|
Amarna Letter EA 299
Amarna letter EA 299, titled: ''"A Plea for Help"'', is a fairly short clay tablet Amarna letter from ''"governor"'' Yapahu of city-state Gazru. The clay tablet surface has been partially eroded, but the cuneiform is still mostly legible. The tablet is medium in color (lt tan—medium lt chocolate: (see here) and is about 12 cm tall, and a wide tablet, about 8.5 cm. The tablet is located in the British Museum, no. 29832. The Amarna letters, about 300, numbered up to EA 382, are a mid 14th century BC, about 1360 BC and 30–35 years later, correspondence. The initial corpus of letters were found at Akhenaten's city Akhetaten, in the floor of the Bureau of Correspondence of Pharaoh; others were later found, adding to the body of letters. The letter EA 299: ''"A Plea for Help"'' EA 299, letter number three of four from Yapahu of Gazru. (Not a linear, line-by-line translation.) ''Obverse'' (See here (or High Def :Paragraph I :(Lines 1-11)—To the king, my lor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letter
The Amarna letters (; sometimes referred to as the Amarna correspondence or Amarna tablets, and cited with the abbreviation EA, for "El Amarna") are an archive, written on clay tablets, primarily consisting of diplomatic correspondence between the Ancient Egypt, Egyptian administration and its representatives in Canaan and Amurru kingdom, Amurru, or neighboring kingdom leaders, during the New Kingdom, spanning a period of no more than thirty years between c. 1360–1332 BC (see Amarna letters#Chronology, here for dates).Moran, p.xxxiv The letters were found in Upper Egypt at el-Amarna, the modern name for the ancient Egyptian capital of ''Akhetaten'', founded by pharaoh Akhenaten (1350s–1330s BC) during the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. The Amarna letters are unusual in Egyptological research, because they are written not in the language of ancient Egypt, but in cuneiform, the writing system of ancient Mesopotamia. Most are in a variety of Akkadian language, Akkadian sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courier
A courier is a person or organisation that delivers a message, package or letter from one place or person to another place or person. Typically, a courier provides their courier service on a commercial contract basis; however, some couriers are government or state agency employees (for example: a diplomatic courier). Duties and functions Couriers are distinguished from ordinary mail services by features such as speed, security, tracking, signature, specialization and individualization of express services, and swift delivery times, which are optional for most everyday mail services. As a premium service, couriers are usually more expensive than standard mail services, and their use is normally limited to packages where one or more of these features are considered important enough to warrant the cost. Courier services operate on all scales, from within specific towns or cities, to regional, national and global services. Large courier companies include DHL, DTDC, FedEx, EMS Inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iš (cuneiform)
The cuneiform sign iš is a common use sign in the Amarna letters and the ''Epic of Gilgamesh.'' It is used syllabically for ''iš''; also for ''mel'', ''mil'', and a Sumerogramic usage for ''IŠ'' (Epic of Gilgamesh). Alphabetically as "iš", its most common usage, it can be used for "i" or "š". In Akkadian, the four vowels ''a, e, i, o'', are all interchangeable, and the three different "s", can also be interchanged: ''s, ṣ, š''. ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' use For the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', the following usage is found in Tablets I-XII: ''iš''-(134 times); ''mel''-(1); ''mil''-(8); IŠ-(18 times). Some common uses of "iš" in the Amarna letters One of the most common uses of "iš" in the Amarna letters, is the use of the Akkadian language word ''"ištu"'', which means "from", ("since"), in the English language. In the ''vassal city-state'' letters, in dialogue with the Pharaoh-in-Egypt, there is often mention of having listened to the correspondence – "words of the ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ša (cuneiform)
The cuneiform ša sign is a common, multi-use sign, a syllabic for ''ša'', and an alphabetic sign used for ''š'', or ''a''; it is common in both the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' over hundreds of years, and the 1350 BC Amarna letters. Besides ''ša'' usage in word components of verbs, nouns, etc., it has a major usage between words. In Akkadian, for English language ''"who"'', it is an interrogative pronoun; in the Akkadian language as ''ša'', (as "that", "what"; ("that (of)", "which (of)"), in English it used for ''who, what, which, etc.''. Ša, and Ka, the stroke differences The difference in the construction of the signs ''ka'' and ''ša'' are as follows: "ka" when scribed in the Amarna letters often shows the distinctiveness of the right section of the sign, versus the left section. For ''ša'', the right section is constructed with two wedge strokes (one scribed above the other), between the two verticals, at right. For ''ka'', the right side mostly, in the Amarna letters ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ut (cuneiform)
The cuneiform ud sign, also ut, and with numerous other syllabic and Sumerogram uses, is a common sign for the mid 14th-century BC Amarna letters and the ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. The sign is constructed upon the single vertical stroke , with various positionings of two wedge-strokes at the left, sometimes approximately centered, or often inscribed upwards to the left, the second wedge-stroke (or 'angled line-stroke'), occasionally inscribed/ligatured upon the first. The wedge-strokes can have any size, are often smaller than the vertical, but as an example, Amarna letter EA 256, can be almost as large as the vertical. In the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', sign ''ud'' is listed as used for the following linguistic elements: :* lah :* par :* pir :* tam :* tú :* ud :* ut :* uṭ Sumerograms :* BABBAR--"silver" :* UD--"daily", "day", (2nd "daily"-(no. 2)) :* UTU--"sun" The usage numbers for each linguistic element in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' are as follows: ''lah''--(2), ''par''--(5) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
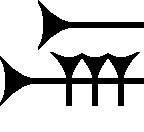
Meš (cuneiform)
The cuneiform MEŠ, or meš is a plural form attached at the end of Mesopotamian cuneiform words as a suffix. As part of a name (PN, personal name, or other), or major class being referenced, in capital letters (a Sumerogram form), it is typically separated from other capital letter Sumerograms with a period. The name of the group can follow, in lower case letters, for example: (men-massu, Amarna letter EA 365), LÚ.MEŠ– ma- as-sà-meš, (and using a secondary suffix meš, not being typical). The MEŠ cuneiform is a vertical stroke, followed by three or four angled smaller wedge-strokes. The strokes can also be "not angled", but 45 degree wedges, smaller, or large. For example, Amarna letter EA 161, Aziru to Pharaoh, shows a series of six preparation items listed sequentially. The following wedges (on the meš or Sumerogram .MEŠ wedges, are large, and the scribe has a scribing base line, that follows the vertical stroke, a baseline on which the wedges are placed sequentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
An (cuneiform)
The cuneiform an sign (or sumerogram AN, in Akkadian consisting of ASH 𒀸 and MAŠ 𒈦), is a common, multi-use sign, a syllabic for ''an'', and an alphabetic sign used for ''a'', or ''n''; it is common in both the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' over hundreds of years, and the 1350 BC Amarna letters, and other cuneiform texts. It is also used for the designation of a "god", and is sometimes represented as a superscript: d, or capitalized: D, for " dingir", English language, "god". The example photo at right shows (2nd list), a list of 14 named gods, all with "an"; the first pair on the list ''AN-UTU'', or DUTU, refers to the "sun-god", using Ud (cuneiform), as the sumerogram, namely UTU (sun Sumerogram). Cuneiform ''an'' can also be found in compound form with another cuneiform sign, an example being DAGAL, . The older version of DAGAL used the 'god symbol' as a star within the sign: ; (older version of DAGAL, incorporating "star": ). ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' usage In the ''Epic of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ia (cuneiform)
The cuneiform ia sign 𒅀, is a combined sign, containing i (cuneiform) ligatured with a (cuneiform); it has the common meaning in the suffix form ''-ia'', for the meaning of "-mine". In the Amarna letters, the letters written to the Pharaoh of Egypt (Mizri/Misri in the letters), the Pharaoh is often referenced as "Lord-mine", or especially: ''King-Lord-mine'': "My King, My Lord". In Akkadian, the form is "Šarru-Bēlu-ia"-(King-Lord-mine), since the spelling in some Amarna letters is sometimes ŠÁR- RI for Šarru, (LUGAL = ŠÁR). ''Ia'' is also used in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. It is listed in Parpola's Glossary (Parpola, 1971), for Akkadian language words: meaning ''"mine"'', ''"(to) me"'', and ''"me"'', and one usage for the word "battering ram", ''iašubů''. Amarna letter usage of "ia" Besides the usage of Akkadian language words beginning with ''ia'', the common examples of — ''iāši'', "(to) me", ''iāti'', "me", ''iā'u'', "mine", and ''iānu'', "there is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
En (cuneiform)
En (Borger 2003 nr. 164 ; U+12097 𒂗, see also Ensí) is the Sumerian cuneiform for "lord" or "priest". Originally, it seems to have been used to designate a high priest or priestess of a Sumerian city-state's patron-deity – a position that entailed political power as well. It may also have been the original title of the ruler of Uruk. See ''Lugal, ensi and en'' for more details. Deities including En as part of their name include DEnlil, DEnki, DEngurun, and DEnzu. Enheduanna, Akkadian 2285 BC – 2250 BC was the first known holder of the title, "En Priestess." Archaic forms The corresponding Emesal dialect word was UMUN, which may preserve an archaic form of the word. Earlier Emeg̃ir (the standard dialect of Sumerian) forms can be postulated as ''*ewen'' or ''*emen'', eventually dropping the middle consonant and becoming the familiar EN. Amarna letters: bêlu The 1350 BC Amarna letters use EN for bêlu, though not exclusively. The more common spelling is mostly 'be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diš (cuneiform)
Diš is a cuneiform sign represented by 𒁹 or . It has many uses in cuneiform texts, including in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. Description 𒁹 is a cuneiform sign. In Unicode, it is represented by U+12079 (DISH) Use of the vertical sign In the Amarna letters, it is commonly used to denote ''Male individuals''. (Women are denoted by sal (cuneiform), . ) The sign is also used to denote "numbers of items". The sign is used for 1. Examples of multiple uses in the Amarna letters, is to address the Pharaoh, often as ''"servant-yours, at 2 Feet, .. I bow."'' An example of multiple uses in the Amarna letters, often the bowing down is done: ''" .. 7 and 7 times (I bow) !"'', with seven small strokes as units of number "1". ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' usage In the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', there are also uses for "diš", and "tiš". (In the Akkadian language, "d" & "t", are interchangeable (voiced vs unvoiced). The ''ana'', (''diš'') sign usage in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' is as follows: ''a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Na (cuneiform)
The cuneiform na sign is a common, multi-use sign, a syllabic for ''na'', and an alphabetic sign used for ''n'', or ''a''; it is common in both the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' over hundreds of years, and the 1350 BC Amarna letters. In the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' it also has sumerogramic (capital letter (majuscule)) usage for NA. An example usage for ''NA'' in the Epic is for the spelling of ''NA.GAD'', (also '' LÚ.NA.GAD'', and the plural '' LÚ.NA.GAD. MEŠ''), for Akkadian language "nāqidu", ''"herdsman"''. The usage for ''NA'' in herdsman is only for 3 spellings. The commonness of cuneiform ''na'', in the top 25 used signs by Buccellati (Buccellati 1979), (2nd highest usage, exceeded by a: ''a (cuneiform)'') is because of usage for the spelling of ''a-na'' (Akkadian language "ana") -, the common preposition spelling for English language: ''to, for, by, of, at, etc.''. It is also a component for the Akkadian language preposition: ''i-na'' (''ina''), meaning: ''in, into, by, etc.''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A (cuneiform)
The cuneiform sign 𒀀 ( DIŠ, DIŠ OVER DIŠ) for a, and in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' the sumerogram A, Akkadian for ''mû'', "water", which is used in the ''Gilgamesh flood myth'', Chapter XI of the Epic, or other passages. The sign is also used extensively in the Amarna letters. Cuneiform ''a'' is the most common of the four vowels in the Akkadian language, ''a'', ''e'', ''i'', and ''u''. All vowels can be interchangeable, depending on the scribe, though spellings of Akkadian words in dictionaries, will be formalized, and typically: unstressed, a 'long-vowel', or thirdly, a 'combined' vowel (often spelled with two signs (same vowel, ending the first sign, and starting the next sign), thus combined into the single vowel, ''â'', ''ê'', ''î'', or ''û''.). Cuneiform ''a'' is the most common of the four vowels, as can be shown by usage in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', the usage numbers being (ú (u, no. 2) is more common than u, (no. 1), which has additional usages, numera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)