|
Ambrosden
Ambrosden is a village and civil parish in Cherwell, Oxfordshire, England, southwest of Bicester to which it is linked by the A41 road, and from Oxford. The 2011 Census recorded the parish's population as 2,248. The parish is bounded by the River Ray to the south, its tributary the River Bure to the west, the outskirts of Bicester to the north and field boundaries to the east. The village is east of Alchester Roman Town. Ambrosden has a Church of England parish church and a public house. Since the Second World War Ambrosden has housed British Army personnel stationed at St. George's Barracks, which is at Arncott about south of Ambrosden. The Ministry of Defence had many new houses built at Ambrosden in the early 1950s. Geography Ambrosden is about southeast of Bicester (the nearest railway station), connected by the A41 road. The site of Alchester Roman town is about west of the village, and the village of Arncott is about to the south. In 1932 Langford, Wretchwick, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arncott
Arncott or Arncot is a village and civil parish about southeast of Bicester in Oxfordshire. The 2011 Census recorded the parish's population as 1,738. There are two neighbourhoods: Lower and Upper Arncott. Upper Arncott is the larger neighbourhood and includes the village green, recreation ground, shop and most of Arncott's housing. Lower Arncott is close to River Ray and includes the Tally Ho hotel and the Plough public house. Upper and Lower Arncott are separated by the Bicester Military Railway. Manors Arncott's toponym comes from the Old English ''Earnigcote'' meaning "Earn's Cottage" (10th century). Upper Arncott In 983 Æthelred the Unready granted the manor of Upper Arncott to the Benedictine Abingdon Abbey. As a result it became known as ''Arncot Abbatis''. In 1538 the abbey was suppressed in the Dissolution of the Monasteries and surrendered Upper Arncott to the Crown. When the church of Osney Abbey was made the cathedral church of the new Diocese of Oxford the Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Kennett
White Kennett (10 August 166019 December 1728) was an English bishop and antiquarian. He was educated at Westminster School and at St Edmund Hall, Oxford, where, while an undergraduate, he published several translations of Latin works, including Erasmus' ''In Praise of Folly''. Kennett was vicar of Ambrosden, Oxfordshire from 1685 until 1708. During his incumbency he returned to Oxford as tutor and vice-principal of St Edmund Hall, where he gave considerable impetus to the study of antiquities. George Hickes gave him lessons in Old English. In 1695 he published ''Parochial Antiquities''. In 1700 he became rector of St Botolph's Aldgate, London, and in 1701 Archdeacon of Huntingdon. For a eulogistic sermon on the recently deceased William Cavendish, 1st Duke of Devonshire, Kennett was in 1707 recommended to the deanery of Peterborough. He afterwards joined the Low Church party, strenuously opposed the Sacheverell movement, and in the Bangorian controversy supported with great z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicester
Bicester ( ) is a historical market towngarden town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in the Cherwell (district), Cherwell district of northeastern Oxfordshire in Southern England that also comprises an Eco-towns, eco town at North West Bicester, North-East Bicester and self-build village aGraven Hill Its local market continues to thrive and is now located on Sheep Street, a very wide pedestrian zone in the Conservation area (United Kingdom), conservation area of the town. Bicester is also known for Bicester Village, a nearby shopping centre selling discounted branded clothing. Between 1951 and 2001 this historic market centre was one of the fastest-growing towns in Oxfordshire. Development has been favoured by its proximity to junction 9 of the M40 motorway linking it to London, Birmingham and Banbury. It has good road links to Oxford, Kidlington, Brackley, Buckingham, Aylesbury and Witney and railway stations on two different lines: and . It has its own civil parish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
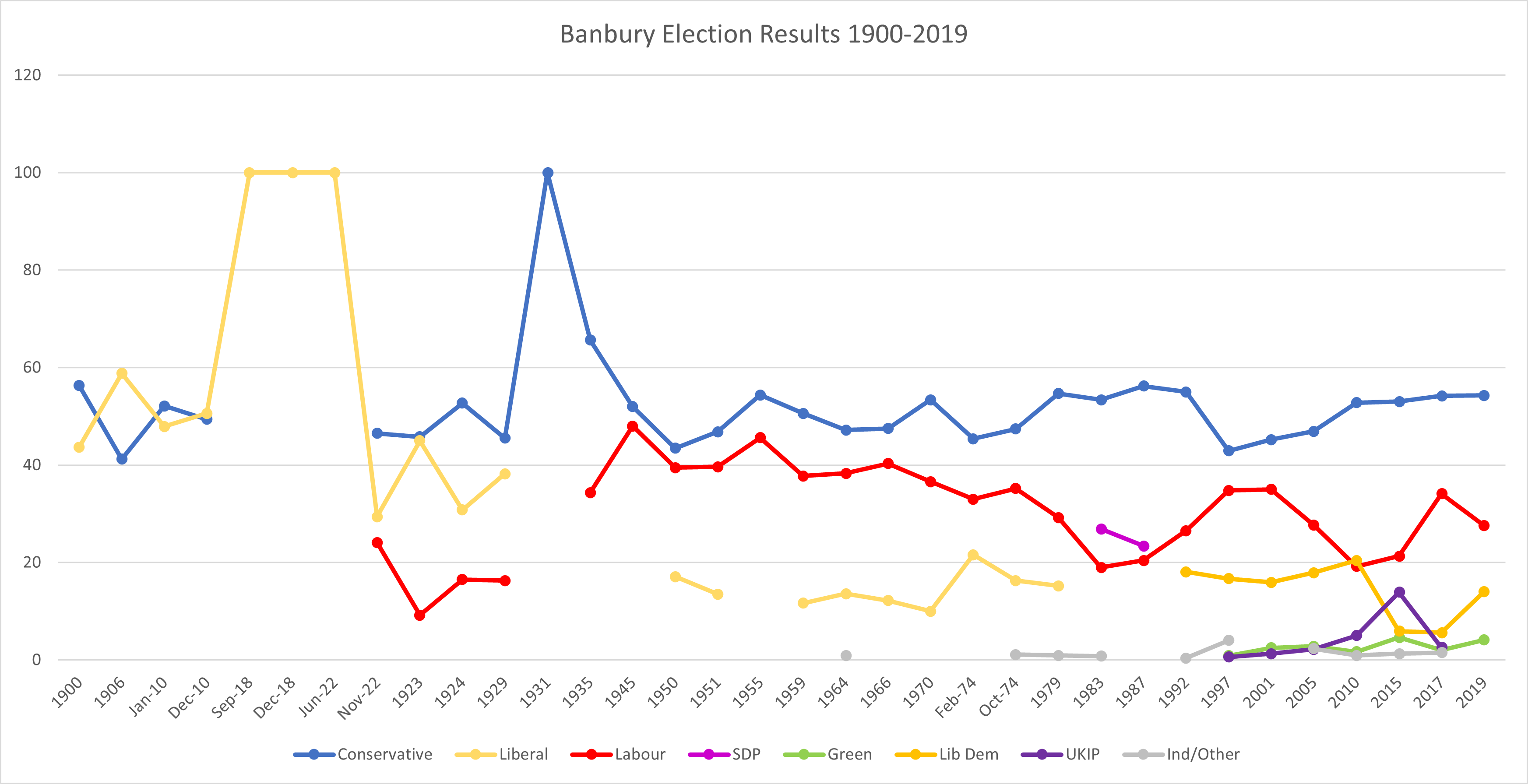
