|
Amanitas
The genus ''Amanita'' contains about 600 species of agarics, including some of the most toxic known mushrooms found worldwide, as well as some well-regarded edible species. This genus is responsible for approximately 95% of the fatalities resulting from mushroom poisoning, with the death cap accounting for about 50% on its own. The most potent toxin present in these mushrooms is α-Amanitin. The genus also contains many edible mushrooms, but mycologists discourage mushroom hunters, other than experts, from selecting any of these for human consumption. Nonetheless, in some cultures, the larger local edible species of ''Amanita'' are mainstays of the markets in the local growing season. Samples of this are ''Amanita zambiana'' and other fleshy species in central Africa, ''Amanita basii, A. basii'' and similar species in Mexico, ''Amanita caesarea, A. caesarea'' and the "Blusher" ''Amanita rubescens'' in Europe, and ''Amanita chepangiana, A. chepangiana'' in South-East Asia. Other s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
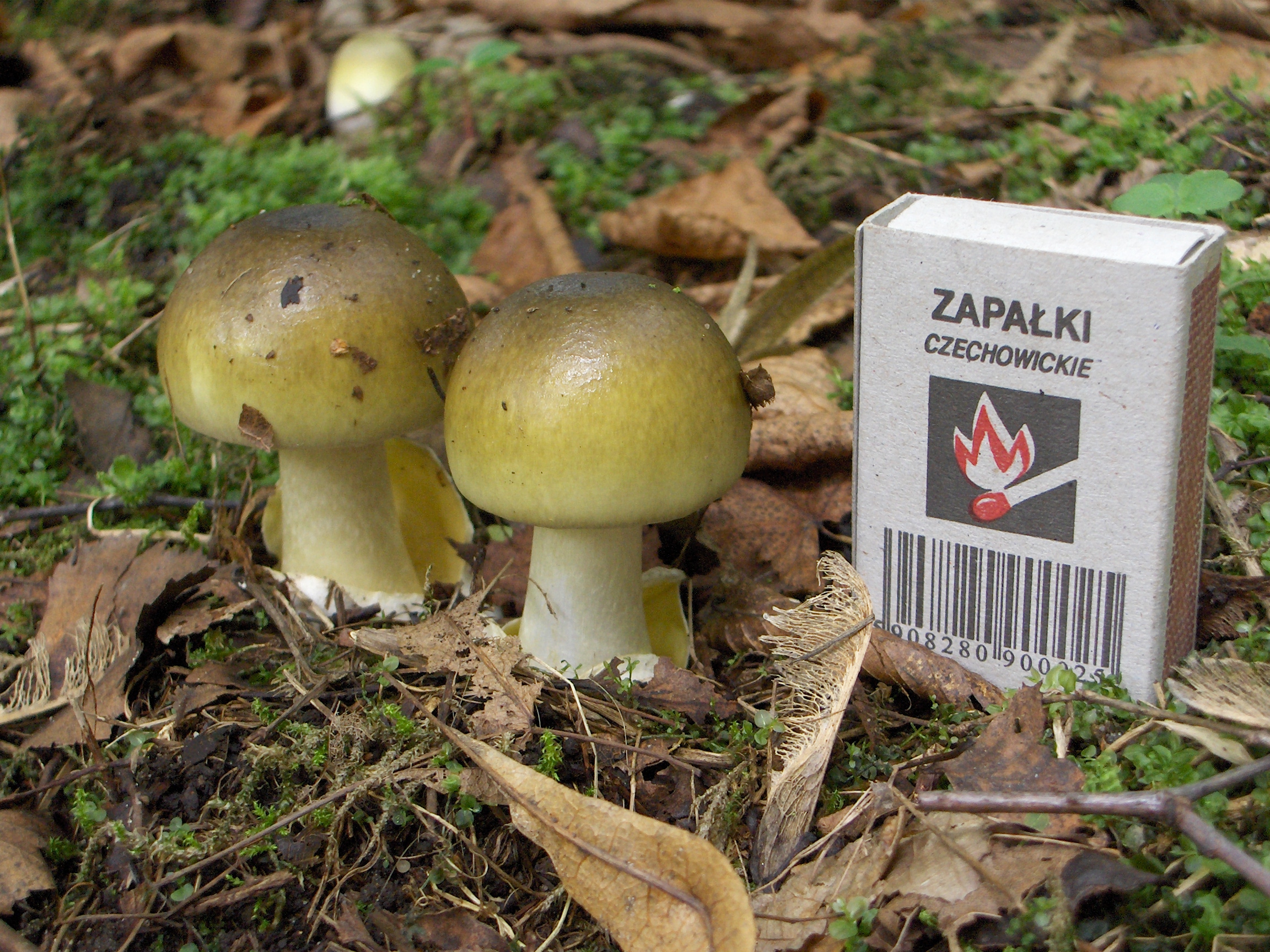
Amanita Phalloides Young
The genus ''Amanita'' contains about 600 species of agarics, including some of the most toxic known mushrooms found worldwide, as well as some well-regarded edible species. This genus is responsible for approximately 95% of the fatalities resulting from mushroom poisoning, with the death cap accounting for about 50% on its own. The most potent toxin present in these mushrooms is α-Amanitin. The genus also contains many edible mushrooms, but mycologists discourage mushroom hunters, other than experts, from selecting any of these for human consumption. Nonetheless, in some cultures, the larger local edible species of ''Amanita'' are mainstays of the markets in the local growing season. Samples of this are '' Amanita zambiana'' and other fleshy species in central Africa, '' A. basii'' and similar species in Mexico, '' A. caesarea'' and the "Blusher" ''Amanita rubescens'' in Europe, and '' A. chepangiana'' in South-East Asia. Other species are used for colouring sauces, such as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amanita Muscaria
