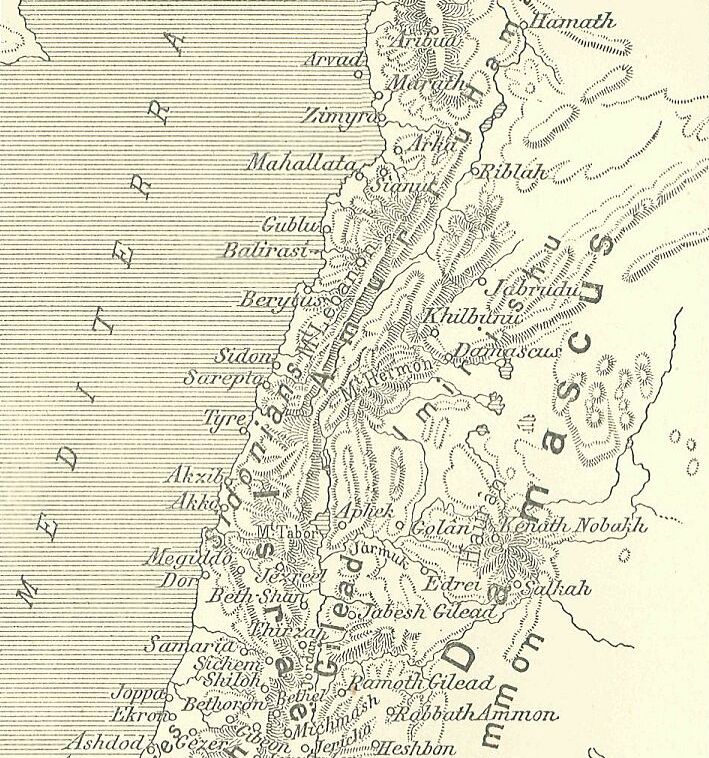
|
Amarna Letter EA 245
Amarna letter EA 245, titled: ''"Assignment of Guilt,"'' is a medium length clay tablet Amarna letter from Biridiya the governor-'mayor' of Magidda. It is letter number four of five from Biridiya. The letter is in pristine condition except for a missing flake (lower-right, obverse) causing a lacuna at the end of a few lines. The cuneiform characters are finely inscribed, with some photos that can even show the individual strokes of the cuneiform characters (the stroke sequence). The letter is 47-lines long, and about 5-in tall. Letter EA 245 (see here-(Obverse), is numbered BM 29855, at the British Museum. The Amarna letters, about 300, numbered up to EA 382, are a mid 14th century BC, about 1350 BC and 20–25 years later, correspondence. The initial corpus of letters were found at Akhenaten's city Akhetaten, in the floor of the Bureau of Correspondence of Pharaoh; others were later found, adding to the body of letters. The letter EA 245: ''"Assignment of Guilt"'' EA 245, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letters
The Amarna letters (; sometimes referred to as the Amarna correspondence or Amarna tablets, and cited with the abbreviation EA, for "El Amarna") are an archive, written on clay tablets, primarily consisting of diplomatic correspondence between the Ancient Egypt, Egyptian administration and its representatives in Canaan and Amurru kingdom, Amurru, or neighboring kingdom leaders, during the New Kingdom, spanning a period of no more than thirty years between c. 1360–1332 BC (see Amarna letters#Chronology, here for dates).Moran, p.xxxiv The letters were found in Upper Egypt at el-Amarna, the modern name for the ancient Egyptian capital of ''Akhetaten'', founded by pharaoh Akhenaten (1350s–1330s BC) during the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. The Amarna letters are unusual in Egyptological research, because they are written not in the language of ancient Egypt, but in cuneiform, the writing system of ancient Mesopotamia. Most are in a variety of Akkadian language, Akkadian sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma (cuneiform)
The cuneiform ma sign, is found in both the 14th century BC Amarna letters and the ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. In the Epic it is also used as the Sumerogram MA, (for Akkadian language "mina", ''manû'', a weight measure, as MA.NA, or MA.NA.ÀM). The ''ma'' sign is often used at the end of words, besides its alphabetic usage inside words as syllabic ''ma'', elsewhere for ''m'', or ''a''. The usage of cuneiform ''ma'' in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', is only exceeded by the usage of a (cuneiform) (1369 times, and 58, A (Sumerogram), versus 1047 times for ''ma'', 6 for MA (Sumerogram)). The high usage for ''a'' is partially a result of the prepositional use for ''a-na''-(Akkadian "ana", ''to, for'', etc.); "''i''", also has an increased prepositional use of i (cuneiform), for Akkadian ''ina'', ( i- na), for ''in, into, etc.'' References * Moran, William L. 1987, 1992. ''The Amarna Letters.'' Johns Hopkins University Press, 1987, 1992. 393 pages.(softcover, ) * Parpola, 1971. ''Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Di (cuneiform)
The cuneiform di sign, also de, ṭe, ṭi, and sumerograms DI and SÁ is a common-use sign of the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', the 1350 BC Amarna letters, and other cuneiform texts. In the Akkadian language for forming words, it can be used syllabically for: ''de, di, ṭe, and ṭi''; also alphabetically for letters ''d'', ''ṭ'', ''e'', or ''i''. (All the four vowels in Akkadian are interchangeable for forming words (''a, e, i, u''), thus the many choices of scribes is apparent for composing actual 'dictionary-entry' words.) Some consonant-pairs (d/t), are also interchangeable (for example the ''d'', ''t'', and ''ṭ''). ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' usage The usage numbers for ''di/de'' in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' are as follows: ''de''-(8) times, ''di''-(161), ''ṭe''-(7), ''ṭi''-(19), ''DI''-(1), ''SÁ''-(2) times. Besides ''ša'' usage in word components of verbs, nouns, etc., it has a major usage between words. In Akkadian, for English language ''"who"'', it is an interrogati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