Banbury (UK Parliament Constituency)
Banbury, also informally known as Banbury and North Oxfordshire, is a constituency in Oxfordshire created in 1553 and represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since 2015 by Victoria Prentis of the Conservative Party. She currently serves as Attorney General for England and Wales. In terms of electorate, Banbury was the 16th largest constituency in the United Kingdom at the time of the 2015 general election. Constituency profile The constituency has relatively high economic dependence on agriculture, as well as modern industry (particularly motorsport), research and development, public services and, to a lesser extent, defence. It contains two large market towns, Banbury and Bicester, where the majority of the electorate live. It is a partly rural seat, with the northwest of the constituency on the edge of the Cotswolds. The area has experienced significant urban growth and is popular with commuters who favour its fast transport links to Birmingham, Oxford a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambrosius Aurelianus
Ambrosius Aurelianus ( cy, Emrys Wledig; Anglicised as Ambrose Aurelian and called Aurelius Ambrosius in the ''Historia Regum Britanniae'' and elsewhere) was a war leader of the Romano-British who won an important battle against the Anglo-Saxons in the 5th century, according to Gildas. He also appeared independently in the legends of the Britons, beginning with the 9th-century ''Historia Brittonum''. Eventually, he was transformed by Geoffrey of Monmouth into the uncle of King Arthur, the brother of Arthur's father Uther Pendragon, as a ruler who precedes and predeceases them both. He also appears as a young prophet who meets the tyrant Vortigern; in this guise, he was later transformed into the wizard Merlin. According to Gildas Ambrosius Aurelianus is one of the few people whom Gildas identifies by name in his sermon ''De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae'', and the only one named from the 5th century. ''De Excidio'' is considered the oldest extant British document about the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherwell (district)
Cherwell ( ) is a local government district in northern Oxfordshire, England. The district takes its name from the River Cherwell, which drains south through the region to flow into the River Thames at Oxford. Towns in Cherwell include Banbury and Bicester. Kidlington is a contender for largest village in England. The district was formed on 1 April 1974, under the Local Government Act 1972, by a merger of the municipal borough of Banbury, Bicester urban district, Banbury Rural District and Ploughley Rural District. Geography The Northern half of the Cherwell district consists mainly of soft rolling hills going down towards the River Cherwell, but the southern half of the district around Bicester is much flatter. Much of the district is soft rolling hills with the northwest of the district lying at the northern extremity of the Cotswolds. Transport Much of the district is within easy reach of the M40, with junctions 9, 10 and 11 in the district. It also has good rail links w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danelaw
The Danelaw (, also known as the Danelagh; ang, Dena lagu; da, Danelagen) was the part of England in which the laws of the Danes held sway and dominated those of the Anglo-Saxons. The Danelaw contrasts with the West Saxon law and the Mercian law. The term is first recorded in the early 11th century as ''Dena lage''. The areas that constituted the Danelaw lie in northern and eastern England, long occupied by Danes and other Norsemen. The Danelaw originated from the invasion of the Great Heathen Army into England in the 9th century, although the term was not used to describe a geographic area until the 11th century. With the increase in population and productivity in Scandinavia, Viking warriors, having sought treasure and glory in the nearby British Isles, "proceeded to plough and support themselves", in the words of the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' for the year 876. Danelaw can describe the set of legal terms and definitions created in the treaties between Alfred the Great, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Roman Pottery
Pottery was produced in enormous quantities in ancient Rome, mostly for utilitarian purposes. It is found all over the former Roman Empire and beyond. Monte Testaccio is a huge mound, waste mound in Rome made almost entirely of broken amphorae used for transporting and storing liquids and other products – in this case probably mostly Spanish olive oil, which was landed nearby, and was the main fuel for lighting, as well as its use in the kitchen and washing in the Thermae, baths. It is usual to divide Roman domestic pottery broadly into coarse wares and fine wares, the former being the everyday pottery jars, dishes and bowls that were used for cooking or the storage and transport of foods and other goods, and in some cases also as tableware, and which were often made and bought locally. Fine wares were serving vessels or tableware used for more formal dining, and are usually of more decorative and elegant appearance. Some of the most important of these were made at specialised p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toponymy
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of any geographical feature, and full scope of the term also includes proper names of all cosmographical features. In a more specific sense, the term ''toponymy'' refers to an inventory of toponyms, while the discipline researching such names is referred to as ''toponymics'' or ''toponomastics''. Toponymy is a branch of onomastics, the study of proper names of all kinds. A person who studies toponymy is called ''toponymist''. Etymology The term toponymy come from grc, τόπος / , 'place', and / , 'name'. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' records ''toponymy'' (meaning "place name") first appearing in English in 1876. Since then, ''toponym'' has come to replace the term ''place-name'' in professional discourse among geographers. Toponym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watling Street
Watling Street is a historic route in England that crosses the River Thames at London and which was used in Classical Antiquity, Late Antiquity, and throughout the Middle Ages. It was used by the ancient Britons and paved as one of the main Roman roads in Britannia (Roman-governed Great Britain during the Roman Empire). The route linked Dover and London in the southeast, and continued northwest via St Albans to Wroxeter. The line of the road was later the southwestern border of the Danelaw with Wessex and Mercia, and Watling Street was numbered as one of the major highways of medieval England. First used by the ancient Britons, mainly between the areas of modern Canterbury and using a natural ford near Westminster, the road was later paved by the Romans. It connected the ports of Dubris (Dover), Rutupiae (Richborough Castle), Lemanis (Lympne), and Regulbium (Reculver) in Kent to the Roman bridge over the Thames at Londinium (London). The route continued northwest through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills, or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The Roman World", page 50. Warwick Press, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akeman Street
Akeman Street is a Roman road in southern England between the modern counties of Hertfordshire and Gloucestershire. It is approximately long and runs roughly east–west. Akeman Street linked Watling Street just north of Verulamium (near modern St Albans) with the Fosse Way at Corinium Dobunnorum (now Cirencester). Evidence suggests that the route may well have been an older track, metalled and reorganised by the Romans. Its course passes through towns and villages including Hemel Hempstead, Berkhamsted, Tring, Aylesbury, Alchester (outside modern Bicester), Chesterton, Kirtlington, Ramsden and Asthall. Parts of the A41 road between Berkhamsted and Bicester use the course of the former Roman road, as did the Sparrows Herne turnpike between Berkhamsted and Aylesbury. A minor road between Chesterton and Kirtlington also uses its course. Other parts are in use as public footpaths, including a stretch between Tackley and Stonesfield that is part of the Oxfordshire Way. The ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Emrys_Wledig.jpg)