''Amanita muscaria'', commonly known as the fly agaric or fly amanita, is a basidiomycete of the genus ''Amanita''. It is also a muscimol mushroom. Native throughout the temperate and boreal regions of the Northern Hemisphere, ''Amanita muscaria'' has been unintentionally introduced to many countries in the Southern Hemisphere, generally as a symbiont with pine and birch plantations, and is now a true cosmopolitan species. It associates with various deciduous and coniferous trees. Arguably the most iconic toadstool species, the fly agaric is a large white- gilled, white-spotted, usually red mushroom, and is one of the most recognizable and widely encountered in popular culture, including in video games—e.g., the extensive use of a recognizable ''Amanita muscaria'' in the Mario franchise and its Super Mushroom power-up—and television—e.g., the houses in The Smurfs franchise. Despite its easily distinguishable features, ''Amanita muscaria'' is a fungus with several know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Cap
''Amanita phalloides'' (), commonly known as the death cap, is a deadly poisonous basidiomycete fungus, one of many in the genus ''Amanita''. Widely distributed across Europe, but now sprouting in other parts of the world, ''A. phalloides'' forms ectomycorrhizas with various broadleaved trees. In some cases, the death cap has been introduced to new regions with the cultivation of non-native species of oak, chestnut, and pine. The large fruiting bodies (mushrooms) appear in summer and autumn; the caps are generally greenish in colour with a white stipe and gills. The cap colour is variable, including white forms, and is thus not a reliable identifier. These toxic mushrooms resemble several edible species (most notably Caesar's mushroom and the straw mushroom) commonly consumed by humans, increasing the risk of accidental poisoning. Amatoxins, the class of toxins found in these mushrooms, are thermostable: they resist changes due to heat, so their toxic effects are not r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amanita Phalloides
