|
Aliyah (other)
Aliyah (, ; he, עֲלִיָּה ''ʿălīyyā'', ) is the immigration of Jews from the diaspora to, historically, the geographical Land of Israel or the Palestine region, which is today chiefly represented by the State of Israel. Traditionally described as "the act of going up" (towards the Jewish holy city of Jerusalem), moving to the Land of Israel or "making aliyah" is one of the most basic tenets of Zionism. The opposite action—emigration by Jews from the Land of Israel—is referred to in the Hebrew language as ''yerida'' (). The Law of Return that was passed by the Israeli parliament in 1950 gives all diaspora Jews, as well as their children and grandchildren, the right to relocate to Israel and acquire Israeli citizenship on the basis of connecting to their Jewish identity. For much of their history, most Jews have lived in the diaspora outside of the Land of Israel due to various historical conflicts that led to their persecution alongside multiple instances of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aaliyah
Aaliyah Dana Haughton (; January 16, 1979 – August 25, 2001) was an American singer and actress. She has been credited for helping to redefine contemporary R&B, pop and hip hop, earning her the nicknames the "Princess of R&B" and "Queen of Urban Pop". Born in Brooklyn but raised in Detroit, she first gained recognition at the age of 10, when she appeared on the television show ''Star Search'' and performed in concert alongside Gladys Knight. At the age of 12, Aaliyah signed with Jive Records and her uncle Barry Hankerson's Blackground Records. Hankerson introduced her to R. Kelly, who became her mentor, as well as lead songwriter and producer of her debut album, ''Age Ain't Nothing but a Number''. The album sold three million copies in the United States and was certified double platinum by the Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA). After allegations of an illegal marriage with Kelly, Aaliyah ended her contract with Jive and signed with Atlantic Records. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Military History
Jewish military history focuses on the military aspect of history of the Jewish people from ancient times until the modern age. Ancient Israelites While complete details in the Biblical account of a system of fighting forms are not extant, the Midrashic, Talmudic, and Rabbinic accounts testify to fighting and combat strategies used by the ancient Israelites as well as legendary depictions of Israelite combatants. Conflicts documented in steles Merneptah Stele The Merneptah Stele was discovered in 1896 and is dated to . The last 3 of the 28 lines of the text deal with a separate campaign in Canaan. It mentions a victory over Israel by the lines: "The Canaan has been plundered into every sort of woe: Ashkelon has been overcome; Gezer has been captured; Yano'am is made non-existent. Israel is laid waste and his seed is not;" Mesha Stele Mesha Stele was discovered in 1868-70 and was created around 840 BCE by King Mesha of Moab. Mesha tells how Kemosh, the God of Moab, had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Ruppin
Arthur Ruppin (1 March 1876 – 1 January 1943) was a German Zionist proponent of pseudoscientific race theory and one of the founders of the city of Tel Aviv.Todd Samuel Presner, ’German Jewish Studies in the Digital Age:Remarks on Discipline, Method nand Media,' in William Collins Donahue, Martha B. Helfer (eds.) Nexus: Essays in German Jewish Studies Volume 1, Camden House, 2011 pp.7-25 p.22 n.10 Appointed director of Berlin's Bureau for Jewish statistics (''Büro für Statistik der Juden'') in 1904, he moved to Palestine in 1907, and from 1908 was the director of the Palestine Office of the Zionist Organization in Jaffa, organizing Zionist immigration to Palestine. In 1926, Ruppin joined the faculty of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and founded the Department for the Sociology of the Jews. Described posthumously as the "founder of German-Jewish demography" and "father of Israeli sociology", his best known sociological work was ''The Jews in the Modern World'' (1934 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Basin
