|
Alexander Ecker
Johann Alexander Ecker (10 July 1816 – 20 May 1887) was a German anthropologist and anatomist, born in Freiburg im Breisgau. He was the son of Johann Matthias Alexander Ecker (1766–1829), a professor at the University of Freiburg. Biography He studied medicine at the University of Freiburg as a pupil of Karl Heinrich Baumgärtner. He received his medical doctorate at Freiburg in 1837. In 1840 he started work as a prosector at the University of Heidelberg, where during the following year, he became a privat-docent. At Heidelberg, his influences included Friedrich Tiedemann, Friedrich August Benjamin Puchelt, Theodor Ludwig Wilhelm Bischoff and Maximilian Joseph von Chelius. In 1844 he became a full professor at Basel, later returning to Freiburg as a professor of physiology and comparative anatomy (1850). In 1870 he was co-founder of the ''Akademische Gesellschaft''. As an anthropologist, Ecker conducted excavations of early burial sites in the Kaiserstuhl region of sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Ecker
Johann Alexander Ecker (10 July 1816 – 20 May 1887) was a German anthropologist and anatomist, born in Freiburg im Breisgau. He was the son of Johann Matthias Alexander Ecker (1766–1829), a professor at the University of Freiburg. Biography He studied medicine at the University of Freiburg as a pupil of Karl Heinrich Baumgärtner. He received his medical doctorate at Freiburg in 1837. In 1840 he started work as a prosector at the University of Heidelberg, where during the following year, he became a privat-docent. At Heidelberg, his influences included Friedrich Tiedemann, Friedrich August Benjamin Puchelt, Theodor Ludwig Wilhelm Bischoff and Maximilian Joseph von Chelius. In 1844 he became a full professor at Basel, later returning to Freiburg as a professor of physiology and comparative anatomy (1850). In 1870 he was co-founder of the ''Akademische Gesellschaft''. As an anthropologist, Ecker conducted excavations of early burial sites in the Kaiserstuhl region of sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparative Anatomy
Comparative anatomy is the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species. It is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny (the evolution of species). The science began in the classical era, continuing in the early modern period with work by Pierre Belon who noted the similarities of the skeletons of birds and humans. Comparative anatomy has provided evidence of common descent, and has assisted in the classification of animals. History The first specifically anatomical investigation separate from a surgical or medical procedure is associated by Alcmaeon of Croton. Leonardo da Vinci made notes for a planned anatomical treatise in which he intended to compare the hands of various animals including bears. Pierre Belon, a French naturalist born in 1517, conducted research and held discussions on dolphin embryos as well as the comparisons between the skeletons of birds to the skeletons of humans. His research led to modern comparative anato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Baden