''Amanita phalloides'' (), commonly known as the death cap, is a deadly poisonous basidiomycete fungus, one of many in the genus ''Amanita''. Widely distributed across Europe, but now sprouting in other parts of the world, ''A. phalloides'' forms ectomycorrhizas with various broadleaved trees. In some cases, the death cap has been introduced to new regions with the cultivation of non-native species of oak, chestnut, and pine. The large fruiting bodies (mushrooms) appear in summer and autumn; the caps are generally greenish in colour with a white stipe and gills. The cap colour is variable, including white forms, and is thus not a reliable identifier. These toxic mushrooms resemble several edible species (most notably Caesar's mushroom and the straw mushroom) commonly consumed by humans, increasing the risk of accidental poisoning. Amatoxins, the class of toxins found in these mushrooms, are thermostable: they resist changes due to heat, so their toxic effects are not red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
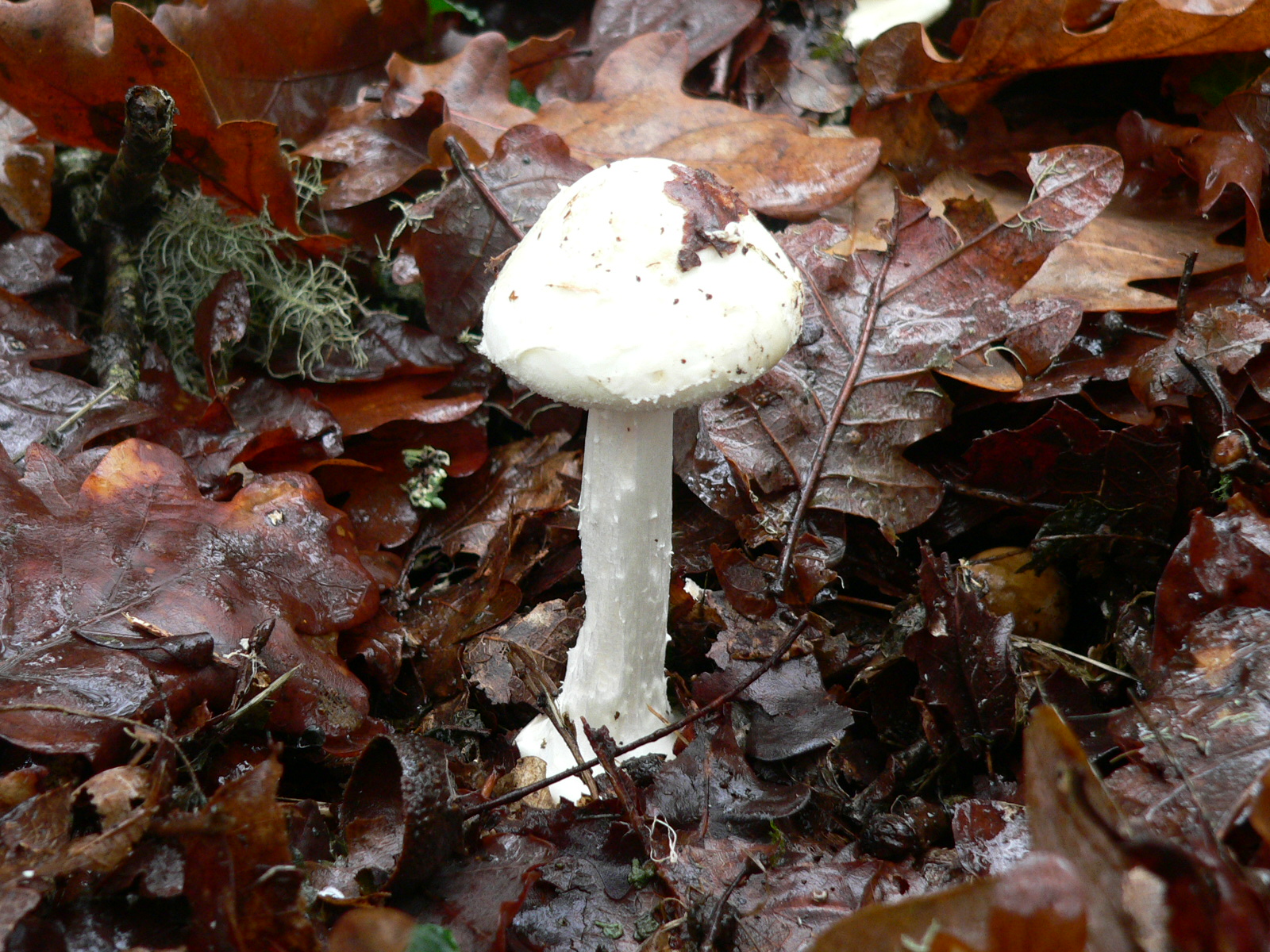
Amanita Virosa
''Amanita virosa'', commonly known in Europe as the destroying angel or the European destroying angel amanita, is a deadly poisonous basidiomycete fungus, one of many in the genus ''Amanita''. Occurring in Europe, ''A. virosa'' mycorrhiza, associates with various deciduous and coniferous trees. The large fruiting bodies (''i.e.'', the mushrooms) appear in summer and autumn; the Pileus (mycology), caps, stipe (mycology), stipes and Lamella (mycology), gills are all white in colour. Immature specimens of ''A. virosa'' resemble several edible species commonly consumed by humans, increasing the risk of accidental poisoning. Small specimens may resemble the common Portobello mushroom to non-experts, but just one cap of ''A. virosa'' is enough to kill an adult human. The symptoms of poisoning generally come several hours afterwards, a fact which makes this fungus even more problematic. Along with its geographical namesakes, ''A. virosa'' is one of the most poisonous of all known mush ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amanita Chepangiana
''Amanita chepangiana'', commonly known as the Chepang slender Caesar, is a species of agaric fungus in the family Amanitaceae native to China and southern Asia. In parts of Yunnan, China, the species is traditionally consumed. However, toxicity analysis found out at least one type of amatoxin and phallotoxin The phallotoxins consist of at least seven compounds, all of which are bicyclic heptapeptides (seven amino acids), isolated from the death cap