|
Alpha Cygni Variables
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter ''aleph'' , whose name comes from the West Semitic word for ' ox'. Letters that arose from alpha include the Latin letter and the Cyrillic letter . Uses Greek In Ancient Greek, alpha was pronounced and could be either phonemically long ( ː or short ( . Where there is ambiguity, long and short alpha are sometimes written with a macron and breve today: . * = ' "a time" * = ' "tongue" In Modern Greek, vowel length has been lost, and all instances of alpha simply represent the open front unrounded vowel . In the polytonic orthography of Greek, alpha, like other vowel letters, can occur with several diacritic marks: any of three accent symbols (), and either of two breathing marks (), as well as combinations of these. It can also combine with the iota subscript (). Greek grammar In the Attic� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letter (alphabet)
In a writing system, a letter is a grapheme that generally corresponds to a phoneme—the smallest functional unit of speech—though there is rarely total one-to-one correspondence between the two. An alphabet is a writing system that uses letters. Definition and usage A letter is a type of grapheme, the smallest functional unit within a writing system. Letters are graphemes that broadly correspond to phonemes, the smallest functional units of sound in speech. Similarly to how phonemes are combined to form spoken words, letters may be combined to form written words. A single phoneme may also be represented by multiple letters in sequence, collectively called a ''multigraph (orthography), multigraph''. Multigraphs include ''digraphs'' of two letters (e.g. English ''ch'', ''sh'', ''th''), and ''trigraphs'' of three letters (e.g. English ''tch''). The same letterform may be used in different alphabets while representing different phonemic categories. The Latin H, Greek eta , an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diacritic
A diacritic (also diacritical mark, diacritical point, diacritical sign, or accent) is a glyph added to a letter or to a basic glyph. The term derives from the Ancient Greek (, "distinguishing"), from (, "to distinguish"). The word ''diacritic'' is a noun, though it is sometimes used in an attributive sense, whereas ''diacritical'' is only an adjective. Some diacritics, such as the acute , grave , and circumflex (all shown above an 'o'), are often called ''accents''. Diacritics may appear above or below a letter or in some other position such as within the letter or between two letters. The main use of diacritics in Latin script is to change the sound-values of the letters to which they are added. Historically, English has used the diaeresis diacritic to indicate the correct pronunciation of ambiguous words, such as "coöperate", without which the letter sequence could be misinterpreted to be pronounced . Other examples are the acute and grave accents, which can indica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copulative A , the union of the sex organs of two sexually reproducing animals for insemination and subsequent internal fertilization
{{disambig ...
Copulative may refer to: * Copula (linguistics), a part of speech * Copulation (zoology) In zoology, copulation is animal sexual behavior in which a male introduces sperm into the female's body, especially directly into her reproductive tract. This is an aspect of mating. Many aquatic animals use external fertilization, whereas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymological ancestor in a common parent language. Because language change can have radical effects on both the sound and the meaning of a word, cognates may not be obvious, and it often takes rigorous study of historical sources and the application of the comparative method to establish whether lexemes are cognate. Cognates are distinguished from loanwords, where a word has been borrowed from another language. Name The English term ''cognate'' derives from Latin , meaning "blood relative". Examples An example of cognates from the same Indo-European root are: ''night'' ( English), ''Nacht'' ( German), ''nacht'' ( Dutch, Frisian), ''nag'' (Afrikaans), ''Naach'' ( Colognian), ''natt'' ( Swedish, Norwegian), ''nat'' ( Danish), ''nátt'' ( Faroese), ''nótt'' ( Icelandic), ''noc'' ( Czech, Slovak, Polish), ночь, ''noch'' ( Russian), но� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syllabic Consonant
A syllabic consonant or vocalic consonant is a consonant that forms the nucleus of a syllable on its own, like the ''m'', ''n'' and ''l'' in some pronunciations of the English words ''rhythm'', ''button'' and ''awful'', respectively. To represent it, the understroke diacritic in the International Phonetic Alphabet is used, . It may be instead represented by an overstroke, if the symbol that it modifies has a descender, such as in . Syllabic consonants in most languages are sonorants, such as nasals and liquids. Very few have syllabic obstruents (i.e., stops, fricatives, and affricates) in normal words, but English has syllabic fricatives in paralinguistic words like ''shh!'' and ''zzz''. Examples Germanic languages In many varieties of High and Low German, pronouncing syllabic consonants may be considered a shibboleth. In High German and Tweants (a Low Saxon dialect spoken in the Netherlands; more Low Saxon dialects have the syllabic consonant), all word-final syllab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Indo-European Language
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists; its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. Far more work has gone into reconstructing PIE than any other proto-language, and it is the best understood of all proto-languages of its age. The majority of linguistic work during the 19th century was devoted to the reconstruction of PIE and its daughter languages, and many of the modern techniques of linguistic reconstruction (such as the comparative method) were developed as a result. PIE is hypothesized to have been spoken as a single language from approximately 4500 BCE to 2500 BCE during the Late Neolithic to Early Bronze Age, though estimates vary by more than a thousand years. According to the prevailing Kurgan hypothesis, the original homeland of the Proto-Indo-Europeans may have been in the Pon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privative A
An alpha privative or, rarely, privative a (from Latin ', from Ancient Greek ) is the prefix ''a-'' or ''an-'' (before vowels) that is used in Indo-European languages such as Sanskrit and Greek and in words borrowed therefrom to express negation or absence, for example the English words of Greek origin '' atypical'', '' anesthetic'', and '' analgesic'', as well as the English word of Sanskrit origin ''ahimsa'' (''ahinsa''). It is derived from a Proto-Indo-European syllabic nasal *', the zero ablaut grade of the negation *', i.e. /n/ used as a vowel. For this reason, it usually appears as ' before vowels (e.g. '' an-alphabetism'', '' an-esthesia'', '' an-archy''). It shares the same root with the Greek prefix ' or ', in Greek or , that is also privative (e.g. '). It is not to be confused with, among other things, an alpha copulative (e.g. '' a-delphós'') or the prefix ' (i.e. the preposition ' with ecthlipsis or elision of its final vowel before a following vowel; e.g. '). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Weir Smyth
Herbert Weir Smyth (August 8, 1857 – July 16, 1937) was an American classical scholar. His comprehensive grammar of Ancient Greek has become a standard reference on the subject in English, comparable to that of William Watson Goodwin, whom he succeeded as Eliott Professor of Greek Literature at Harvard University. Life Herbert Weir Smyth was born in Wilmington, Delaware on August 8, 1857. He was educated at Swarthmore ( A.B. 1876), Harvard (A.B. 1878), Leipzig, and Göttingen ( Ph.D. 1884). From 1883 to 1885, he was instructor in Greek and Sanskrit at Williams College, and then for two years, he was reader in Greek at Johns Hopkins. From 1887 to 1901, he was professor of Greek at Bryn Mawr. In the latter year, he was called to Harvard as professor of Greek and in 1902, and he was appointed Eliott professor of Greek literature, succeeding Goodwin. From 1899 to 1900, he was professor of the Greek language and literature at the American Classical School at Athens. From 1889 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeolic Greek
In linguistics, Aeolic Greek (), also known as Aeolian (), Lesbian or Lesbic dialect, is the set of dialects of Ancient Greek spoken mainly in Boeotia; in Thessaly; in the Aegean island of Lesbos; and in the Greek colonies of Aeolis in Anatolia and adjoining islands. The Aeolic dialect shows many archaisms in comparison to the other Ancient Greek dialects ( Arcadocypriot, Attic, Ionic, and Doric varieties), as well as many innovations. Aeolic Greek is widely known as the language of Sappho and of Alcaeus of Mytilene. Aeolic poetry, which is exemplified in the works of Sappho, mostly uses four classical meters known as the Aeolics: Glyconic (the most basic form of Aeolic line), hendecasyllabic verse, Sapphic stanza, and Alcaic stanza (the latter two are respectively named for Sappho and Alcaeus). Phonology Consonants Labiovelars Proto-Indo-European and Proto-Greek ''*'' changed to Aeolic ''p'' everywhere. By contrast, PIE ''*'' changed to Attic/ Ionic, Arcadoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
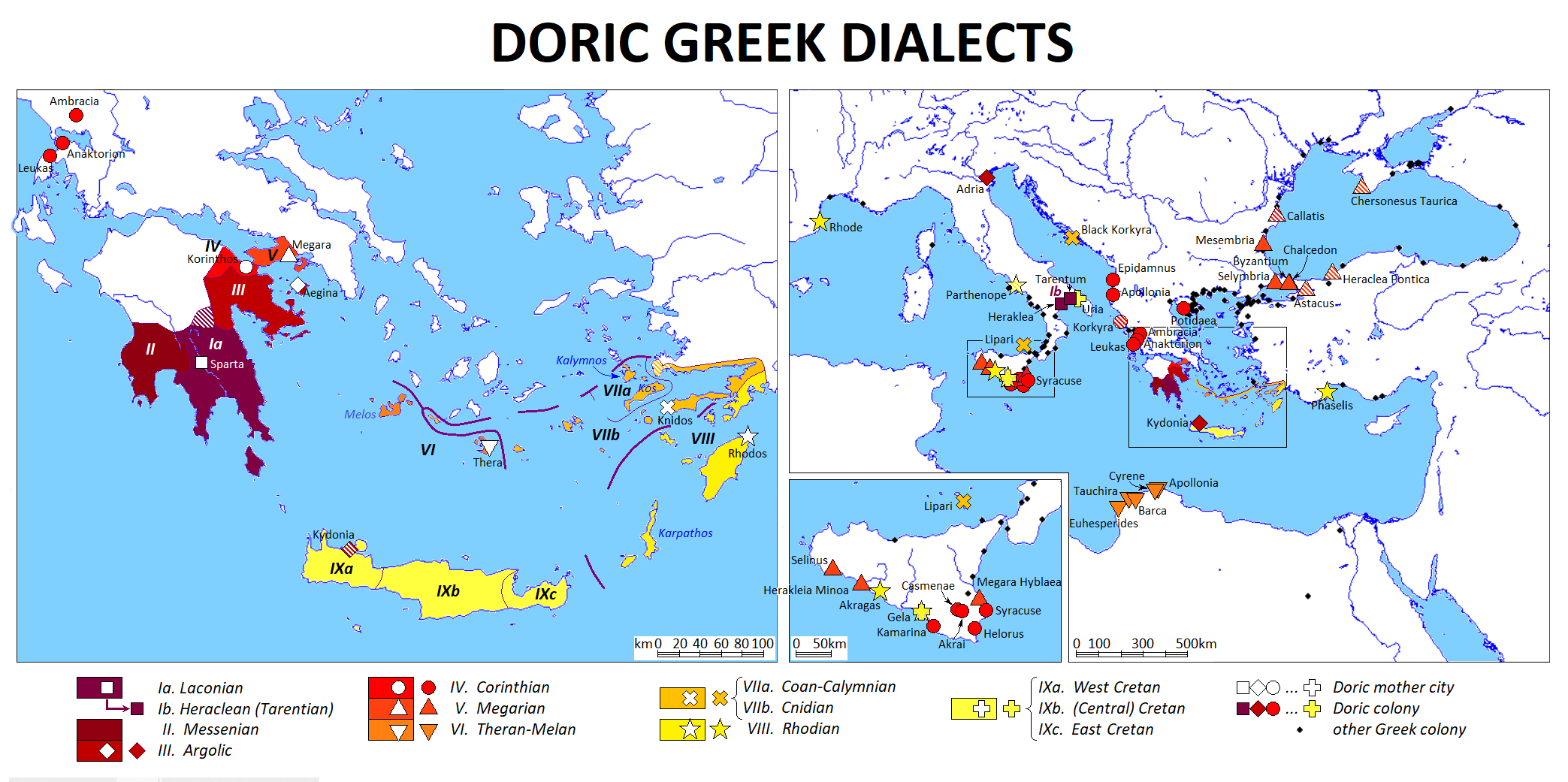
Doric Greek
Doric or Dorian (), also known as West Greek, was a group of Ancient Greek dialects; its Variety (linguistics), varieties are divided into the Doric proper and Northwest Doric subgroups. Doric was spoken in a vast area, including northern Greece (Acarnania, Aetolia, Epirus, Ozolian Locris, western and Opuntian Locris, eastern Locris, Phocis (ancient region), Phocis, Doris (Greece), Doris, and possibly Macedonia (ancient kingdom), ancient Macedonia), most of the Regions of ancient Greece#Peloponnese, Peloponnese (Achaea (ancient region), Achaea, Ancient Elis, Elis, Messenia (ancient region), Messenia, Laconia, Argolid, Aegina, Corinthia (ancient region), Corinthia, and Megara), the Southern Aegean (Kythira, Milos, Santorini, Thera, Crete, Karpathos, and Rhodes), as well as the colonies of some of those regions in Cyrene, Libya, Cyrene, Magna Graecia, the Greek colonisation#Black Sea and Propontis, Black Sea, Greek colonisation#Ionian Sea, Adriatic Sea, and Illyria, the Ionian Sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iota
Iota (; uppercase Ι, lowercase ι; ) is the ninth letter of the Greek alphabet. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Yodh. Letters that arose from this letter include the Latin I and J, the Cyrillic І (І, і), Yi (Ї, ї), and Je (Ј, ј), and iotated letters (e.g. Yu (Ю, ю)). In the system of Greek numerals, iota has a value of 10. Iota represents the close front unrounded vowel . In early forms of ancient Greek, it occurred in both long and short versions, but this distinction was lost in Koine Greek. Iota participated as the second element in falling diphthongs, with both long and short vowels as the first element. Where the first element was long, the iota was lost in pronunciation at an early date, and was written in polytonic orthography as iota subscript, in other words as a very small ι under the main vowel. Examples include ᾼ ᾳ ῌ ῃ ῼ ῳ. The former diphthongs became digraphs for simple vowels in Koine Greek.see Koine Greek phonolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon
Epsilon (, ; uppercase , lowercase or ; ) is the fifth letter of the Greek alphabet, corresponding phonetically to a mid front unrounded vowel or . In the system of Greek numerals it also has the value five. It was derived from the Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician letter He (letter), He . Letters that arose from epsilon include the Roman E, Ë and Latin epsilon, Ɛ, and Cyrillic Ye (Cyrillic), Е, Ye with grave, È, Yo (Cyrillic), Ё, Ukrainian Ye, Є and E (Cyrillic), Э. The name of the letter was originally (), but it was later changed to ( 'simple e') in the Middle Ages to distinguish the letter from the digraph (orthography), digraph , a former diphthong that had come to be pronounced the same as epsilon. The uppercase form of epsilon is identical to Latin but has its own code point in Unicode: . The lowercase version has two typographical variants, both inherited from history of the Greek alphabet, medieval Greek handwriting. One, the most common in modern typograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |