|
Alternaria Leaf Spot
Alternaria leaf spot or Alternaria leaf blight are a group of fungal diseases in plants, that have a variety of hosts. The diseases infects common garden plants, such as cabbage, and are caused by several closely related species of fungi. Some of these fungal species target specific plants, while others have been known to target plant families. One commercially relevant plant genus that can be affected by Alternaria Leaf Spot is ''Brassica'', as the cosmetic issues caused by symptomatic lesions can lead to rejection of crops by distributors and buyers. When certain crops such as cauliflower and broccoli are infected, the heads deteriorate and there is a complete loss of marketability. Secondary soft-rotting organisms can infect stored cabbage that has been affected by Alternaria Leaf Spot by entering through symptomatic lesions. Alternaria Leaf Spot diseases that affect ''Brassica'' species are caused by the pathogens ''Alternaria brassicae'' and ''Alternaria brassicicola ''Altern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungal Disease
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fungi' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Host (biology)
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasite, parasitic, a mutualism (biology), mutualistic, or a commensalism, commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms (e.g. nematodes), cell (biology), cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, a Fabaceae, bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) Rhizobia, nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies nutrient, food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable strategy, evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner. Symbiosis Symbiosis spans a wide variety of possible relationships between organisms, differing in their permanence and their effects on the two parties. If one of the partners in an ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brassica
''Brassica'' () is a genus of plants in the cabbage and mustard family (Brassicaceae). The members of the genus are informally known as cruciferous vegetables, cabbages, or mustard plants. Crops from this genus are sometimes called ''cole crops''derived from the Latin ''caulis'', denoting the stem or stalk of a plant. The genus ''Brassica'' is known for its important agricultural and horticultural crops and also includes a number of weeds, both of wild taxa and escapees from cultivation. ''Brassica'' species and varieties commonly used for food include bok choy, broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, choy sum, kohlrabi, napa cabbage, rutabaga, turnip and some seeds used in the production of canola oil and the condiment mustard. Over 30 wild species and hybrids are in cultivation, plus numerous cultivars and hybrids of cultivated origin. Most are seasonal plants ( annuals or biennials), but some are small shrubs. ''Brassica'' plants have been the subject of much scientific intere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
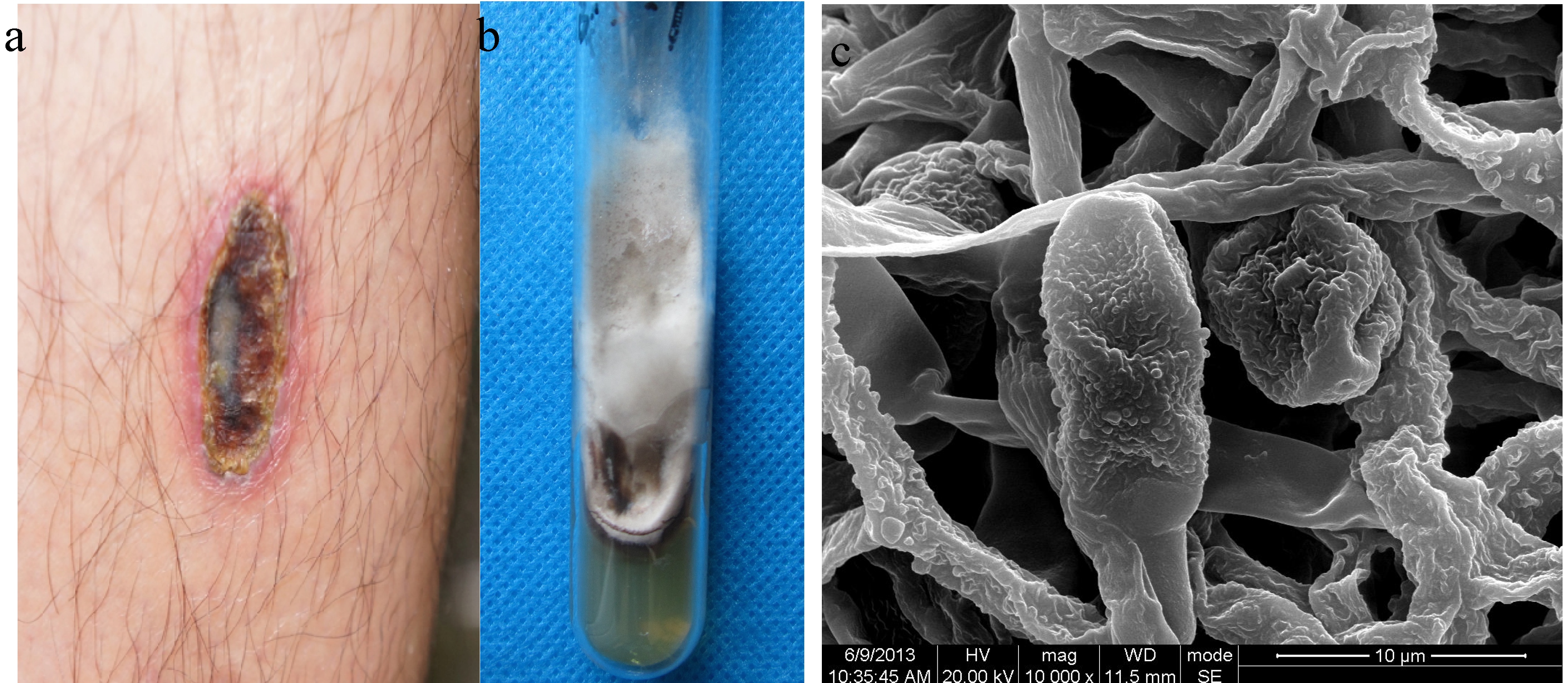
Alternaria Brassicae
''Alternaria brassicae'' is a plant pathogen able to infect most ''Brassica'' species including important crops such as broccoli, cabbage and oil seed rape. It causes damping off if infection occurs in younger plants and less severe leaf spot A leaf spot is a limited, discoloured, diseased area of a leaf that is caused by fungal, bacterial or viral plant diseases, or by injuries from nematodes, insects, environmental factors, toxicity or herbicides. These discoloured spots or lesions ... symptoms on infections of older plants. References External links Index FungorumUSDA ARS Fungal Database brassicae Fungal plant pathogens and diseases Eudicot diseases Fungi described in 1880 {{plant-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternaria Brassicicola
''Alternaria brassicicola'' is a fungal necrotrophic plant pathogen that causes black spot disease on a wide range of hosts, particularly in the genus of ''Brassica'', including a number of economically important crops such as cabbage, Chinese cabbage, cauliflower, oilseeds, broccoli and canola. Although mainly known as a significant plant pathogen, it also contributes to various respiratory allergic conditions such as asthma and rhinoconjunctivitis. Despite the presence of mating genes, no sexual reproductive stage has been reported for this fungus. In terms of geography, it is most likely to be found in tropical and sub-tropical regions, but also in places with high rain and humidity such as Poland. It has also been found in Taiwan and Israel. Its main mode of propagation is vegetative. The resulting conidia reside in the soil, air and water. These spores are extremely resilient and can overwinter on crop debris and overwintering herbaceous plants. Growth and morphology The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternaria Leaf Spot Of Aspen
''Alternaria'' is a genus of Deuteromycetes fungi. All species are known as major plant pathogens. They are also common allergens in humans, growing indoors and causing hay fever or hypersensitivity reactions that sometimes lead to asthma. They are present in the human mycobiome and readily cause opportunistic infections in immunocompromised people such as AIDS patients. There are 299 species in the genus; they are ubiquitous in the environment and are a natural part of fungal flora almost everywhere. They are normal agents of decay and decomposition. The spores are airborne and found in the soil and water, as well as indoors and on objects. The club-shaped spores are single or form long chains. They can grow thick colonies which are usually green, black, or gray. At least 20% of agricultural spoilage is caused by ''Alternaria'' species, with the most severe losses reaching 80% of yield. Many human health disorders can be caused by these fungi, which grow on skin and mucous membr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungal Plant Pathogens And Diseases
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)