mushroom ''(Amanita phalloides)''. They differ from the closely related amatoxins by being one residue sma ... each within the species. Since it is difficult to distinguish from other lethal species, human consumption is generally not recommended. References External links * {{Taxonbar, from=Q2841081 chepangiana Fungi of China Fungi described in 1992 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destroying Angel
The name destroying angel applies to several similar, closely related species of deadly all-white mushrooms in the genus ''Amanita''. They are ''Amanita bisporigera'' and '' A. ocreata'' in eastern and western North America, respectively, and '' A. virosa'' in Europe. Another European species of ''Amanita'' referred to as the destroying angel, ''Amanita verna'' - also referred to as the 'Fool's mushroom' - was first described in France in 1780. Destroying angels are among the most toxic known mushrooms; both they and the closely related death caps (''A. phalloides'') contain amatoxins. Description Destroying angels are characterized by having a white stalk and gills. The cap can be pure white, or white at the edge and yellowish, pinkish, or tan at the center. It has a partial veil, or ring (annulus) circling the upper stalk, and the gills are "free", not attached to the stalk. Perhaps the most telltale of the features is the presence of a volva, or universal veil, so calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
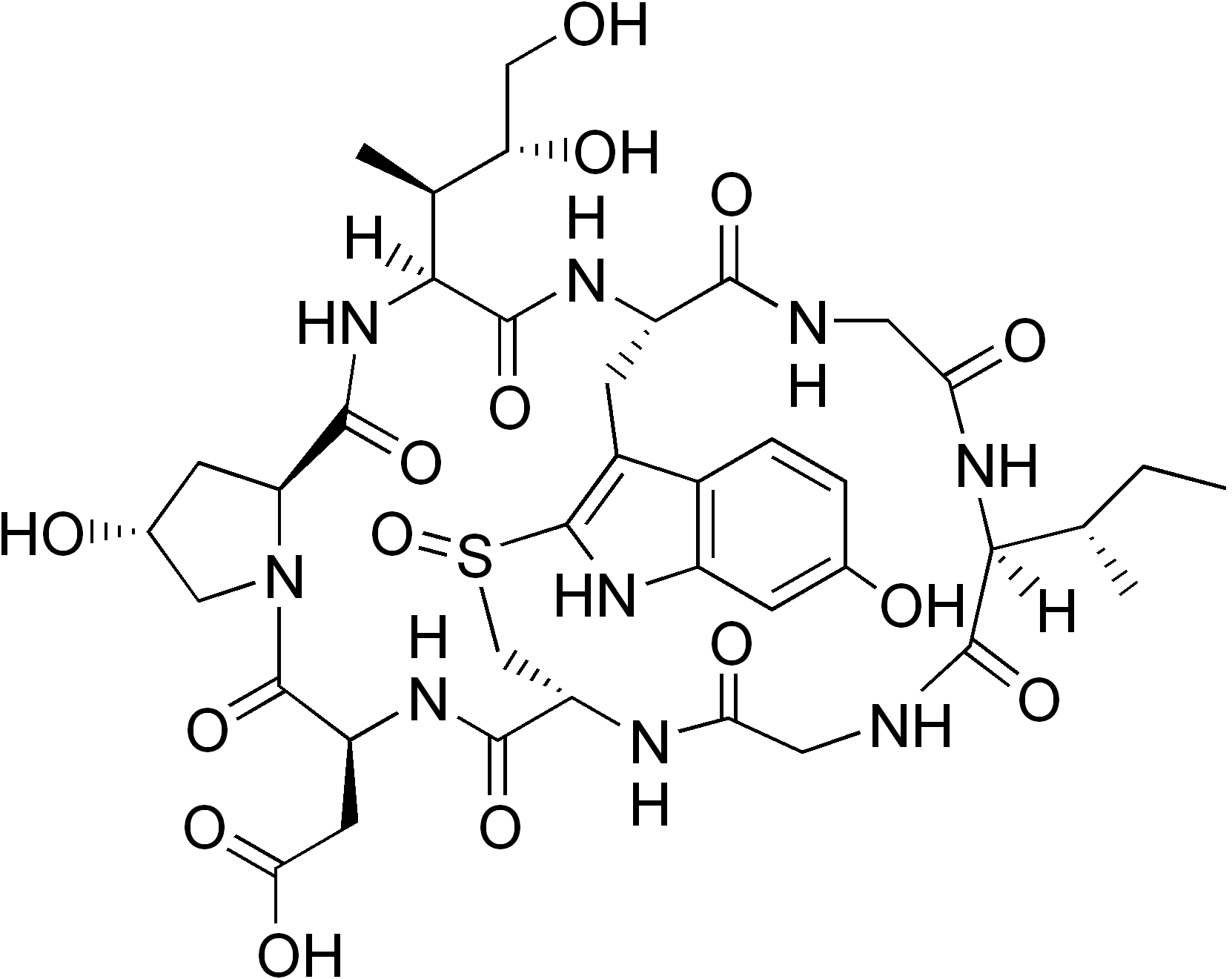
Amatoxin
Amatoxin is the collective name of a subgroup of at least nine related toxic compounds found in three genera of poisonous mushrooms (''Amanita'', ''Galerina'' and ''Lepiota'') and one species (Conocybe filaris) of the genus ''Conocybe''. Amatoxins are lethal in even small doses, as little as half a mushroom, including the immature 'egg' form which appears quite different from the fully-grown mushroom. Although laboratory analysis has found that the spores contain as little as 3% the toxin concentration of the main mushroom body, anecdotes have been repeated in field guides that claim foragers have fallen ill from spores alone after collecting but then discarding toxic Amanitas, unknowingly leaving their spore dust on the remaining harvest. Unlike many ingested poisons, they cannot be destroyed by heat without destroying the mushrooms beyond edibility first, so cooking the poisonous mushrooms does not diminish their lethality. Structure The compounds have a similar structure, tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, chevalier de Lamarck (1 August 1744 – 18 December 1829), often known simply as Lamarck (; ), was a French naturalist, biologist, academic, and soldier. He was an early proponent of the idea that biological evolution occurred and proceeded in accordance with Naturalism (philosophy), natural laws. Lamarck fought in the Seven Years' War against Prussia, and was awarded a commission for bravery on the battlefield. Posted to Monaco, Lamarck became interested in natural history and resolved to study medicine.#Packard, Packard (1901), p. 15. He retired from the army after being injured in 1766, and returned to his medical studies. Lamarck developed a particular interest in botany, and later, after he published the three-volume work ''Flore françoise'' (1778), he gained membership of the French Academy of Sciences in 1779. Lamarck became involved in the Jardin des Plantes and was appointed to the Chair of Botany in 1788. When the French Nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricus
''Agaricus'' is a genus of mushrooms containing both edible and poisonous species, with over 400 members worldwide and possibly again as many disputed or newly-discovered species. The genus includes the common ("button") mushroom (''Agaricus bisporus'') and the field mushroom ('' A. campestris''), the dominant cultivated mushrooms of the West. Members of ''Agaricus'' are characterized by having a fleshy cap or pileus, from the underside of which grow a number of radiating plates or gills, on which are produced the naked spores. They are distinguished from other members of their family, Agaricaceae, by their chocolate-brown spores. Members of ''Agaricus'' also have a stem or stipe, which elevates it above the object on which the mushroom grows, or substrate, and a partial veil, which protects the developing gills and later forms a ring or annulus on the stalk. The genus contains the most widely consumed and best-known mushroom today, '' A. bisporus'', with '' A. arvensis'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |