|
Alessio Ciulli
Alessio Ciulli (born in Firenze, 22 July 1977) is an Italian British biochemist. Currently, he is the Professor of Chemical & Structural Biology at the School of Life Sciences, University of Dundee, where he founded and directs Dundee' new Centre for Targeted Protein Degradation (CeTPD). He is also the scientific co-founder and advisor of Amphista Therapeutics. Educational background Alessi Ciulli attended University of Florence in his hometown with an undergraduate laurea in chemistry and graduated magna cum laude. Under the late Prof Ivano Bertini, his final year laurea project was in computational drug design and NMR spectroscopy of matrix metalloproteases. Awarded with a Gates Cambridge Scholarship, he did his PhD under the supervision of the late Professor Chris Abell at the University of Cambridge and in collaboration with Astex Technology ( now Astex Pharmaceuticals ) produced a thesis concerned with studying weak protein-ligand interactions using biophysical and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico anno 2013, datISTAT/ref> Florence was a centre of medieval European trade and finance and one of the wealthiest cities of that era. It is considered by many academics to have been the birthplace of the Renaissance, becoming a major artistic, cultural, commercial, political, economic and financial center. During this time, Florence rose to a position of enormous influence in Italy, Europe, and beyond. Its turbulent political history includes periods of rule by the powerful Medici family and numerous religious and republican revolutions. From 1865 to 1871 the city served as the capital of the Kingdom of Italy (established in 1861). The Florentine dialect forms the base of Standard Italian and it became the language of culture throughout Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Craig Crews
Craig M. Crews (born June 1, 1964) is an American scientist at Yale University. He is the John C. Malone Professor of Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology, and also holds joint appointments in the departments of Chemistry and Pharmacology. Crews is the Executive Director of the Yale Center for Molecular Discovery and a former Editor of the journal '' Cell Chemical Biology''. His research interests focus on chemical biology, particularly on controlled proteostasis. Crews is a pioneer in the field of targeted protein degradation and his lab's research led to the development of the anti-cancer drug carfilzomib (Kyprolis). He is the founder of Arvinas, the first biotechnology company to bring PROTAC drugs into clinical trials. In 2019, he was named an American Cancer Society Research Professor at the Yale University. Education and training Crews graduated from the University of Virginia in 1986 with a bachelor's degree in chemistry, after which he performed research at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academics Of The University Of Dundee
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 387 BC, established what is known today as the Old Academy. By extension, ''academia'' has come to mean the accumulation, dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Florence Alumni
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellow Of The Royal Society Of Edinburgh
Fellowship of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (FRSE) is an award granted to individuals that the Royal Society of Edinburgh, Scotland's national academy of science and letters, judged to be "eminently distinguished in their subject". This society received a royal charter in 1783, allowing for its expansion. Elections Around 50 new fellows are elected each year in March. there are around 1,650 Fellows, including 71 Honorary Fellows and 76 Corresponding Fellows. Fellows are entitled to use the post-nominal letters FRSE, Honorary Fellows HonFRSE, and Corresponding Fellows CorrFRSE. Disciplines The Fellowship is split into four broad sectors, covering the full range of physical and life sciences, arts, humanities, social sciences, education, professions, industry, business and public life. A: Life Sciences * A1: Biomedical and Cognitive Sciences * A2: Clinical Sciences * A3: Organismal and Environmental Biology * A4: Cell and Molecular Biology B: Physical, Engineering and I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellow Of The Royal Society Of Chemistry