The Grand Duchy of Baden (german: Großherzogtum Baden) was a state in the southwest German Empire on the east bank of the Rhine. It existed between 1806 and 1918. It came into existence in the 12th century as the Margraviate of Baden and subsequently split into the states of Baden-Durlach and Baden-Baden, which were reunified in 1771. It then became the much-enlarged Grand Duchy of Baden after the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire from 1803 to 1806 and was a sovereign country until it joined the German Empire in 1871. In 1918, it became part of the Weimar Republic as the Republic of Baden. Baden was bordered to the north by the Kingdom of Bavaria and the Grand Duchy of Hessen-Darmstadt; to the west, along most of its length, by the river Rhine, which separated Baden from the Bavarian Rhenish Palatinate and Alsace in modern France; to the south by Switzerland; and to the east by the Kingdom of Württemberg, the Principality of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen and Bavaria. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as well as the second most populous city in the area of the former East Germany after (East) Berlin. Together with Halle (Saale), the city forms the polycentric Leipzig-Halle Conurbation. Between the two cities (in Schkeuditz) lies Leipzig/Halle Airport. Leipzig is located about southwest of Berlin, in the southernmost part of the North German Plain (known as Leipzig Bay), at the confluence of the White Elster River (progression: ) and two of its tributaries: the Pleiße and the Parthe. The name of the city and those of many of its boroughs are of Slavic origin. Leipzig has been a trade city since at least the time of the Holy Roman Empire. The city sits at the intersection of the Via Regia and the Via Imperii, two important medieval trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spinal cord, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). In humans, the spinal cord begins at the occipital bone, passing through the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it ends. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around long in adult men and around long in adult women. The diameter of the spinal cord ranges from in the cervical and lumbar regions to in the thoracic area. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of nerve signals from the motor cortex to the body, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; Swabian: ; ) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located on the Neckar river in a fertile valley known as the ''Stuttgarter Kessel'' (Stuttgart Cauldron) and lies an hour from the Swabian Jura and the Black Forest. Stuttgart has a population of 635,911, making it the sixth largest city in Germany. 2.8 million people live in the city's administrative region and 5.3 million people in its metropolitan area, making it the fourth largest metropolitan area in Germany. The city and metropolitan area are consistently ranked among the top 20 European metropolitan areas by GDP; Mercer listed Stuttgart as 21st on its 2015 list of cities by quality of living; innovation agency 2thinknow ranked the city 24th globally out of 442 cities in its Innovation Cities Index; and the Globalization and World Cities Research Network ranked the city as a Beta-status global city in their 2020 survey. Stuttgart was one of the host cities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Zermelo
Ernst Friedrich Ferdinand Zermelo (, ; 27 July 187121 May 1953) was a German logician and mathematician, whose work has major implications for the foundations of mathematics. He is known for his role in developing Zermelo–Fraenkel axiomatic set theory and his proof of the well-ordering theorem. Furthermore, his 1929 work on ranking chess players is the first description of a model for pairwise comparison that continues to have a profound impact on various applied fields utilizing this method. Life Ernst Zermelo graduated from Berlin's Luisenstädtisches Gymnasium (now ) in 1889. He then studied mathematics, physics and philosophy at the University of Berlin, the University of Halle, and the University of Freiburg. He finished his doctorate in 1894 at the University of Berlin, awarded for a dissertation on the calculus of variations (''Untersuchungen zur Variationsrechnung''). Zermelo remained at the University of Berlin, where he was appointed assistant to Planck, under whose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petro-occipital Fissure
This grooved surface of the foramen magnum is separated on either side from the petrous portion of the temporal bone by the petro-occipital fissure, which is occupied in the fresh state by a plate of cartilage; the fissure is continuous behind with the jugular foramen, and its margins are grooved for the inferior petrosal sinus The inferior petrosal sinuses are two small sinuses situated on the inferior border of the petrous part of the temporal bone, one on each side. Each inferior petrosal sinus drains the cavernous sinus into the internal jugular vein. Structure The .... References External links * Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
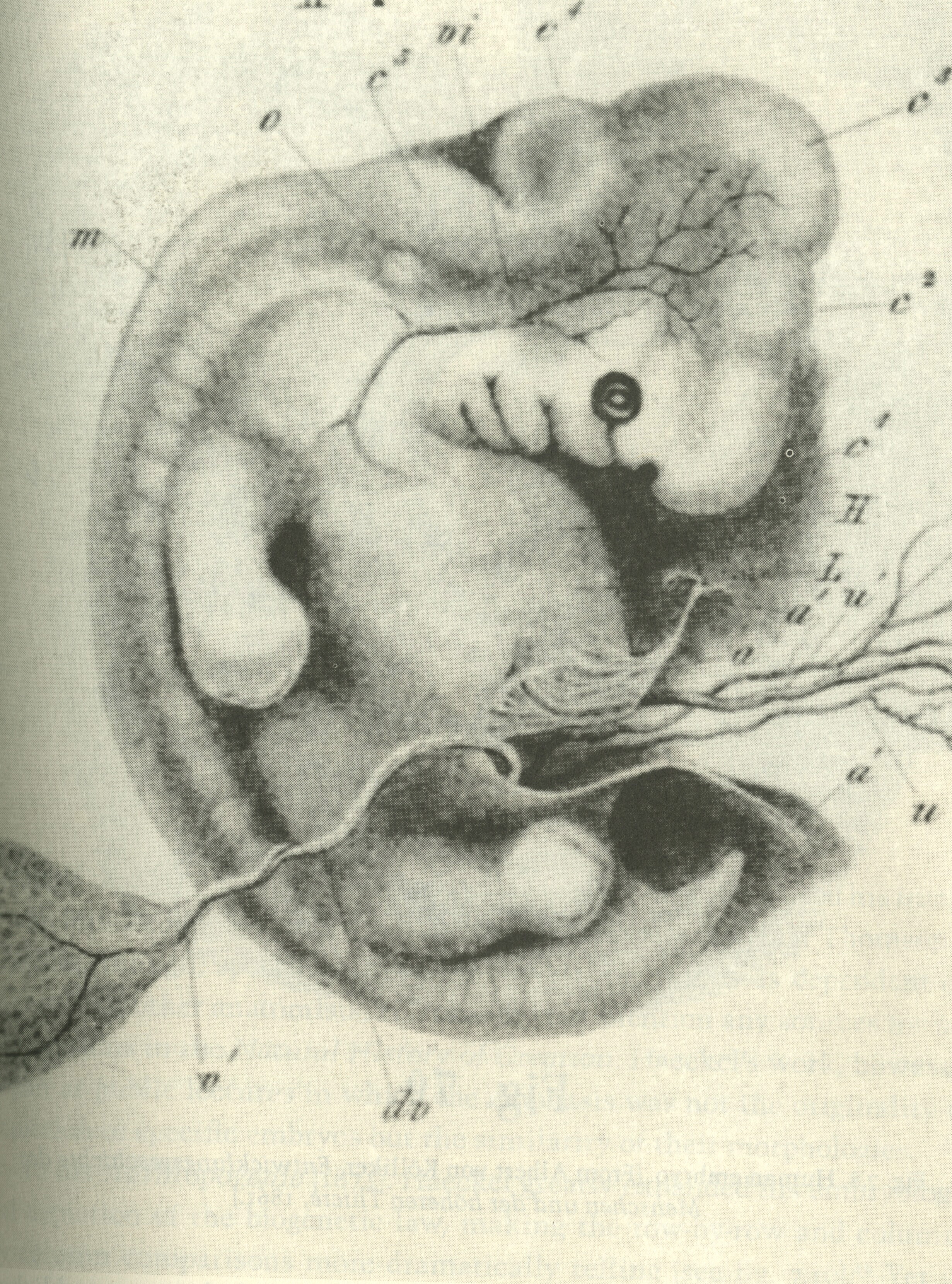
Fetus
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal development begins from the ninth week after fertilization (or eleventh week gestational age) and continues until birth. Prenatal development is a continuum, with no clear defining feature distinguishing an embryo from a fetus. However, a fetus is characterized by the presence of all the major body organs, though they will not yet be fully developed and functional and some not yet situated in their final anatomical location. Etymology The word ''fetus'' (plural ''fetuses'' or '' feti'') is related to the Latin '' fētus'' ("offspring", "bringing forth", "hatching of young") and the Greek "φυτώ" to plant. The word "fetus" was used by Ovid in Metamorphoses, book 1, line 104. The predominant British, Irish, and Commonwealth spelling is '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting of allocortex. It is separated into two cortices, by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The two hemispheres are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum. The cerebral cortex is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system. It plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The cerebral cortex is part of the brain responsible for cognition. In most mammals, apart from small mammals that have small brains, the cerebral cortex is folded, providing a greater surface area in the confined volume of the cranium. Apart from minimising brain and cranial volume, cortical folding is crucial for the brain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Lindenschmit The Elder
Ludwig Lindenschmit (the Elder) (September 4, 1809 – February 14, 1893) was a German history painter, prehistorian and art instructor who was a native of Mainz. He was a younger brother to history painter Wilhelm Lindenschmit (1806–1848), and father to prehistorian Ludwig Lindenschmit (the Younger) (1850–1922). He studied art in Vienna and Munich, and beginning in 1831, was a high school art teacher in his hometown of Mainz. Here, he taught classes in art until the 1870s, and as his career progressed, his interest in prehistoric Germanic antiquities grew. In 1848 he published ''Das Germanische Totenlager von Selzen'', an important treatise on Germanic sepulchral mounds. In 1851, he became head of the Romano-Germanic Central Museum in Mainz. Lindenschmit was an outspoken critic of the "three-age system" developed by archaeologist Christian Jürgensen Thomsen (1788–1865). With anatomist Alexander Ecker (1816–1887), he founded the ''Archiv für Anthropologie''. As a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistory
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)






