|
Allen Peak
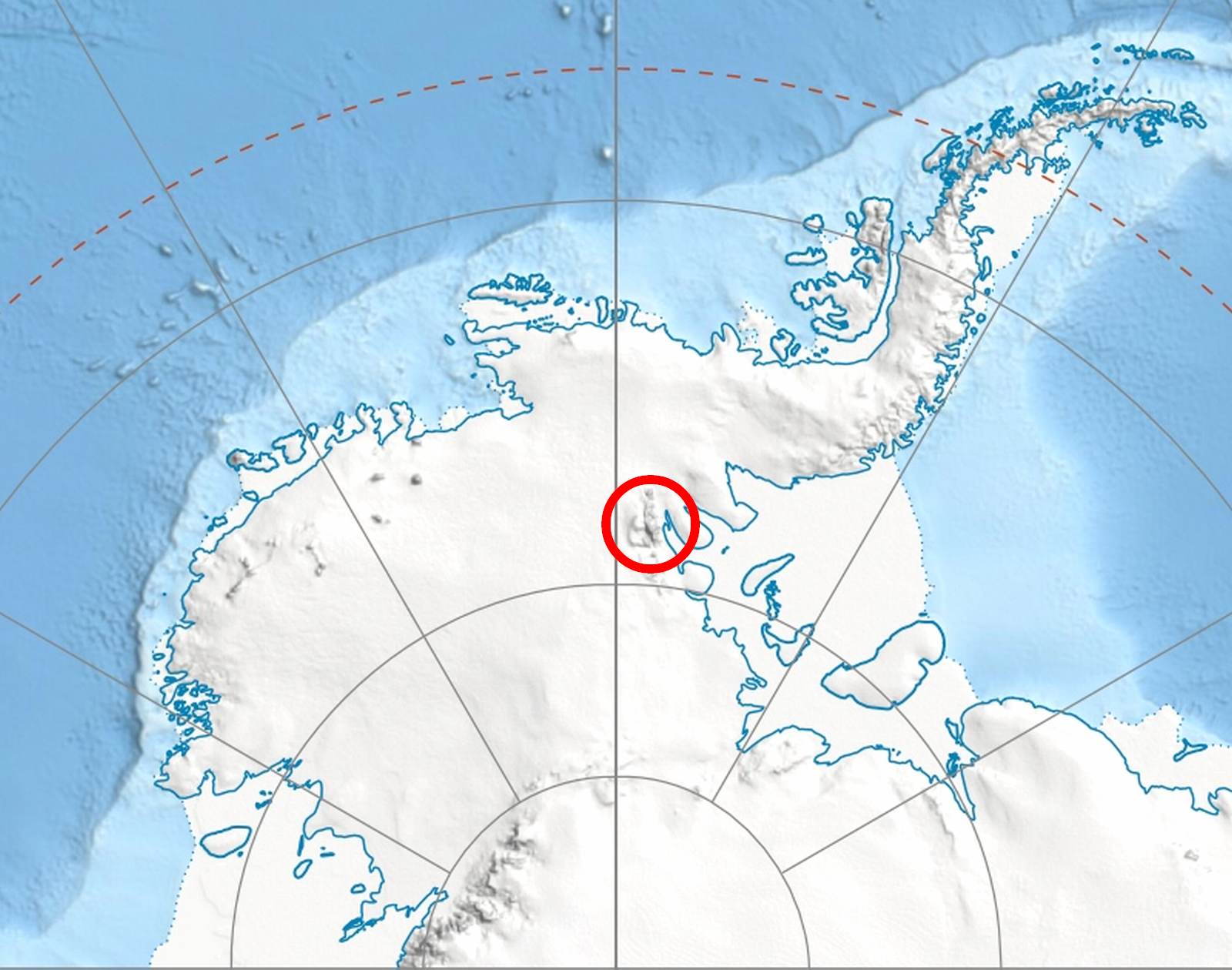
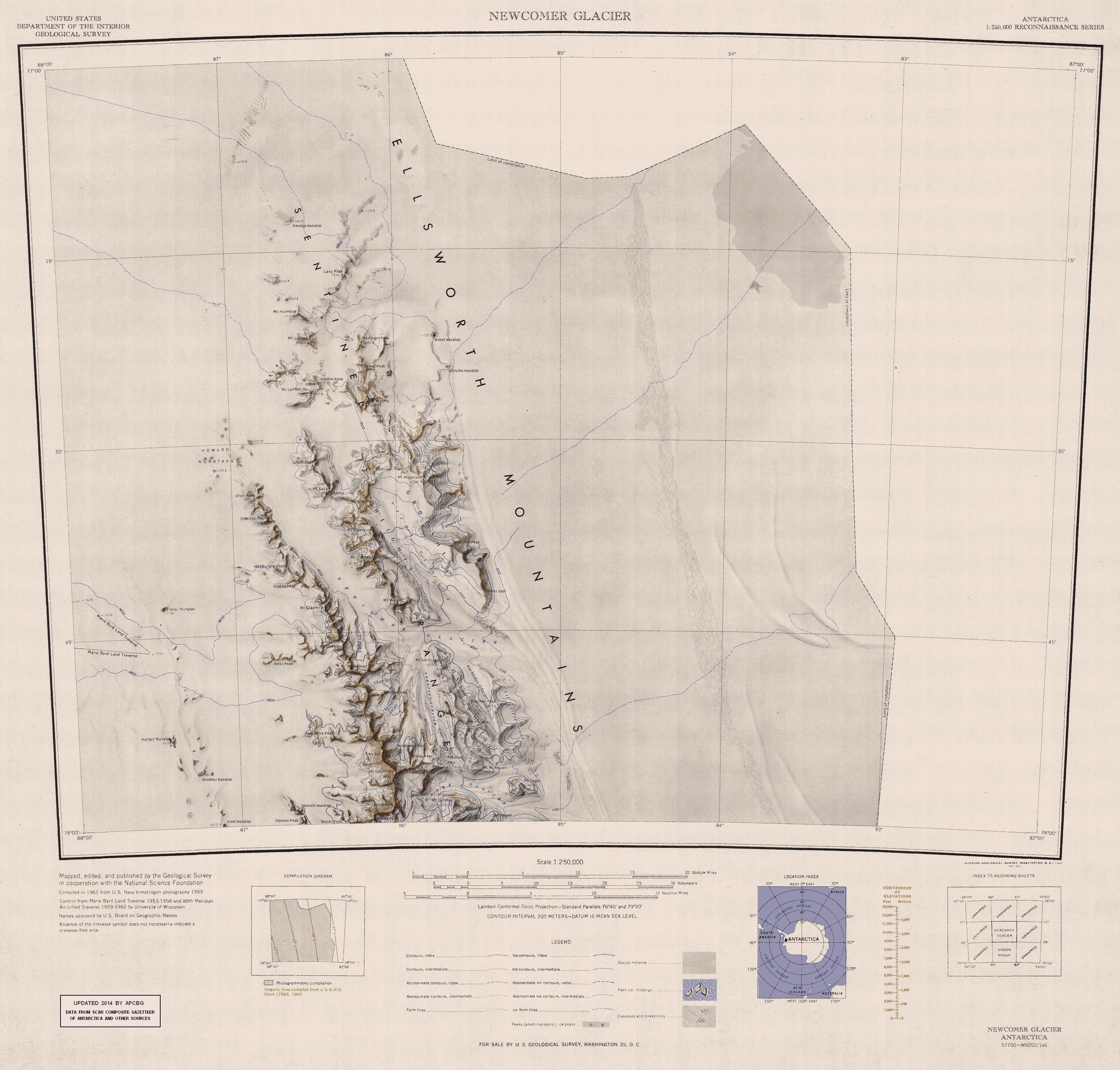
Allen Peak () is a peak in Antarctica, standing west of Mount Wyatt Earp and forming the northern extremity of the main ridge of the Sentinel Range. It was discovered by Lincoln Ellsworth on his trans-Antarctic flight of 23 November 1935, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names after Robert J. Allen Jr., a United States Geological Survey (USGS) cartographer and Antarctic specialist, 1950–79, a consultant to the USGS Branch of International Activities from 1980, and a member of the Branch of Special Maps, who helped prepare the 1962 map of this range. See also * Mountains in Antarctica This is a list of all the Ultra prominent peaks (with topographic prominence greater than 1,500 metres) in Antarctica. Some islands in the South Atlantic have also been included and can be found at the end of the list. Antarctica South Atl ... References Mountains of Ellsworth Land {{EllsworthLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summit (topography)
A summit is a point on a surface that is higher in elevation than all points immediately adjacent to it. The topographic terms acme, apex, peak (mountain peak), and zenith are synonymous. The term (mountain top) is generally used only for a mountain peak that is located at some distance from the nearest point of higher elevation. For example, a big, massive rock next to the main summit of a mountain is not considered a summit. Summits near a higher peak, with some prominence or isolation, but not reaching a certain cutoff value for the quantities, are often considered ''subsummits'' (or ''subpeaks'') of the higher peak, and are considered part of the same mountain. A pyramidal peak is an exaggerated form produced by ice erosion of