Fellowship of the Royal Society of Chemistry (FRSC) is an award conferred by the Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) in the United Kingdom. FRSC award Achieving Fellow status in the chemical profession denotes to the wider community a high level of accomplishment as a professional chemist. Eligibility for Fellow status applies to applicants who are Members of the Royal Society of Chemistry (MRSC), with a minimum of 5 years professional experience. In addition, they must have made an outstanding contribution to the advancement of the chemical sciences; or to the advancement of the chemical sciences as a profession; or have been distinguished in the management of a chemical sciences organization. In all cases FRSC sponsor references are required. The award of designatory letters FRSC is subject to the final approval of the RSC Applications Committee. In addition to the above, all RSC membership requires acceptance and adherence to a specific code of conduct and an established set of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
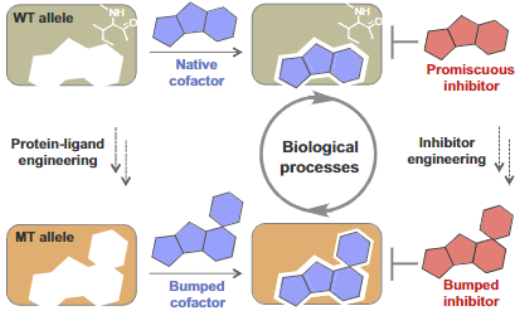
Bump And Hole
The bump-and-hole method is a tool in chemical genetics for studying a specific Protein isoform, isoform in a protein family without perturbing the other members of the family. The unattainability of isoform-selective inhibition due to structural homology in protein families is a major challenge of chemical genetics. With the bump-and-hole approach, a Protein–ligand complex, protein–ligand interface is engineered to achieve selectivity through Steric effects, steric complementarity while maintaining biochemical competence and orthogonality to the wild type pair. Typically, a "bumped" ligand/inhibitor analog is designed to bind a corresponding "hole-modified" protein. Bumped ligands are commonly bulkier derivatives of a Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor of the target protein. Hole-modified proteins are Protein production, recombinantly expressed with an amino acid substitution from a larger to smaller residue, e.g. glycine or alanine, at the cofactor binding site. The designed li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
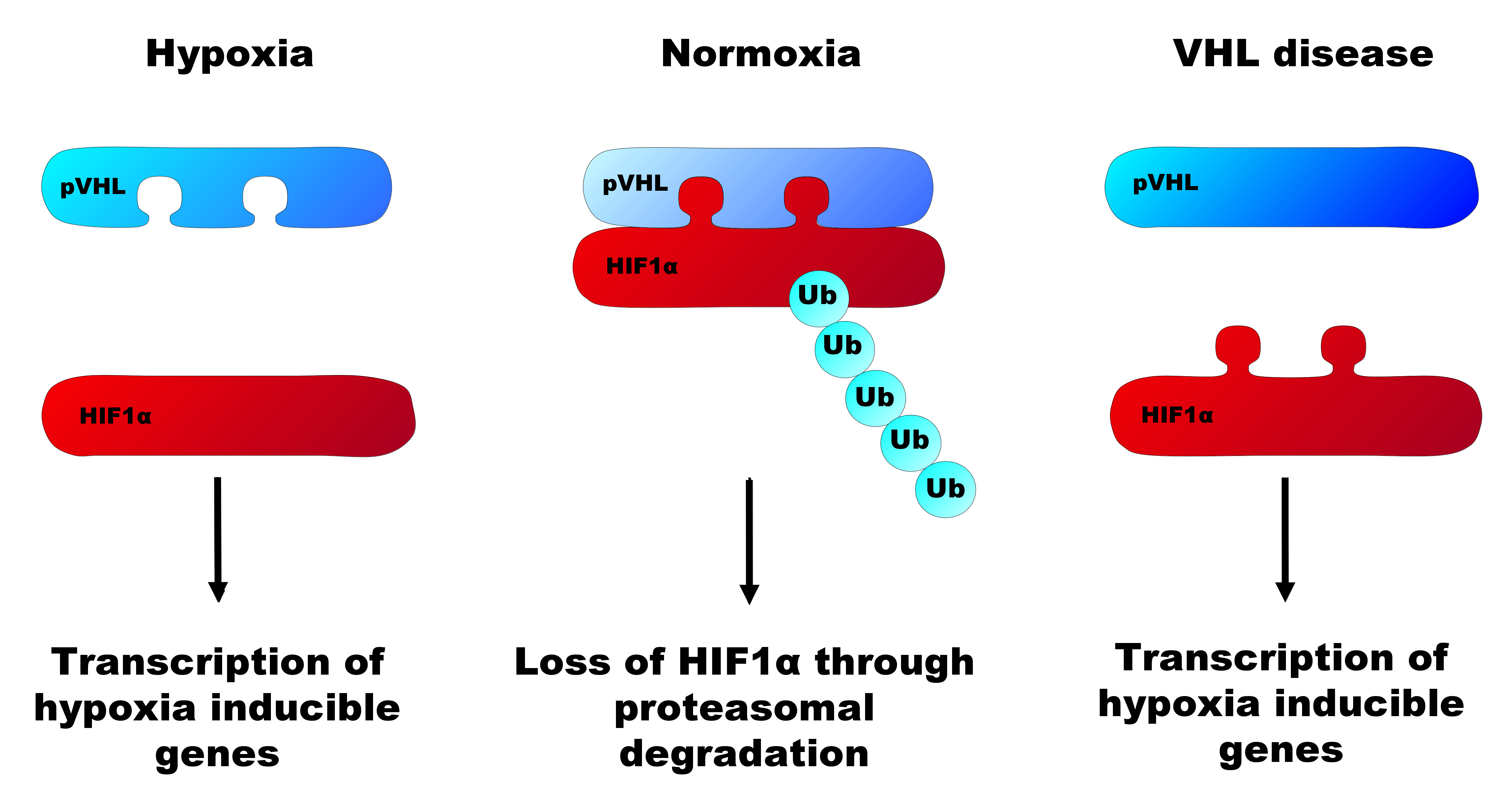
Von Hippel–Lindau Tumor Suppressor
) hockey league, Supreme Hockey League The Von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor also known as pVHL is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''VHL'' gene. Mutations of the VHL gene are associated with Von Hippel–Lindau disease. Function The protein encoded by the VHL gene is the substrate recognition component of a protein complex that includes elongin B, elongin C, and cullin-2, and possesses E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. This complex is involved in the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), which are transcription factors that play a central role regulating gene expression in response to changing oxygen levels. RNA polymerase II subunit POLR2G/RPB7 is also reported to be a target of this protein. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been observed. The resultant protein is produced in two forms, an 18 kDa and a 30 kDa protein that functions as a tumor suppressor. The main action of the VH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
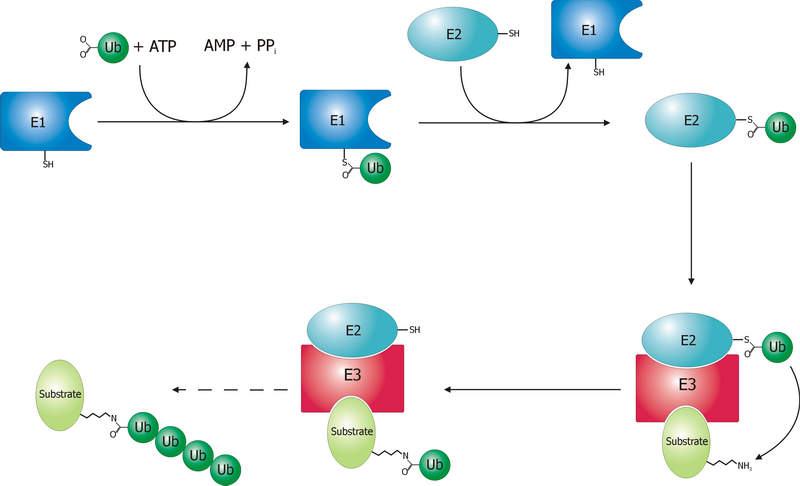
Ubiquitin Ligase