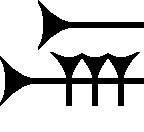
Ba (cuneiform)
The cuneiform sign ba, is a common-use sign of the Amarna letters, the ''Epic of Gilgamesh,'' and other cuneiform texts (for example Hittite texts). Linguistically, it has the alphabetical usage in texts for ''b'', ''a'', or syllabically for ''ba'', and also a replacement for ''"b"'', by ''"p"''. The a is replaceable in word formation by any of the 4 vowels: ''a, e, i,'' or ''u''. ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' usage The ''ba'' sign usage in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' is as follows: ''ba''-(282 times); ''BA''-(7). References * Moran, William L. 1987, 1992. ''The Amarna Letters.'' Johns Hopkins University Press, 1987, 1992. 393 pages.(softcover, ) * Parpola, 1971. ''The Standard Babylonian Epic of Gilgamesh'', Parpola, Simo, Neo-Assyrian Text Corpus Project, c 1997, Tablet I thru Tablet XII, Index of Names, Sign List, and Glossary-(pp. 119–145), 165 pages. ---- Image:Amarna_letter-_Royal_Letter_from_Ashur-uballit,_the_king_of_Assyria,_to_the_king_of_Egypt_M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hannathon
Hannathon, and of the 1350-1335 BC Amarna letters, Hinnatuna, or Hinnatuni/Hinnatunu, is the Biblical city/city-state of Hannathon, (meaning: ''"the Gift of Grace"''); in the Amarna letters correspondence as ''Hinnatuna'', it is a site in southern Canaan, site uncertain. Ancient settlement of Tel Hanaton in Lower Galilee has been suggested as a candidate. Amarna letters mentioning ''Hinnatuna'' Hinnatuna is referenced in 2 Amarna letters, EA 8, and EA 245 ('EA' stands for 'El Amarna'). Amarna letter EA 8 is a letter to Pharaoh by Burna-Buriash of Karaduniyaš-(i.e. Babylon). The letter, entitled: ''"Merchants murdered, vengeance demanded"'', states near the letter beginning: ''"...Now, my merchants who were on their way with Ahu-tabu, were detained in Canaan for business matters. After Ahu-tabu went on to my brother-(the pharaoh), –in'' Hinnatuna ''of Canaan, Šum-Adda, the son of Balumme, and Šutatna, the son of Šaratum of Akka-(modern Acre), having sent their men, k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Na (cuneiform)
The cuneiform na sign is a common, multi-use sign, a syllabic for ''na'', and an alphabetic sign used for ''n'', or ''a''; it is common in both the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' over hundreds of years, and the 1350 BC Amarna letters. In the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' it also has sumerogramic (capital letter (majuscule)) usage for NA. An example usage for ''NA'' in the Epic is for the spelling of ''NA.GAD'', (also '' LÚ.NA.GAD'', and the plural '' LÚ.NA.GAD. MEŠ''), for Akkadian language "nāqidu", ''"herdsman"''. The usage for ''NA'' in herdsman is only for 3 spellings. The commonness of cuneiform ''na'', in the top 25 used signs by Buccellati (Buccellati 1979), (2nd highest usage, exceeded by a: ''a (cuneiform)'') is because of usage for the spelling of ''a-na'' (Akkadian language "ana") -, the common preposition spelling for English language: ''to, for, by, of, at, etc.''. It is also a component for the Akkadian language preposition: ''i-na'' (''ina''), meaning: ''in, into, by, etc.''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A (cuneiform)
The cuneiform sign 𒀀 ( DIŠ, DIŠ OVER DIŠ) for a, and in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' the sumerogram A, Akkadian for ''mû'', "water", which is used in the ''Gilgamesh flood myth'', Chapter XI of the Epic, or other passages. The sign is also used extensively in the Amarna letters. Cuneiform ''a'' is the most common of the four vowels in the Akkadian language, ''a'', ''e'', ''i'', and ''u''. All vowels can be interchangeable, depending on the scribe, though spellings of Akkadian words in dictionaries, will be formalized, and typically: unstressed, a 'long-vowel', or thirdly, a 'combined' vowel (often spelled with two signs (same vowel, ending the first sign, and starting the next sign), thus combined into the single vowel, ''â'', ''ê'', ''î'', or ''û''.). Cuneiform ''a'' is the most common of the four vowels, as can be shown by usage in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', the usage numbers being (ú (u, no. 2) is more common than u, (no. 1), which has additional usages, numera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labaya
Labaya (also transliterated as Labayu or Lib'ayu) was a 14th-century BCE ruler or warlord in the central hill country of southern Canaan. He lived contemporaneously with Pharaoh Akhenaten. Labaya is mentioned in several of the Amarna Letters (abbreviated "EA", for 'el Amarna'). He is the author of letters EA 252– 54. Labaya was active over the whole length of Samaria and slightly beyond, as he gave land to Habiru in the vicinity of Šakmu (Shechem) and he and his sons threatened such powerful towns as Jerusalem and Gazru (Gezer) to the south, and Megiddo to the north. Career The Amarna letters give an incomplete look at Labaya's career. In the first of Labaya's letters thus far discovered (EA 252), he defends himself to the Pharaoh against complaints of other city rulers about him, for example, the complaint that he has hired mercenaries from among the Habiru. Labaya further admitted to having invaded Gezer and insulting its king Milkilu. He denied any knowledge of his s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ú (cuneiform)
The cuneiform sign ú is a common-use sign of the Amarna letters, the ''Epic of Gilgamesh,'' and other cuneiform texts (for example Hittite texts). It has a secondary sub-use in the Epic of Gilgamesh for šam. Linguistically, it has the alphabetical usage in texts for ''u'', but can replace any of the four vowels, so also used for ''a'', or ''e'', or ''i''. ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' usage The ''ú'' sign usage in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' is as follows: (''šam'', 45 times, ''ú'', 493, ''KÚŠ'', 2, and ''Ú'', 4 times).Parpola, 1971. ''The Standard Babylonian Epic of Gilgamesh'', Sign List, pp. 155-165, sign no. 318, p. 160. ''Ú'' is logogram, for Akkadian "tullal", a ''soapwort''. šam syllabic use in the Epic of Gilgamesh The following words use the syllabic '' šam'' as the first syllable in the word entries under ''š'' in the glossary. #''šamhatu'', for English, ''"harlot"''. #''šamhiš'', ''"proudly, stoutly",''. #''šammmu'', ''"drug, plant, grass"''. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Un (cuneiform)
UN is an abbreviation for the United Nations, an intergovernmental organization with 193 member states. UN or Un may also refer to: Music * UN (band), a Korean musical group * U.N. (group), a hip hop group * ''UN'' (album), an album by Dan Black * ''Un'' (album), by the anarchist band Chumbawamba Places * Un, a village in Lum Choar, Cambodia * Un, Surat, a town in Gujarat, India * Un, Uttar Pradesh, a town in India Other uses * Lance Rivera, known as Lance "Un" Rivera, American film producer * Transaero (IATA code:UN) * National Exam (Indonesia) (''Ujian Nasional'') * Uranium mononitride, part of the uranium nitride family of compounds See also * UN number A UN number (United Nations number) is a four-digit number that identifies hazardous materials, and articles (such as explosives, flammable liquids, oxidizers, toxic, toxic liquids, etc.) in the framework of international trade and transport. Some ..., a four-digit number that identifies a hazardous substance * U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)