|
Amarna Letter EA 26
Amarna letter EA 26, titled ''To the Queen Mother: Some Missing Gold Statues'', is a shorter-length clay tablet Amarna letter from Tushratta of Mittani. Unlike the next letter EA 27 from Tushratta, which is more than twice as tall, and about twice as wide-(XXVII paragraphs), EA 26 is topical and synoptic about recent events about the desire for 'gold statues' (VII paragraphs). The letter is addressed to the Pharaoh's wife, Teye, and its dimensions are approximately: tall, wide, and thick. EA 26 has missing edges, left and right. The piece pictured is the Oriental Institute of Chicago's piece which is part of the obverse, lower-left corner, at the beginning of lines of text. The entire obverse of EA 26 can be seehere with its missing edges and scuffed/eroded surfaces on the edges. The Oriental Institute piece shows the high quality of inscribed cuneiform, as visible in undamaged sections of EA 26. The letter EA 26: ''To the Queen Mother: Some Missing Gold Statues'' EA 26, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayyab Letter Mp3h8880
Ayyab was a ruler of AéÀtartu (present day Tell Ashtara) south of Damascus. According to the Amarna letters, cities/city-states and their kings in the region ã just like countries to the north, such as Hatti of the Hittites, fell prey to a wave of attacks by Habiru raiders. The Amarna correspondence corpus covers a period from 1350ã 1335 BC. Another ruler of AéÀtartu cited in the Amarna letters is BiridaéÀwa. The letters do not clearly indicate their title, leading some scholars to describe them as kings of Damascus (DimaéÀqu) while others believe they were high Egyptian officials, possibly mayors.Wayne Thomas Pitard''Ancient Damascus: A Historical Study of the Syrian City-State from Earliest Times Until Its Fall to the Assyrians in 732 B.C.E.''Eisenbrauns, 1987. p. 67. Ayyab's letter EA 364 Ayyab is the author of only one letter to the Egyptian pharaoh, letter EA 364-( EA for 'el Amarna'). Title: ''Justified war'' :To the king, my lord: Message of ''Ayyab'', your servant. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letter EA 271
Amarna letter EA 271, titled: ''"The Power of the 'Apiru,"'' is a moderately short, tallish, rectangular clay tablet letter, approximately 3 in wide x 4 in tall, from Milkilu the mayor/ruler of Gazru (Gezer), of the mid 14th century BC Amarna letters. The Canaanite city-states were visited by the scribes, with short 'status reports' sent to the Pharaoh (King) reporting on city or regional accounts, for example the troubles with the habiru, or other external affairs. Many of the Canaanite letters are short, with some nearly identical phraseology of words, as well as the layout of the individual clay tablet letters. Milkilu authored EA 268 through EA 271. Amarna letter EA 270-(29 lines) is nearly identical in shape to EA 271-(27 lines), with the beginning lines of the obverse, nearly identical in wording, and spacing. The Amarna letters, about 300, numbered up to EA 382, are a mid 14th century BC, about 1350 BC and 20ã25 years later, correspondence. The initial corpus of letters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
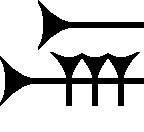
Te (cuneiform)
The cuneiform te sign is found in both the 14th century BC Amarna letters and the Epic of Gilgamesh; it is also notable in the Hittite language, and for that language, besides its usage as ''te'', it is a Sumerogram (logogram or ideogram), and is used as a component in the word for "envoy", (Lû-àE-mu), or Lû-ÿ˜E-mi, . 'Envoy' is used in the famous Hittite annals, narrating the story of Prince Zannanza who after going to Egypt to become husband (and Pharaoh) to Queen Nefertiti, was intercepted and killed. The usage of ''te'' in the Epic of Gilgamesh, is only for syllabic or alphabetic ''te'', 124 times. The sign also comes in two forms, with two pairs of the left 4-signs, or one above a row of 3-signs, either group tilted, down to the right. References *Held, Schmalstieg, Gertz, 1987. ''Beginning Hittite''. Warren H. Held, Jr, William R. Schmalstieg, Janet E. Gertz, c. 1987, Slavica Publishers, Inc. w/ Glossaries, Sign List, Indexes, etc., 218 pages. * Moran, William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MUNUS (Sumerogram)
MUNUS, Þˋ, or SAL is the capital-letter (majuscule) Sumerogram for the Akkadian language word "ÿÈuhártu",Rainey, 1970 ''young woman'', or ''woman''. The word is commonly used in the Amarna letters diplomatic letters, as well as elsewhere, for example in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. Epic of Gilgamesh The cuneiform character for woman, or ''"young woman"'', has many alternative uses in the Epic of Gilgamesh; it is used for the following: ''mim'', (21 times); ''rag'', (2); ''rak'', (10); ''raq'', (1); ''sal'', (1); ''éÀal'', (25); ''Mû'', (43 times). References Further reading * {{cite book , author= Parpola, Simo, with Mikko Luuko, and Kalle Fabritius , title=The Standard Babylonian, Epic of Gilgamesh , publisher=The Neo-Assyrian Text Corpus Project , year=1997 , isbn=951-45-7760-4 , id=(Volume 1) in the original Akkadian cuneiform and transliteration; commentary and glossary are in English *Rainey Rainey is a name of British-Irish origin. People with the surname * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Na (cuneiform)
The cuneiform na sign is a common, multi-use sign, a syllabic for ''na'', and an alphabetic sign used for ''n'', or ''a''; it is common in both the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' over hundreds of years, and the 1350 BC Amarna letters. In the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' it also has sumerogramic (capital letter (majuscule)) usage for NA. An example usage for ''NA'' in the Epic is for the spelling of ''NA.GAD'', (also '' Lû.NA.GAD'', and the plural '' Lû.NA.GAD. MEé ''), for Akkadian language "náqidu", ''"herdsman"''. The usage for ''NA'' in herdsman is only for 3 spellings. The commonness of cuneiform ''na'', in the top 25 used signs by Buccellati (Buccellati 1979), (2nd highest usage, exceeded by a: ''a (cuneiform)'') is because of usage for the spelling of ''a-na'' (Akkadian language "ana") -, the common preposition spelling for English language: ''to, for, by, of, at, etc.''. It is also a component for the Akkadian language preposition: ''i-na'' (''ina''), meaning: ''in, into, by, etc.''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A (cuneiform)
The cuneiform sign Þ ( DIé , DIé OVER DIé ) for a, and in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' the sumerogram A, Akkadian for ''mû£'', "water", which is used in the ''Gilgamesh flood myth'', Chapter XI of the Epic, or other passages. The sign is also used extensively in the Amarna letters. Cuneiform ''a'' is the most common of the four vowels in the Akkadian language, ''a'', ''e'', ''i'', and ''u''. All vowels can be interchangeable, depending on the scribe, though spellings of Akkadian words in dictionaries, will be formalized, and typically: unstressed, a 'long-vowel', or thirdly, a 'combined' vowel (often spelled with two signs (same vowel, ending the first sign, and starting the next sign), thus combined into the single vowel, ''ûÂ'', ''ûˆ'', ''ûÛ'', or ''û£''.). Cuneiform ''a'' is the most common of the four vowels, as can be shown by usage in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', the usage numbers being (û¤ (u, no. 2) is more common than u, (no. 1), which has additional usages, numera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumerogram
A Sumerogram is the use of a Sumerian cuneiform character or group of characters as an ideogram or logogram rather than a syllabogram in the graphic representation of a language other than Sumerian, such as Akkadian or Hittite. Sumerograms are normally transliterated in majuscule letters, with dots separating the signs. In the same way, a written Akkadian word that is used ideographically to represent a language other than Akkadian (such as Hittite) is known as an ''Akkadogram''. This type of logogram characterized, to a greater or lesser extent, every adaptation of the original Mesopotamian cuneiform system to a language other than Sumerian. The frequency and intensity of their use varied depending on period, style, and genre. The name of the cuneiform sign written in majuscule letters is a modern Assyriological convention. Most signs have a number of possible Sumerian sound values. The readers of Assyrian or Hittite texts using these Sumerograms would not necessarily have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akkadian Language
Akkadian (, Akkadian: )John Huehnergard & Christopher Woods, "Akkadian and Eblaite", ''The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the World's Ancient Languages''. Ed. Roger D. Woodard (2004, Cambridge) Pages 218-280 is an extinct East Semitic language that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia ( Akkad, Assyria, Isin, Larsa and Babylonia) from the third millennium BC until its gradual replacement by Akkadian-influenced Old Aramaic among Mesopotamians by the 8th century BC. It is the earliest documented Semitic language. It used the cuneiform script, which was originally used to write the unrelated, and also extinct, Sumerian (which is a language isolate). Akkadian is named after the city of Akkad, a major centre of Mesopotamian civilization during the Akkadian Empire (c. 2334ã2154 BC). The mutual influence between Sumerian and Akkadian had led scholars to describe the languages as a '' Sprachbund''. Akkadian proper names were first attested in Sumerian texts from around the mid 3rd-mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacuna (manuscripts)
A lacuna ( lacunae or lacunas) is a gap in a manuscript, inscription, text, painting, or musical work. A manuscript, text, or section suffering from gaps is said to be "lacunose" or "lacunulose". Weathering, decay, and other damage to old manuscripts or inscriptions are often responsible for lacunae - words, sentences, or whole passages that are missing or illegible. Palimpsests are particularly vulnerable. To reconstruct the original text, the context must be considered. In papyrology and textual criticism, this may lead to competing reconstructions and interpretations. Published texts that contain lacunae often mark the section where text is missing with a bracketed ellipsis. For example, "This sentence contains 20 words, and ..nouns," or, "Finally, the army arrived at ..and made camp." Notable examples See also * Unfinished work Unfinished may refer to: *Unfinished creative work, a work which a creator either chose not to finish or was prevented from finishing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuni (Amarna Letters)
{{disambiguation ...
Yuni may refer to: * ''Yuni'' (film), 2021 internationally co-produced drama film *Yuni, Hokkaido, a town in Sorachi Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan * Yuni Station, a railway station in Yuni *Yuni Shara (born 1972), Indonesian singer * Yuni (''Star Twinkle PreCure''), a character in the anime series ''Star Twinkle PreCure'' * Yuni (wrestler), Japanese professional wrestler See also * Yuny (other) * Yuna (other) Yuna may refer to: Geography *Yuna River, Dominican Republic * Yuna, Western Australia Music * ''Yuna'' (album), a 2012 album by Malaysian singer Yuna * ''Yuna'' (EP), a 2008 album by Malaysian acoustic singer Yuna People Japanese *Yuna Aoi, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courier
A courier is a person or organisation that delivers a message, package or letter from one place or person to another place or person. Typically, a courier provides their courier service on a commercial contract basis; however, some couriers are government or state agency employees (for example: a diplomatic courier). Duties and functions Couriers are distinguished from ordinary mail services by features such as speed, security, tracking, signature, specialization and individualization of express services, and swift delivery times, which are optional for most everyday mail services. As a premium service, couriers are usually more expensive than standard mail services, and their use is normally limited to packages where one or more of these features are considered important enough to warrant the cost. Courier services operate on all scales, from within specific towns or cities, to regional, national and global services. Large courier companies include DHL, DTDC, FedEx, EMS Inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
é u (cuneiform)
The cuneiform éÀu sign is a common, multi-use syllabic and alphabetic sign for ''éÀu'', ''éÀ'', and ''u''; it has a subsidiary usage for syllabic ''qat''; it also has a majuscule-(capital letter) Sumerogram usage for é U, for Akkadian language "qátu", the word for "hand". The human hand is the shape of cuneiform character ''éÀu'', and thus the origin of its creation (late 4th millennium BC, or early 3rd millennium BC). The scribal usage of a sign allows for any of the 4 vowels (no vowel 'o' in Akkadian), ''a, e, i, u'' to be interchangeable; thus a usage for syllabic ''qat'' could conceivably be used for the following (k can replace 'q', and d can replace 't'): ''q, a,'' or ''t''; also ''ka, qa, ad, at''. (The "éÀ" (shibilant s) is also interchangeable with the other two esses, "s", and "ÿÈ", for "''éÀu''"!) The ''éÀu'' sign has a common usage in the Amarna letters and the ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. Its usage numbers in the Epic are as follows:Parpola, 1971. ''The Standard Babylo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