A ubiquitin ligase (also called an E3 ubiquitin ligase) is a protein that recruits an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that has been loaded with ubiquitin, recognizes a protein substrate, and assists or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin from the E2 to the protein substrate. In simple and more general terms, the ligase enables movement of ubiquitin from a ubiquitin carrier to another thing (the substrate) by some mechanism. The ubiquitin, once it reaches its destination, ends up being attached by an isopeptide bond to a lysine residue, which is part of the target protein. E3 ligases interact with both the target protein and the E2 enzyme, and so impart substrate specificity to the E2. Commonly, E3s polyubiquitinate their substrate with Lys48-linked chains of ubiquitin, targeting the substrate for destruction by the proteasome. However, many other types of linkages are possible and alter a protein's activity, interactions, or localization. Ubiquitination by E3 ligases reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteolysis Targeting Chimera
A proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC) is a heterobifunctional small molecule composed of two active domains and a linker, capable of removing specific unwanted proteins. Rather than acting as a conventional enzyme inhibitor, a PROTAC works by inducing selective intracellular proteolysis. PROTACs consist of two covalently linked protein-binding molecules: one capable of engaging an E3 ubiquitin ligase, and another that binds to a target protein meant for degradation. Recruitment of the E3 ligase to the target protein results in ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of the target protein via the proteasome. Because PROTACs need only to bind their targets with high selectivity (rather than inhibit the target protein's enzymatic activity), there are currently many efforts to retool previously ineffective inhibitor molecules as PROTACs for next-generation drugs. Initially described by Kathleen Sakamoto, Craig Crews and Ray Deshaies in 2001, the PROTAC technology has been applie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reader (academic Rank)
The title of reader in the United Kingdom and some universities in the Commonwealth of Nations, for example India, Australia and New Zealand, denotes an appointment for a senior academic with a distinguished international reputation in research or scholarship. In the traditional hierarchy of British and other Commonwealth universities, reader (and principal lecturer in the new universities) are academic ranks above senior lecturer and below professor, recognising a distinguished record of original research. Reader is similar to a professor without a chair, similar to the distinction between ''professor extraordinarius'' and ''professor ordinarius'' at some European universities, professor and chaired professor in Hong Kong and "professor name" (or associate professor) and chaired professor in Ireland. Readers and professors in the UK would correspond to full professors in the United States.Graham WebbMaking the most of appraisal: career and professional development planning for le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christ's College, Cambridge
Christ's College is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge. The college includes the Master, the Fellows of the College, and about 450 undergraduate and 170 graduate students. The college was founded by William Byngham in 1437 as God's House. In 1505, the college was granted a new royal charter, was given a substantial endowment by Lady Margaret Beaufort, and changed its name to Christ's College, becoming the twelfth of the Cambridge colleges to be founded in its current form. Alumni of the college include some of Cambridge University’s most famous members, including Charles Darwin and John Milton. Within Cambridge, Christ's has a reputation for high academic standards. It has averaged 1st place on the Tompkins Table from 1980 to 2006 and third place from 2006 to 2013, returning to first place in 2018, 2019 and 2022. Simon McDonald is the college's current Master. Robert Evans is the chaplain; he was ordained in the Church of England. History Christ's Colleg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |