|
Amelioration Act
The Amelioration Act 1798Leeward Islands Act No. 36, vol. 1., The Laws of the Island of Antigua Consisting of the Acts of the Leeward Islands, 1690–1798, and Acts of Antigua, 1668–1845 (London: Samuel Bagster, 1805–46) (sometimes referred to as the Melioration Act or the Slavery Amelioration Act) was a statute passed by the Leeward Islands to improve the conditions of slaves in the British Caribbean colonies. It introduced financial compensation for slaves, and therefore penalties for owners, for instances of cruelty or serious neglect. The Act prohibited marriages between slaves according to Christian religious ceremony. The Act was effectively repealed by the Slave Trade Act 1807, which made it illegal to trade in slaves in any British territory. The Act applied in all of the British Leeward Island colonies in the Caribbean until its implied repeal by the Slavery Abolition Act 1833. The Act is most often noted for its provisions for financial penalties for inflicting cru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statute
A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative authority that governs the legal entities of a city, state, or country by way of consent. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. Statutes are rules made by legislative bodies; they are distinguished from case law or precedent, which is decided by courts, and regulations issued by government agencies. Publication and organization In virtually all countries, newly enacted statutes are published and distributed so that everyone can look up the statutory law. This can be done in the form of a government gazette which may include other kinds of legal notices released by the government, or in the form of a series of books whose content is limited to legislative acts. In either form, statutes are traditionally published in chronological order based on date of enactment. A universal problem encountered by lawmakers throughout human history is how to organize published statutes. Such publications h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur William Hodge
Arthur William Hodge (1763–1811) was a plantation farmer, member of the Executive Council and Legislative Assembly, and slave owner in the British Virgin Islands, who was hanged on 8 May 1811, for the murder of one of his slaves. He was the first West Indian slave owner to be executed for the murder of a slave considered his property, and perhaps the only British West Indian slave owner, or British subject, to be executed for murdering his slave. He was not however the first white person to have been lawfully executed for the killing of a slave, as some historians have claimed. Early life Arthur William Hodge was born in the British Virgin Islands, the son of Arthur Hodge of Tortola. He studied at Oriel College, Oxford, matriculating in December 1781. He briefly served in the British Army and was commissioned as a second lieutenant in the 23rd Regiment of Foot on 3 December 1782. One of his three wives, Ann Hoggins (1779–1808), was a sister-in-law of the Marquess of Exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
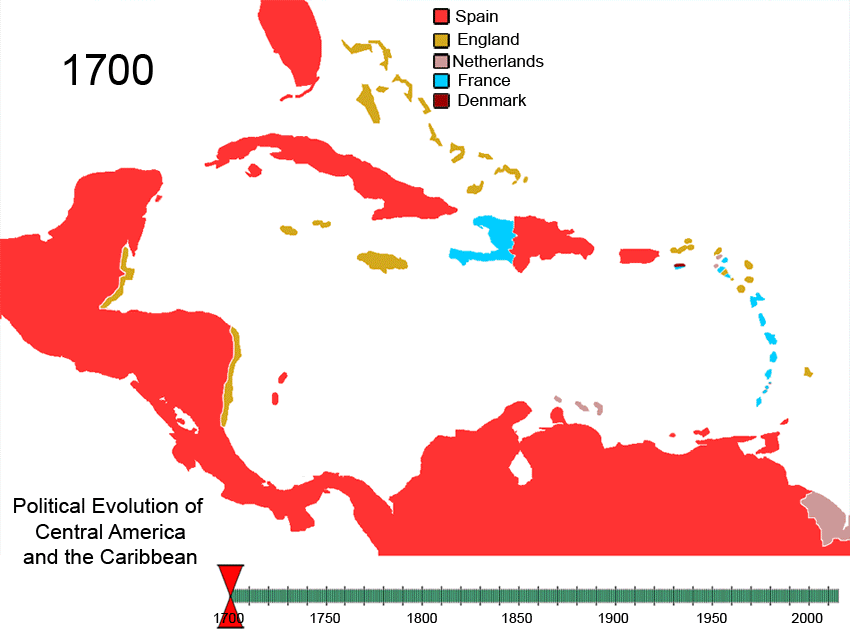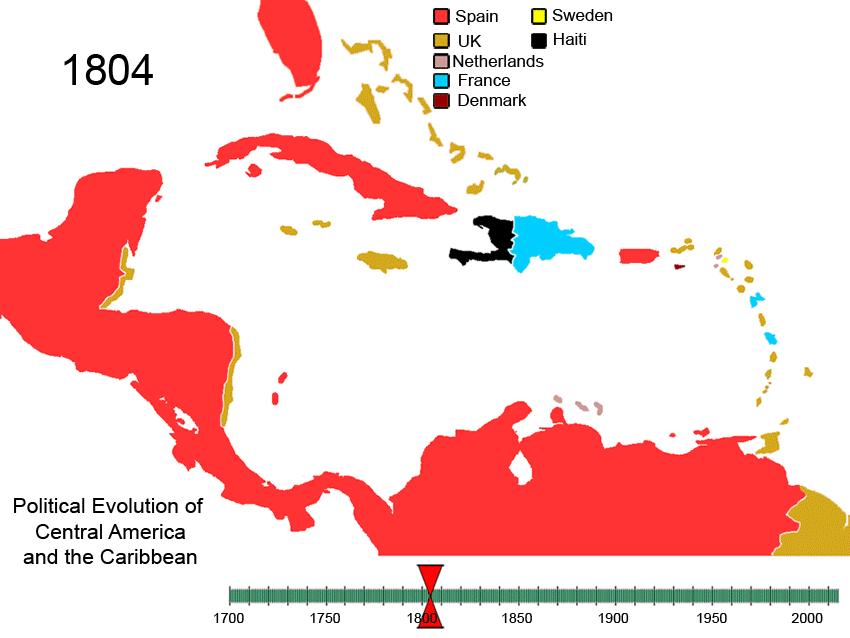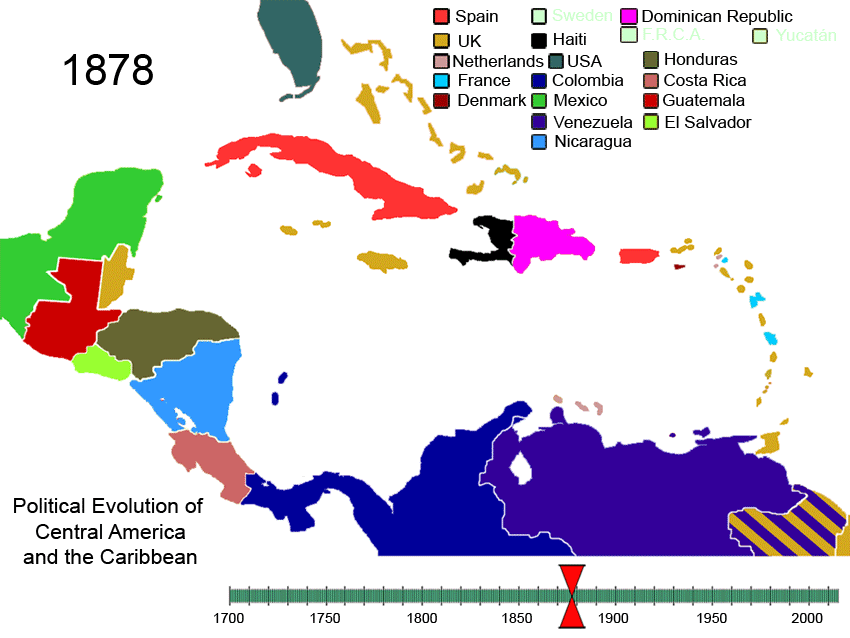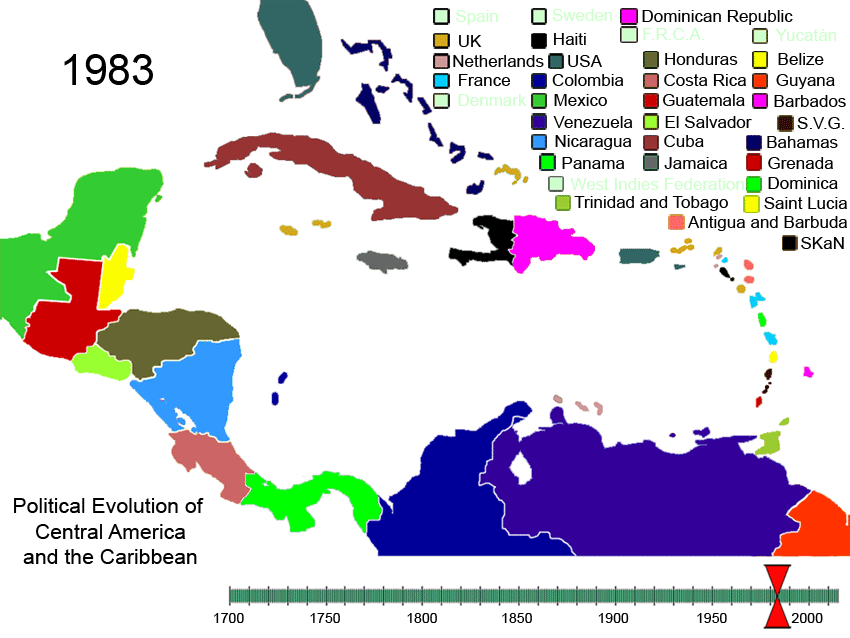
History Of The Caribbean
The history of the Caribbean reveals the significant role the region played in the colonial struggles of the European powers since the 15th century. In 1492, Christopher Columbus landed in the Caribbean and claimed the region for Spain. The following year, the first Spanish settlements were established in the Caribbean. Although the Spanish conquests of the Aztec empire and the Inca empire in the early sixteenth century made Mexico and Peru more desirable places for Spanish exploration and settlement, the Caribbean remained strategically important. From the 1620s and 1630s onwards, non-Hispanic privateers, traders, and settlers established permanent colonies and trading posts on the Caribbean islands neglected by Spain. Such colonies spread throughout the Caribbean, from the Bahamas in the North West to Tobago in the South East. Furthermore, during this period, French and English buccaneers settled on the island of Tortuga, the northern and western coasts of Hispaniola ( Haiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavery Legislation
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perform some form of work while also having their location or residence dictated by the enslaver. Many historical cases of enslavement occurred as a result of breaking the law, becoming indebted, or suffering a military defeat; other forms of slavery were instituted along demographic lines such as race. Slaves may be kept in bondage for life or for a fixed period of time, after which they would be granted freedom. Although slavery is usually involuntary and involves coercion, there are also cases where people voluntarily enter into slavery to pay a debt or earn money due to poverty. In the course of human history, slavery was a typical feature of civilization, and was legal in most societies, but it is now outlawed in most countries of the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1798 In Law
Events January–June * January – Eli Whitney contracts with the U.S. federal government for 10,000 muskets, which he produces with interchangeable parts. * January 4 – Constantine Hangerli enters Bucharest, as Prince of Wallachia. * January 22 – A coup d'état is staged in the Netherlands ( Batavian Republic). Unitarian Democrat Pieter Vreede ends the power of the parliament (with a conservative-moderate majority). * February 10 – The Pope is taken captive, and the Papacy is removed from power, by French General Louis-Alexandre Berthier. * February 15 – U.S. Representative Roger Griswold (Fed-CT) beats Congressman Matthew Lyon (Dem-Rep-VT) with a cane after the House declines to censure Lyon earlier spitting in Griswold's face; the House declines to discipline either man.''Harper's Encyclopaedia of United States History from 458 A. D. to 1909'', ed. by Benson John Lossing and, Woodrow Wilson (Harper & Brothers, 1910) p171 * March &nda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consolidated Slave Law
The Consolidated Slave Law was a law which was enacted by the Barbados legislature in 1826. Following Bussa's Rebellion, London officials were concerned about further risk of revolts and instituted a policy of amelioration. This was resisted by white Barbadian planters. In consequence, the Consolidated Slave Act was a compromise: it simultaneously granted concessions to the slaves whilst also providing reassurances to the slave owners. Three concessions to the slaves were: * The right to own property * The right to give evidence in courts in all cases * A reduction in manumission fees Three concessions granted to the slave owners were: * That a white person could kill a slave during a revolt with impunity * The capital punishment of any slave who threatened the life of a white person * That all free black people needed a correct evidence of the such rights or they will be presumed to be enslaved See also * Amelioration Act 1798 * William Huskisson William Huskisson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavery In The British And French Caribbean
Slavery in the British and French Caribbean refers to slavery in the parts of the Caribbean dominated by France or the British Empire. History In the Caribbean, England colonised the islands of St. Kitts and Barbados in 1623 and 1627 respectively, and later, Jamaica in 1655. In these islands and England's other Caribbean colonies, white colonists would gradually introduce a system of slave-based labor to underpin a new economy based on cash crop production. French institution of slavery In the mid-16th century, enslaved people were trafficked from Africa to the Caribbean by European mercantilists. Originally, white European indentured servants worked alongside enslaved African people in the "New World" (the Americas). At this time, there were not widespread theories of race or racism that would cause different treatment for white indentured servants and enslaved African people. Francois Bernier, who is considered to have presented the first modern concept of race, publish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eighth Amendment To The United States Constitution
The Eighth Amendment (Amendment VIII) to the United States Constitution protects against imposing excessive bail, excessive fines, or cruel and unusual punishments. This amendment was adopted on December 15, 1791, along with the rest of the United States Bill of Rights. The amendment serves as a limitation upon the federal government to impose unduly harsh penalties on criminal defendants before and after a conviction. This limitation applies equally to the price for obtaining pretrial release and the punishment for crime after conviction. The phrases in this amendment originated in the English Bill of Rights of 1689. The prohibition against cruel and unusual punishments has led courts to hold that the Constitution totally prohibits certain kinds of punishment, such as drawing and quartering. Under the Cruel and Unusual Punishment Clause, the Supreme Court has struck down the application of capital punishment in some instances, but capital punishment is still permitted in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill Of Rights 1689
The Bill of Rights 1689 is an Act of the Parliament of England, which sets out certain basic civil rights and clarifies who would be next to inherit the Crown, and is seen as a crucial landmark in English constitutional law. It received Royal Assent on 16 December 1689 and is a restatement in statutory form of the Declaration of Right presented by the Convention Parliament to William III and Mary II in February 1689, inviting them to become joint sovereigns of England. Largely based on the ideas of political theorist John Locke, the Bill sets out certain constitutional requirements of the Crown to seek the consent of the people as represented in Parliament. As well as setting limits on the powers of the monarch, it established the rights of Parliament, including regular parliaments, free elections, and freedom of speech. It also listed individual rights, including the prohibition of cruel and unusual punishment and the right not to pay taxes levied without the approval o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murder
Murder is the unlawful killing of another human without justification (jurisprudence), justification or valid excuse (legal), excuse, especially the unlawful killing of another human with malice aforethought. ("The killing of another person without justification or excuse, especially the crime of killing a person with malice aforethought or with recklessness manifesting extreme indifference to the value of human life.") This state of mind may, depending upon the jurisdiction (area), jurisdiction, distinguish murder from other forms of unlawful homicide, such as manslaughter. Manslaughter is killing committed in the absence of Malice (law), ''malice'',This is "malice" in a technical legal sense, not the more usual English sense denoting an emotional state. See malice (law). brought about by reasonable Provocation (legal), provocation, or diminished capacity. Involuntary manslaughter, ''Involuntary'' manslaughter, where it is recognized, is a killing that lacks all but the most a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar Plantations In The Caribbean
Sugar plantations in the Caribbean were a major part of the economy of the islands in the 18th, 19th, and 20th centuries. Most Caribbean, Caribbean islands were covered with Sugarcane, sugar cane fields and mills for refining the crop. The main source of labor, until Abolitionism, the abolition of chattel slavery, was Atlantic slave trade, enslaved Africans. After the abolition of slavery, Indentured servitude, indentured laborers from India, China, Portugal and other places were brought to the Caribbean to work in the sugar industry. These plantations produced 80 to 90 percent of the sugar consumed in Western Europe, later supplanted by European-grown sugar beet. The sugar trade Sugar cane development in the Americas The Portuguese introduced sugar plantations in the 1550s off the coast of their Brazilian settlement colony, located on the island Sao Vincente. As the Portuguese and Spanish maintained a strong colonial presence in the Caribbean, the Iberian Peninsula amassed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Leeward Islands
The British Leeward Islands was a British colony from 1671 to 1958, consisting of the English (later British) overseas possessions in the Leeward Islands. It ceased to exist from 1816 to 1833, during which time it was split into two separate colonies (Antigua–Barbuda–Montserrat and Saint Christopher–Nevis–Anguilla–Virgin Islands). It was dissolved in 1958 after the separation of the British Virgin Islands, and the remaining islands became parts of the West Indies Federation. History The Leeward Islands was established as an English colony in 1671. In 1816, the islands were divided in two regions: Antigua, Barbuda, and Montserrat in one colony, and Saint Christopher, Nevis, Anguilla, and the Virgin Islands in the other. The Leeward Islands were united again as a semi-federal entity in 1833, coming together until 1872 under the administration of the Governor of Antigua. The islands then became known as the Federal Colony of the Leeward Islands from 1872 to 1956. From 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)