In biogeography, the Mediterranean Basin (; also known as the Mediterranean Region or sometimes Mediterranea) is the region of lands around the Mediterranean Sea that have mostly a Mediterranean climate, with mild to cool, rainy winters and warm to hot, dry summers, which supports characteristic Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub vegetation. Geography The Mediterranean Basin covers portions of three continents: Europe, Africa, and Asia. It is distinct from the drainage basin, which extends much further south and north due to major rivers ending in the Mediterranean Sea, such as the Nile and Rhône. Conversely, the Mediterranean Basin includes regions not in the drainage basin. It has a varied and contrasting topography. The Mediterranean Region offers an ever-changing landscape of high mountains, rocky shores, impenetrable scrub, semi-arid steppes, coastal wetlands, sandy beaches and a myriad islands of various shapes and sizes dotted amidst the clear blue sea. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
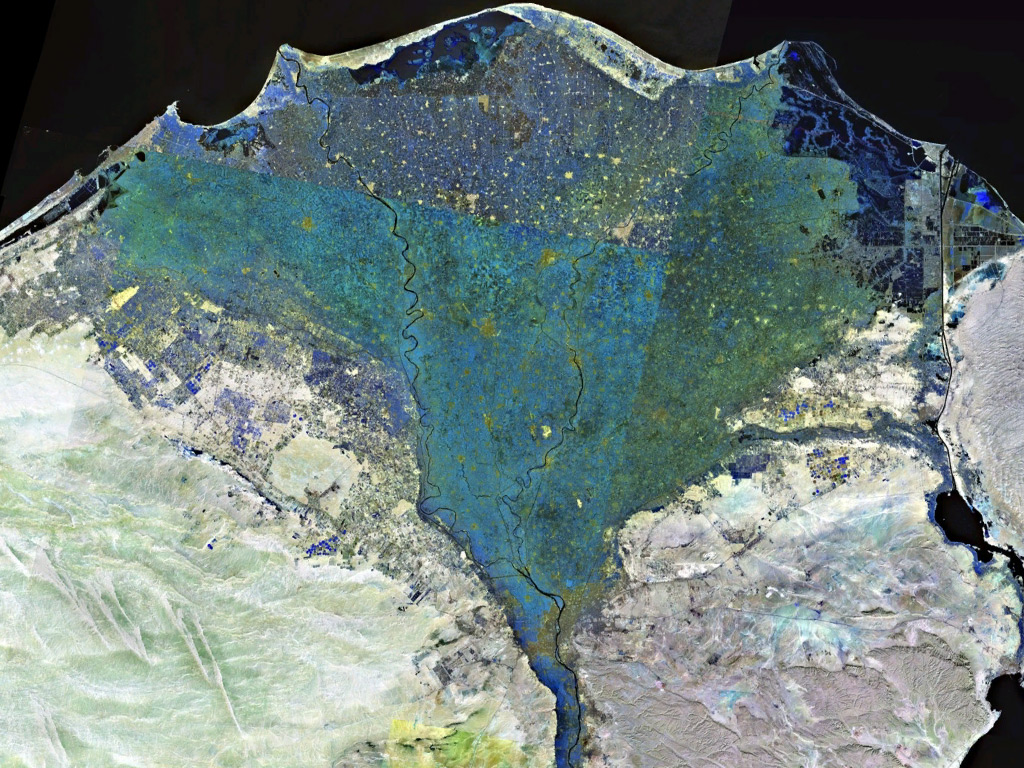
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east, it covers of Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same name. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta and enters the coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbinical Judaism
Rabbinic Judaism ( he, יהדות רבנית, Yahadut Rabanit), also called Rabbinism, Rabbinicism, or Judaism espoused by the Rabbanites, has been the mainstream form of Judaism since the 6th century CE, after the codification of the Babylonian Talmud. Rabbinic Judaism has its roots in Pharisaic Judaism and is based on the belief that Moses at Mount Sinai received both the Written Torah (''Torah she-be-Khetav'') and the Oral Torah (''Torah she-be-al Peh'') from God. The Oral Torah, transmitted orally, explains the Written Torah. At first, it was forbidden to write down the Oral Torah because the rabbis feared that it would become rigid and lose its flexibility, but after the destruction of the Second Temple they decided to write it down in the Talmud and other rabbinic texts. Rabbinic Judaism contrasts with the Sadducees, Karaite Judaism and Samaritanism, which do not recognize the Oral Torah as a divine authority nor the rabbinic procedures used to interpret Jewish scripture. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Vertical datum). The term ''elevation'' is mainly used when referring to points on the Earth's surface, while ''altitude'' or ''geopotential height'' is used for points above the surface, such as an aircraft in flight or a spacecraft in orbit, and '' depth'' is used for points below the surface. Elevation is not to be confused with the distance from the center of the Earth. Due to the equatorial bulge, the summits of Mount Everest and Chimborazo have, respectively, the largest elevation and the largest geocentric distance. Aviation In aviation the term elevation or aerodrome elevation is defined by the ICAO as the highest point of the landing area. It is often measured in feet and can be found in approach charts of the aerodrome. It is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Population By Country
As of 2020, the world's "core" Jews, Jewish population (those identifying as Jews above all else) was estimated at 15 million, 0.2% of the 8 billion worldwide population. This number rises to 18 million with the addition of the "connected" Jewish population, including those who say they are partly Jewish or that have Jewish backgrounds from at least one Jewish parent, and rises again to 21 million with the addition of the "enlarged" Jewish population, including those who say they have Jewish backgrounds but no Jewish parents and all non-Jewish household members who live with Jews. Counting all those who are eligible for Israeli citizenship under Israel's Law of Return, in addition to Israeli Jews, raised the total to 23.8 million. Two countries account for 81% of those recognised as Jews or of sufficient Jewish ancestry to be eligible for citizenship in Israel under its Law of Return: the United States with 51% and Israel with 30% (including the West Bank with 2%). An additional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli-occupied Territories
Israeli-occupied territories are the lands that were captured and occupied by Israel during the Six-Day War of 1967. While the term is currently applied to the Palestinian territories and the Golan Heights, it has also been used to refer to areas that were formerly occupied by Israel, namely the Sinai Peninsula and southern Lebanon. Prior to Israel's victory in the Six-Day War, governance of the Palestinian territories was split between Egypt and Jordan, with the former having occupied the Gaza Strip and the latter having annexed the West Bank; the Sinai Peninsula and the Golan Heights were under the sovereignty of Egypt and Syria, respectively. The first conjoined usage of the terms "occupied" and "territories" with regard to Israel was in United Nations Security Council Resolution 242, which was drafted in the aftermath of the Six-Day War and called for: "the establishment of a just and lasting peace in the Middle East" to be achieved by "the application of both the followi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
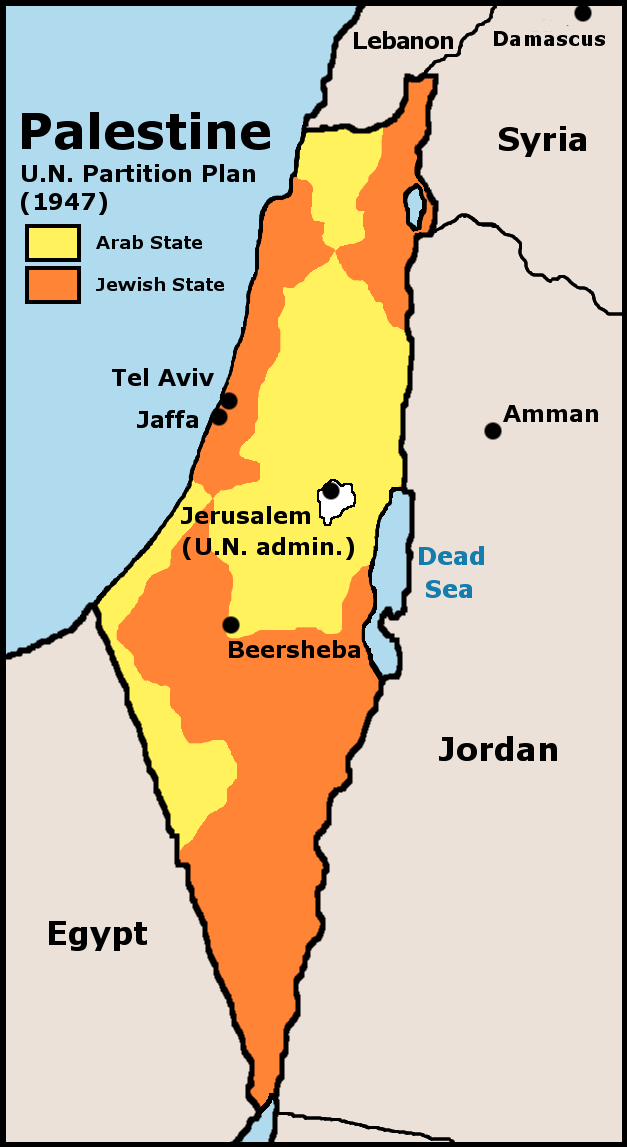
Israeli Declaration Of Independence
The Israeli Declaration of Independence, formally the Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel ( he, הכרזה על הקמת מדינת ישראל), was proclaimed on 14 May 1948 ( 5 Iyar 5708) by David Ben-Gurion, the Executive Head of the World Zionist Organization, Chairman of the Jewish Agency for Palestine, and soon to be first Prime Minister of Israel. It declared the establishment of a Jewish state in Eretz-Israel, to be known as the State of Israel, which would come into effect on termination of the British Mandate at midnight that day. The event is celebrated annually in Israel with a national holiday Independence Day on 5 Iyar of every year according to the Hebrew calendar. Background The possibility of a Jewish homeland in Palestine had been a goal of Zionist organizations since the late 19th century. In 1917 British Foreign Secretary Arthur Balfour stated in a letter to British Jewish community leader Walter, Lord Rothschild that: His Majesty's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Return To Zion
The return to Zion ( he, שִׁיבָת צִיּוֹן or שבי ציון, , ) is an event recorded in Ezra–Nehemiah of the Hebrew Bible, in which the Jews of the Kingdom of Judah—subjugated by the Neo-Babylonian Empire—were freed from the Babylonian captivity following the Persian conquest of Babylon. After their release, the Persian king Cyrus the Great issued a proclamation known as the Edict of Cyrus that enabled the freed Jewish populace, exiled from Judah, to return to Jerusalem and the Land of Judah, which had begun to function as a self-governing Jewish province under the Achaemenid Persian Empire. Babylonian exile The Neo-Babylonian Empire under the rule of Nebuchadnezzar II occupied the Kingdom of Judah between 597–586 BCE. The Babylonian army had destroyed the First Temple in Jerusalem. According to the Hebrew Bible, the king of Judah, Zedekiah, was forced to watch his own two sons being slaughtered, and thereafter, his own eyes were put out and he was exi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)