a mountain top. Summit may also refer to the highest point along a line, trail, or route. The highest summit in the world is Mount Everest with a height of above sea level. The first official ascent was made by Tenzing Norgay and Sir Edmund Hill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Wyatt Earp
Mount Wyatt Earp () is a mainly snow-covered peak, 2,370 m, standing 3 nautical miles (6 km) west-northwest of Mount Ulmer in the north part of Sentinel Range, Antarctica. It is connected to Matsch Ridge and Mount Ulmer by Skamni Saddle Skamni Saddle ( bg, седловина Скамни, ‘Sedlovina Skamni’ \se-dlo-vi-'na 'skam-ni\) is the 1.3 km long ice-covered saddle of elevation 1750 m in northern Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica connecting Mount .... The mountain was discovered by Lincoln Ellsworth on his trans-Antarctic flight of November 23, 1935. Named by the US-ACAN for the ship Wyatt Earp, used by Ellsworth in four expeditions to Antarctica between 1933 and 1939. Further reading * M.J. Hambrey, P.F. Barker, P.J. Barrett, V. Bowman, B. Davies, J.L. Smellie, M. Tranter, editors, Antarctic Palaeoenvironments and Earth-Surface Processes', PP 89–90 * David J. Cantrill, Imogen Poole, The Vegetation of Antarctica through Geologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentinel Range
The Sentinel Range is a major mountain range situated northward of Minnesota Glacier and forming the northern half of the Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica. The range trends NNW-SSE for about and is 24 to 48 km (15 to 30 mi) wide. Many peaks rise over and Vinson Massif (4892 m) in the southern part of the range is the highest elevation on the continent.Sentinel Range. SCAR Composite Antarctic Gazetteer. Sentinel Range comprises a main ridge (featuring Vinson Massif in its southern portion) and a number of distinct heights, ridges and mountains on its east side, including (south to north) Owen Ridge, |
Lincoln Ellsworth
Lincoln Ellsworth (May 12, 1880 – May 26, 1951) was a polar explorer from the United States and a major benefactor of the American Museum of Natural History. Biography Lincoln Ellsworth was born on May 12, 1880, to James Ellsworth and Eva Frances Butler in Chicago, Illinois. He also lived in Hudson, Ohio, as a child. He attended The Hill School and took two years longer than usual to graduate, before entering the Sheffield Scientific School at Yale University. His academic performance was poor, and he subsequently enrolled at Columbia University and McGill before ending his academic career. Lincoln Ellsworth's father, James, a wealthy coal man from the United States, spent US$100,000 to fund Roald Amundsen's 1925 attempt to fly from Svalbard to the North Pole. Amundsen, accompanied by Lincoln Ellsworth, pilot Hjalmar Riiser-Larsen, flight mechanic Karl Feucht and two other team members, set out in two Dornier Wal flying boats, the N24 and N25, in an attempted to reach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert J
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredth an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains In Antarctica
This is a list of all the Ultra prominent peaks (with topographic prominence greater than 1,500 metres) in Antarctica. Some islands in the South Atlantic have also been included and can be found at the end of the list. Antarctica South Atlantic The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe an ... Sources * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Ultras Of Antarctica Antarctica Ultras * Ultras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |