|
Amazon Basin (sedimentary Basin)
The Amazon Basin is a large sedimentary basin (620,000 square kilometres (240,000 sq mi)) located near the middle and lower course of the Amazon River, south the Guiana Shield and north of the Central Brazilian Shield. The basin developed on a rift that originated about 550 million years ago during the Cambrian. Location The Amazon Basin is located south of the Guiana Shield, north of the Central Brazilian Shield, east of the Solimões Basin, and west of the Marajó Basin. It is bound to the west by the Púrus Arch and in the east by the Gurupá Arch. The basin has an elongated shape with a WSW-ENE orientation. Its long axis runs from the vicinity of Manaus to the area near the confluence of Xingu River with the Amazon River. Evolution of the Basin The Amazon Basin was developed on a rift, called the Sub-Amazonal Rift, that originated about 550 million years ago during continental collision of the West African Craton. Parts of the rift were reactivated during the openi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazon River
The Amazon River (, ; es, Río Amazonas, pt, Rio Amazonas) in South America is the largest river by discharge volume of water in the world, and the disputed longest river system in the world in comparison to the Nile. The headwaters of the Apurímac River on Nevado Mismi had been considered for nearly a century as the Amazon basin's most distant source, until a 2014 study found it to be the headwaters of the Mantaro River on the Cordillera Rumi Cruz in Peru. The Mantaro and Apurímac rivers join, and with other tributaries form the Ucayali River, which in turn meets the Marañón River upstream of Iquitos, Peru, forming what countries other than Brazil consider to be the main stem of the Amazon. Brazilians call this section the Solimões River above its confluence with the Rio Negro forming what Brazilians call the Amazon at the Meeting of Waters ( pt, Encontro das Águas) at Manaus, the largest city on the river. The Amazon River has an average discharge of about – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazon Alluvium Deposit - Autazes
Amazon most often refers to: * Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek mythology * Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin * Amazon River, in South America * Amazon (company), an American multinational technology company Amazon or Amazone may also refer to: Places South America * Amazon Basin (sedimentary basin), a sedimentary basin at the middle and lower course of the river * Amazon basin, the part of South America drained by the river and its tributaries * Amazon Reef, at the mouth of the Amazon basin Elsewhere * 1042 Amazone, an asteroid * Amazon Creek, a stream in Oregon, US People * Amazon Eve (born 1979), American model, fitness trainer, and actress * Lesa Lewis (born 1967), American professional bodybuilder nicknamed "Amazon" Art and entertainment Fictional characters * Amazon (Amalgam Comics) * Amazon, an alias of the Marvel supervillain Man-Killer * Amazons (DC Comics), a group of superhuman characters * The Amazon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
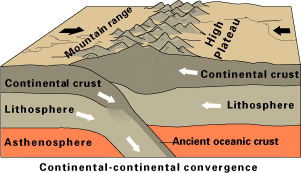
Continental Collision
In geology, continental collision is a phenomenon of plate tectonics that occurs at convergent boundaries. Continental collision is a variation on the fundamental process of subduction, whereby the subduction zone is destroyed, mountains produced, and two continents sutured together. Continental collision is only known to occur on Earth. Continental collision is not an instantaneous event, but may take several tens of millions of years before the faulting and folding caused by collisions stops. The collision between India and Asia has been going on for about 50 million years already and shows no signs of abating. Collision between East and West Gondwana to form the East African Orogen took about 100 million years from beginning (610 Ma) to end (510 Ma). The collision between Gondwana and Laurasia to form Pangea occurred in a relatively brief interval, about 50 million years long. Subduction zone: the collision site The process begins as two conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonics
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents known as cratons, and the ways in which the relatively rigid plates that constitute the Earth's outer shell interact with each other. Tectonics also provide a framework for understanding the earthquake and volcanic belts that directly affect much of the global population. Tectonic studies are important as guides for economic geologists searching for fossil fuels and ore deposits of metallic and nonmetallic resources. An understanding of tectonic principles is essential to geomorphologists to explain erosion patterns and other Earth surface features. Main types of tectonic regime Extensional tectonics Extensional tectonics is associated with the stretching and thinning of the crust or the lithosphere. This type of tectonics is found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the Atlanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West African Craton
The West African Craton (WAC) is one of the five cratons of the Precambrian basement rock of Africa that make up the African Plate, the others being the Kalahari craton, Congo craton, Saharan Metacraton and Tanzania Craton.Jessell M.W., Liégeois J-P. (2015). "100 years of research on the West African Craton". ''Journal of African Earth Sciences''. 112(B): 377– 381. Cratons themselves are tectonically inactive, but can occur near active margins,Ennih N. & Liégeois J-P. (2008). ''The Boundaries of the West African Craton''. Geological Society, London, Special Publications. 297: 1–17. with the WAC extending across 14 countries in Western Africa, coming together in the late Precambrian and early Palaeozoic eras to form the African continent. It consists of two Archean centers juxtaposed against multiple Paleoproterozoic domains made of greenstone belts, sedimentary basins, regional granitoid-tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite, tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite (TTG) plutons, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xingu River
The Xingu River ( ; pt, Rio Xingu, ; Mẽbêngôkre: ''Byti'', ) is a river in north Brazil. It is a southeast tributary of the Amazon River and one of the largest clearwater rivers in the Amazon basin, accounting for about 5% of its water. __TOC__ Description and history The first Indigenous Park in Brazil was created in the river basin by the Brazilian government in the early 1960s. This park marks the first indigenous territory recognized by the Brazilian government and it was the world's largest indigenous preserve on the date of its creation. Currently, fourteen tribes live within Xingu Indigenous Park, surviving on natural resources and extracting from the river most of what they need for food and water. The Brazilian government is building the Belo Monte Dam, which will be the world's third-largest hydroelectric dam, on the Lower Xingu. Construction of this dam is under legal challenge by environment and indigenous groups, who assert the dam would have negative enviro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurupá
Gurupá or Santo Antonio de Gurupá is a municipality on the Amazon River in state of Pará, northern Brazil located near the world's largest river island, Marajó, 300 km upstream from the upper mouth of the river on the Atlantic coast. The city is a center for palm heart extraction and commerce. It is a municipal seat and major river boat port. History Gurupá is derived from the tupi language words ''guru'' (mouth) and ''pa'' (wide), and is associated with regions where water channels become wider. The word appears in the name of many localities in Brazil. Gurupá was founded in 1609 as a Dutch trading post that they called Mariocai, after the indigenous peoples living there. It was the third of three trading posts established by the Dutch along the lower reaches of the Amazon and Xingu River The Xingu River ( ; pt, Rio Xingu, ; Mẽbêngôkre: ''Byti'', ) is a river in north Brazil. It is a southeast tributary of the Amazon River and one of the largest clearwat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marajó
Marajó () is a large coastal island in the state of Pará, Brazil. It is the main and largest of the islands in the Marajó Archipelago. Marajó Island is separated from the mainland by Marajó Bay, Pará River, smaller rivers (especially Macacos and Tajapuru), Companhia River, Jacaré Grande River, Vieira Grande Bay and Atlantic Ocean. From approximately 400 BC to 1600 AD, Marajó was the site of an advanced Pre-Columbian society called the Marajoara culture, which may have numbered more than 100,000 people at its peak. Today, the island is known for its large water buffalo population, as well as the ''pororoca'' tidal bore periodically exhibited by high tides overcoming the usual complex hydrodynamic interactions in the surrounding rivers. It is the second-largest island in South America, and the 35th largest island in the world. With a land area of Marajó is comparable in size to Switzerland. Its maximum span is long and in perpendicular width. Geography Maraj� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solimões River
Solimões () is the name often given to upper stretches of the Amazon River in Brazil from its confluence with the Rio Negro upstream to the border of Peru. Geography The Amazon / Solimões river just above the confluence of the Solimões and Rio Negro is already by far the largest river in the world, even though its two largest tributaries (the Negro and the Madeira River) have not yet contributed to the flow volume. The Solimões portion of the Amazon River lies entirely in the state of Amazonas, Brazil, and some portion of the state is often referred to as the "Solimões region". The ecoregion of the Solimões River drainage basin is entirely tropical rainforest. Etymology An Amazonian aboriginal nation called ''Soriman'' was corrupted in Portuguese to ''Solimão'' and ''Soliemoens'', from which the name of this section of the river and region it drains is derived. Use of the name ''Solimões'' for the upper Amazon is mostly confined to Brazilian speakers of Portuguese; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Time Scale
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardized international units of geologic time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)