|
Alpacas
The alpaca (''Lama pacos'') is a species of South American camelid mammal. Traditionally, alpacas were kept in herds that grazed on the level heights of the Andes of Southern Peru, Western Bolivia, Ecuador, and Northern Chile. More recently, alpacas may be found on farms and ranches worldwide, with thousands of animals born and raised annually. Alpacas are especially popular in North America, Europe, and Australia. There are two modern breeds of alpaca, separated based on their respective region of endemism and fiber (wool) type: the Suri alpaca and the Huacaya alpaca. Both breeds produce a highly valued fiber, with Suri alpaca's fiber growing in straight "locks," while Huacaya fiber has a "crimped," wavy texture and grows in bundles. These breeds' fibers are used for making knitted and woven items, similar to sheep's wool. Alpacas are visually and genetically similar to, and often confused with a relative species, the llamas; however, alpacas are visibly shorter and pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
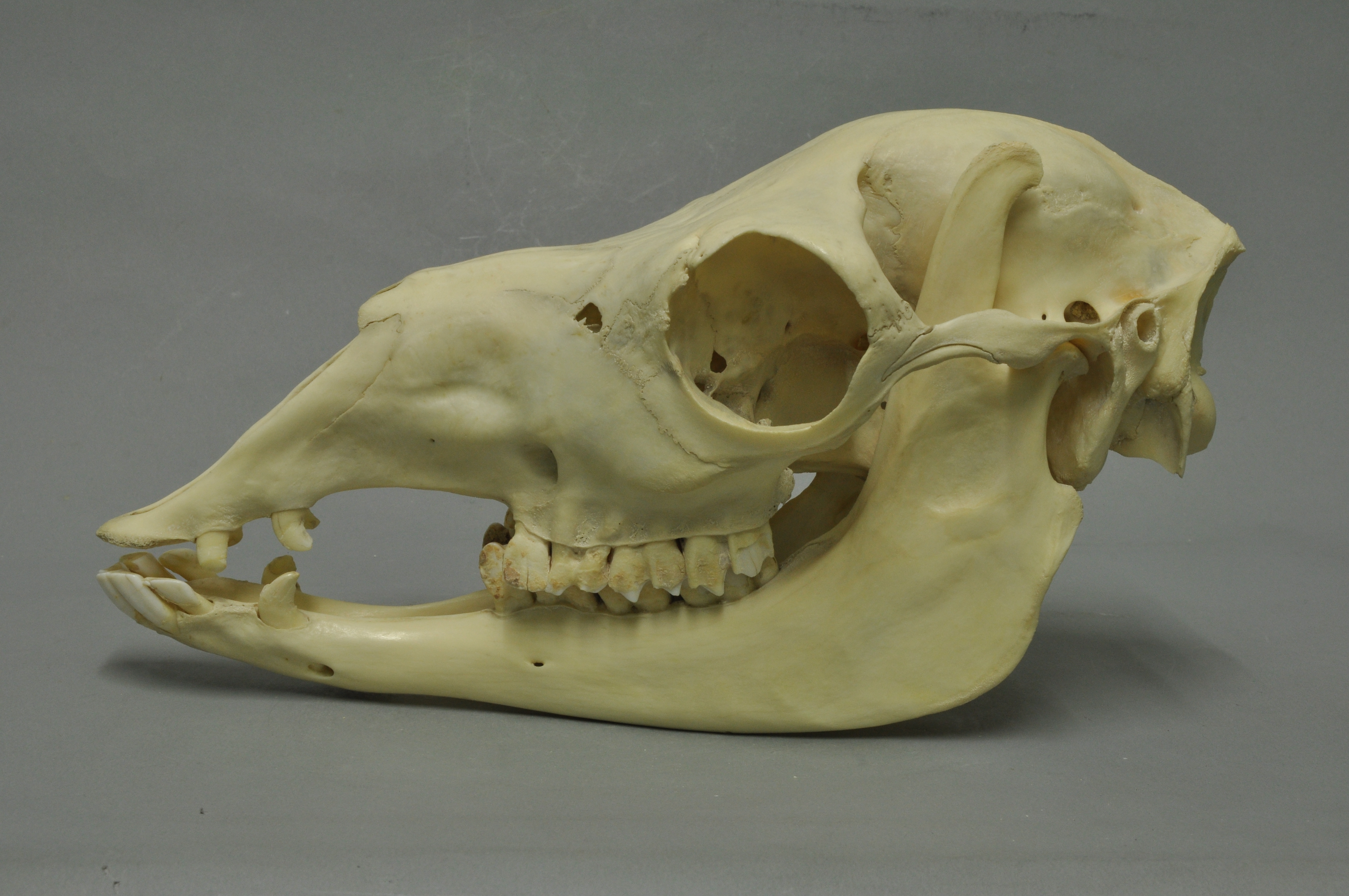
Huacaya Alpaca
The Huacaya alpaca is a breed of alpaca (''Lama pacos'') that has a unique appearance and fiber quality. This breed is the most popular alpaca breed with population numbers reaching 2.8 million in Peru alone. They share biological components with other species in the Camelidae family. Their digestive tract, nutrition requirements, and herd behavior mirror that of all camelids. They also survive amidst similar predation, poison, and disease threats that endanger all camelids alike. Breed The Huacaya alpaca is one of two breeds of alpaca, the other breed being the Suri alpaca. Both breeds were first domesticated by the Incas thousands of years ago from a wild species of camelid, the vicuña. The native homeland of the Huacaya is the Andean highlands of South America, called the Altiplano. It is above sea level and reaches into Peru, Chile, and Bolivia. * An edited version also published as: In the 1980s, these Huacaya were imported to other countries including Australia, Canad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
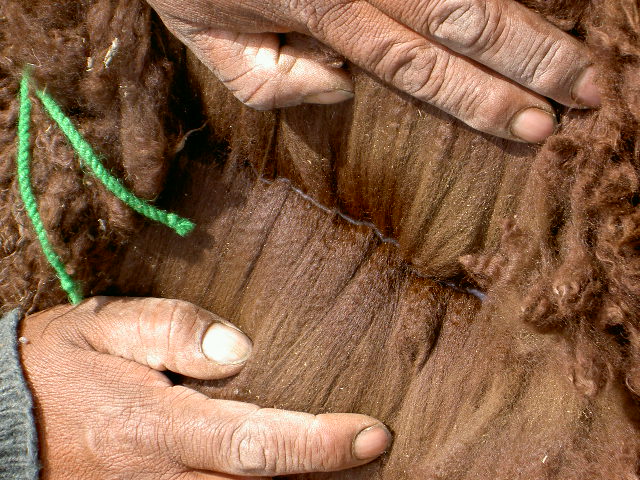
Alpaca Fiber
Alpaca fleece is the natural fiber harvested from an alpaca. There are two different types of alpaca fleece. The most common fleece type comes from a Huacaya. Huacaya fiber grows and looks similar to sheep wool in that the animal looks "fluffy". The second type of alpaca is Suri and makes up less than 10% of the South American alpaca population. Suri fiber is more similar to natural silk and hangs off the body in locks that have a dreadlock appearance. While both fibers can be used in the worsted milling process using light weight yarn or thread, Huacaya fiber can also be used in a woolen process and spun into various weight yarns. It is a soft, durable, luxuriousQuiggle, Charlotte. "Alpaca: An Ancient Luxury." ''Interweave Knits'' Fall 2000: 74-76. and silky natural fiber. While huacaya fiber is similar to sheep's wool, it is warmer, not prickly, and has no lanolin, which makes it hypoallergenic.Stoller, Debbie, ''Stitch 'N Bitch Crochet'', New York: Workman, 2006, p. 18. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llama
The llama (; or ) (''Lama glama'') is a domesticated South American camelid, widely used as a List of meat animals, meat and pack animal by Inca empire, Andean cultures since the pre-Columbian era. Llamas are social animals and live with others as a herd. Their wool is soft and contains only a small amount of lanolin. Llamas can learn simple tasks after a few repetitions. When using a pack, they can carry about 25 to 30% of their body weight for 8 to 13 kilometre, km (5–8 miles). The name ''llama'' (also historically spelled "lama" or "glama") was adopted by European colonization of the Americas, European settlers from Indigenous people in Peru, native Peruvians. The ancestors of llamas are thought to have originated on the Great Plains of North America about 40 million years ago and subsequently migrated to South America about three million years ago during the Great American Interchange. By the end of the last Quaternary glaciation, ice age (10,000–12,000 years ago) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icelandic Sheep
The Icelandic is the Icelandic breed of domestic sheep. It belongs to the Northern European Short-tailed group of sheep, and is larger than most breeds in that group. It is thought to have been introduced to Iceland by Vikings in the late ninth or early tenth century. It is generally short-legged and stocky, slender and light-boned, and usually horned, although polled and polycerate animals can occur; there is a polled strain, the . The fleece is double-coated and may be white or a variety of other colors; the face and legs are without wool. The sheep are highly resistant to cold, and are generally left unshorn for the winter. Icelandic ewes are highly prolific, with a lambing percentage of 175–220%. The (Thoka) gene is carried by some ewes, which may give birth to large litters of lambs. A unique strain within the population is the Leadersheep, which carries a hereditary ability or predisposition to lead other sheep safely over dangerous ground. History It is thoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lama Guanicoe In Parque Nacional Torres Del Paine In Patagonia, Chile
Lama () is a title bestowed to a realized practitioner of the Dharma in Tibetan Buddhism. Not all monks are lamas, while nuns and female practitioners can be recognized and entitled as lamas. The Tibetan word ''la-ma'' means "high mother", and reflects the qualities of the person entitled as a lama."lama" from Historically and currently, the term is bestowed on venerated spiritual masters and may be part of a specific lineage title such as the |
Lamoid
Lamini (members are called ''lamines'') is a tribe of the subfamily Camelinae. It contains one extant genus with four species, all exclusively from South America: llamas, alpacas, vicuñas, and guanacos. The former two are domesticated species, while the latter two are only found in the wild. None display sexual dimorphism. The four species can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Additionally, there are several extinct genera. The digestive system of lamoids allows them to digest certain toxins. Laminoids also lack a gallbladder. Evolutionary history Lamines originated during the Miocene in North America, and migrated into South America during the Pliocene and Pleistocene as part of the Great American Interchange. Most species of lamines, including the genera '' Hemiauchenia'' and '' Palaeolama'' and all North American species, became extinct at the end of the Pleistocene around 12,000 years ago as part of the Quaternary extinction event along with most other large mam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicugna Vicugna
''Lama'' is a genus containing the South American camelids: the wild guanaco and vicuña and the domesticated llama, alpaca, and the extinct chilihueque. Before the Spanish conquest of the Americas, llamas, alpacas, and chilihueques were the only domesticated ungulates of the continent. They were kept not only for their value as beasts of burden, but also for their flesh, hides, and wool. Classification Although they were often compared to sheep by early writers, their affinity to the camel was soon perceived. They were included in the genus ''Camelus'' in the ''Systema Naturae'' of Linnaeus. In 1800, Cuvier moved the llama, alpaca, and guanaco to the genus ''Lama'', and the vicuña to the genus ''Vicugna''. After genetic testing revealed that the alpaca descends from the vicuña it was also moved to genus ''Vicugna.'' The American Society of Mammalogists later moved the species of genus ''Vicugna'' back into genus ''Lama'' due to low genetic distance between the two. The R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miranda Kadwell
Miranda may refer to: People * Miranda (given name), includes list of real and fictional people with given name Miranda * Miranda (surname), includes list of people with surname Miranda * Miranda (footballer, born 1947) (Deoclécio Manuel de Miranda), Brazilian footballer * Miranda (footballer, born 1957) (Donizete Manuel Onofre), Brazilian footballer * Miranda (footballer, born 1984) (João Miranda de Souza Filho), Brazilian footballer * Miranda (footballer, born 1998) (Guilherme dos Santos Rodrigues), Brazilian footballer * Miranda (footballer, born 2000) (Matheus dos Santos Miranda), Brazilian footballer * Miranda Hart (born 1972), English comedian and actress, sometimes mononymously referred to as Miranda Law * ''Miranda v. Arizona'', an American legal case * ''Miranda'' warning, an American police warning given to suspects about their rights, before they are interrogated Places Solar System * Miranda (moon), a moon orbiting Uranus Australia * Miranda, New South Wales ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanaco
The guanaco ( ; ''Lama guanicoe'') is a camelid native to South America, closely related to the llama. Guanacos are one of two wild South American camelids; the other species is the vicuña, which lives at higher elevations. Etymology The guanaco gets its name from the Quechua word ''wanaku''. Young guanacos are called ''chulengos'' or "guanaquitos". Characteristics Guanacos stand between at the shoulder, body length of , and weigh . Their color varies very little (unlike the domestic llama), ranging from a light brown to dark cinnamon and shading to white underneath. Guanacos have grey faces and small, straight ears. The lifespan of a guanaco can be as long as 28 years. Guanacos are one of the largest terrestrial mammals native to South America today.San Diego Zoo's Animal Bytes Other terrestrial mammalian [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, recognising excellence in science, supporting outstanding science, providing scientific advice for policy, education and public engagement and fostering international and global co-operation. Founded on 28 November 1660, it was granted a royal charter by Charles II of England, King Charles II and is the oldest continuously existing scientific academy in the world. The society is governed by its Council, which is chaired by the society's president, according to a set of statutes and standing orders. The members of Council and the president are elected from and by its Fellows, the basic members of the society, who are themselves elected by existing Fellows. , there are about 1,700 fellows, allowed to use the postnominal title FRS (Fellow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
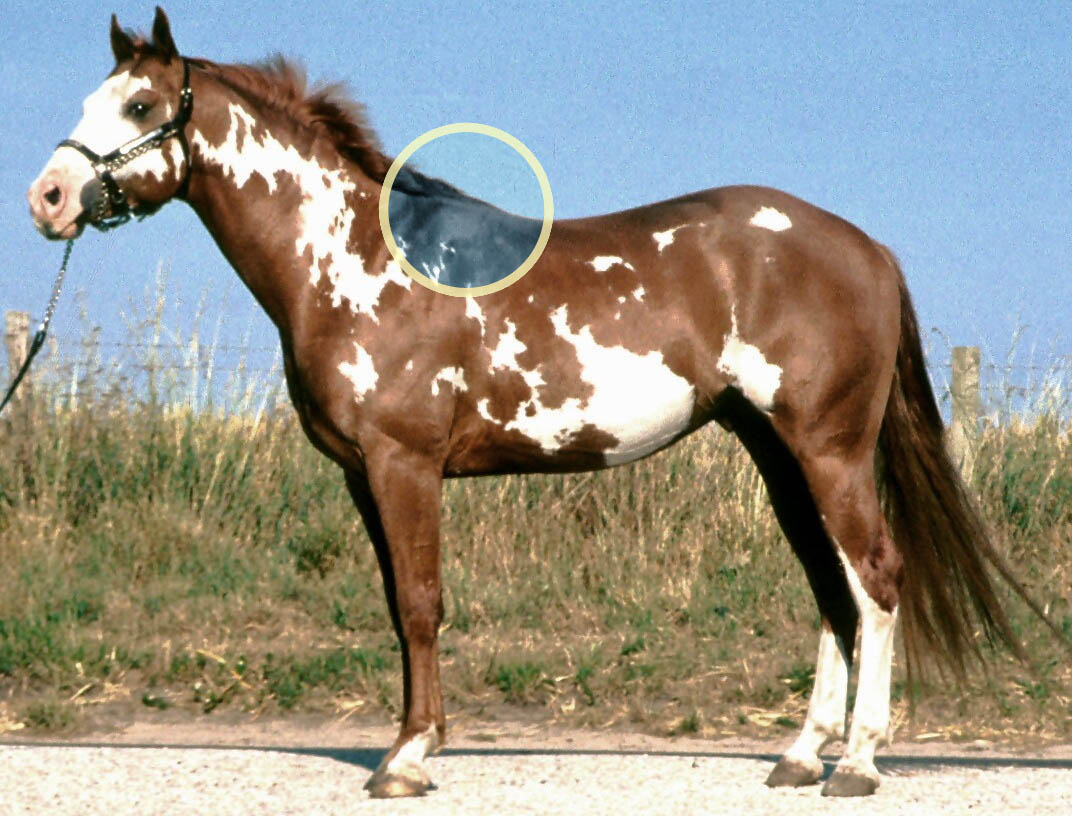
Withers
Withers are the ridge between the shoulder blades of an animal, typically a quadruped. In many species, this ridge is the tallest point of the body. In horses and dogs, it is the standard place to measure the animal's height. In contrast, cattle are often measured to the top of the hips. The term (pronounced ) derives from Old English ''wither'' ("against'), because the withers are the part of a Working_animal#Draft_animals , draft animal that pushes against a Mechanical load, load. Horses The withers in horses are formed by the dorsal spinal processes of roughly the 3rd through 11th thoracic vertebrae, which are unusually long in this area. Most horses have 18 thoracic vertebrae. The processes at the withers can be more than long. Since they do not move relative to the ground as the horse's head does, the withers are used as the measuring point for the height of a horse. Horses are sometimes measured in hand (unit), hands – one hand is . Horse heights are extremely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |