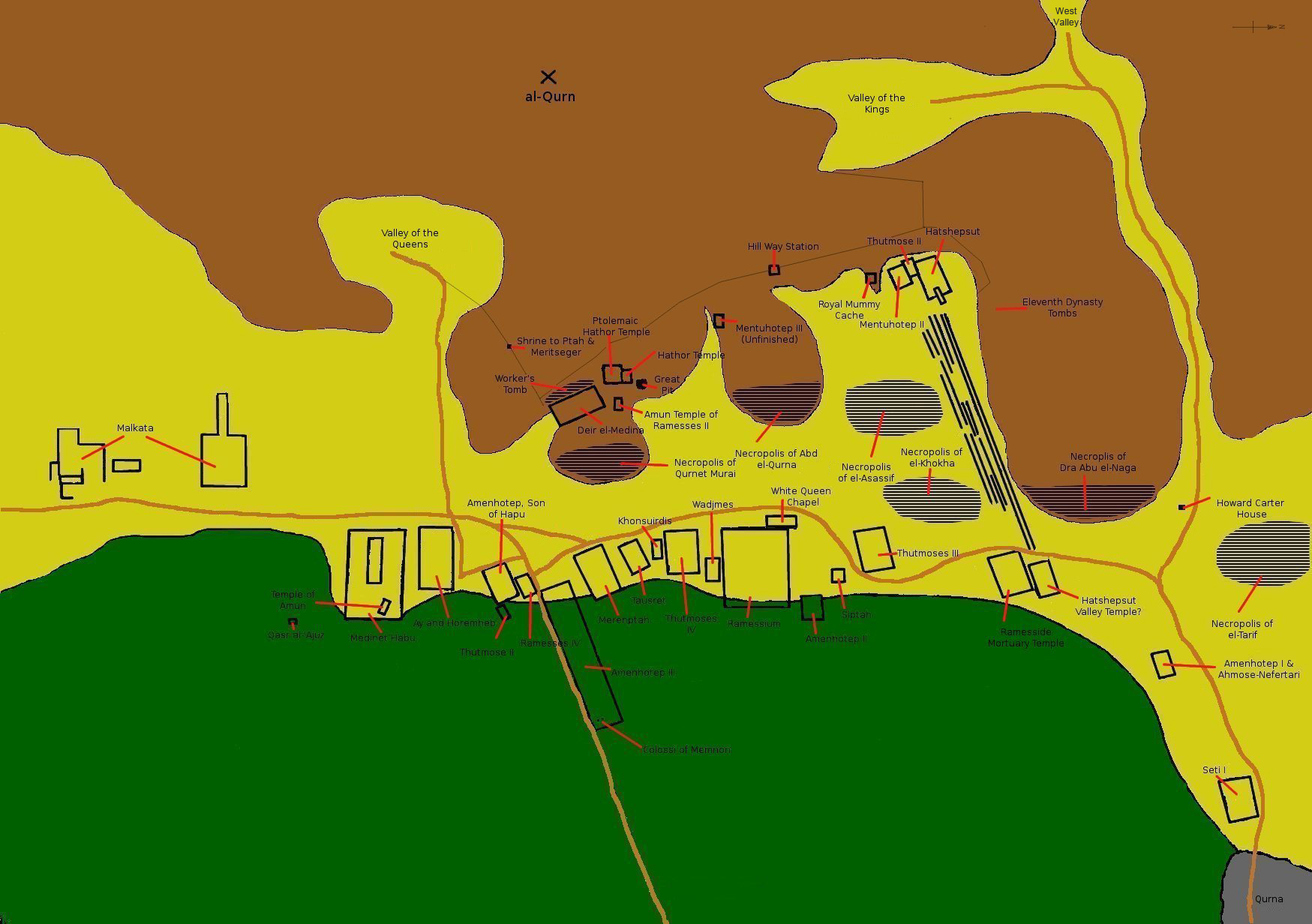
Theban Necropolis
The Theban Necropolis is a necropolis on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Thebes (Luxor) in Upper Egypt. It was used for ritual burials for much of the Pharaonic period, especially during the New Kingdom. Mortuary temples * Deir el-Bahri ** Mortuary temple of Hatshepsut ** Mortuary temple of Mentuhotep II ** Mortuary temple of Thutmose III * Medinet Habu ** Mortuary temple and palace of Ramesses III ** Mortuary Temple of Ay & Horemheb * Mortuary Temple of Amenhotep III ** Colossi of Memnon * Mortuary Temple of Merneptah * Mortuary Temple of Ramesses IV * Mortuary Temple of Thutmose IV * Mortuary Temple of Thutmose III * Mortuary Temple of Twosret * Temple of Nebwenenef * Qurna ** Mortuary Temple of Seti I * Mortuary Temple of Amenhotep II * Ramesseum (Mortuary Temple of Ramesses II) Royal Necropolis * Valley of the Kings (Modern: "''Wadi el-Muluk''") * Valley of the Queens (Modern: "''Biban el-Harim''") * Royal Cache * Bab el-Gasus Necropolis * Deir el-Medin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |