|
Alcohol And Cardiovascular Disease
Excessive alcohol intake is associated with an elevated risk of alcoholic liver disease (ALD), heart failure, some cancers, and accidental injury, and is a leading cause of preventable death in industrialized countries. Some studies have suggested that one drink per day may have cardiovascular benefits. However, these studies are controversial, and the common view is that no level of alcohol consumption improves health. There is far more evidence for the harmful effects of alcohol than for any beneficial effects. It is also recognized that the alcohol industry may promote the unsubstantiated benefits of moderate drinking. Alcohol intake and cardiovascular disease Some early reviews showed that light alcohol consumption may have a protective effect on cardiovascular health. For instance, a meta-analysis from 2010 found that patients with cardiovascular disease who were light to moderate alcohol consumers, were less likely to suffer from cardiovascular and all-cause mortality. How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
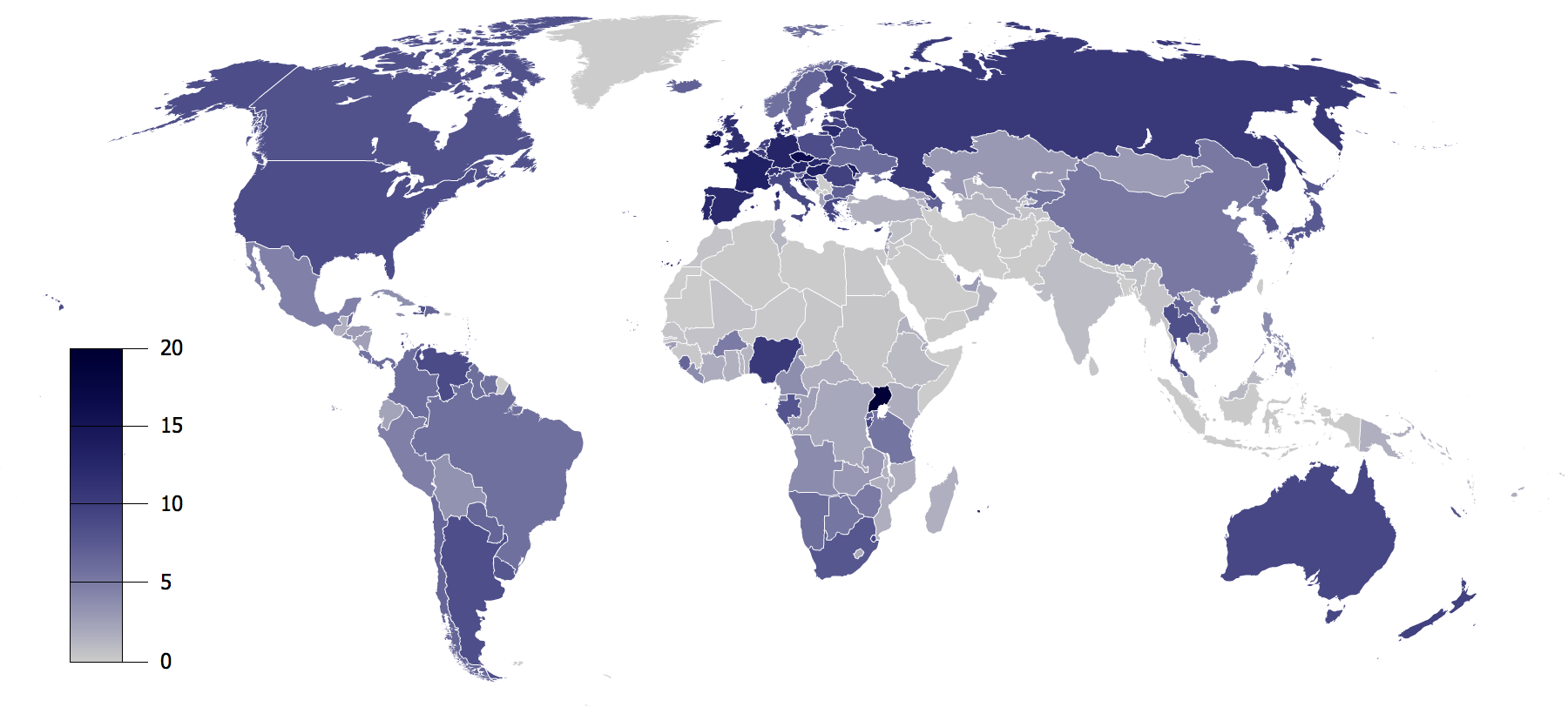
Alcohol By Country
Alcohol most commonly refers to: * Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom * Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks Alcohol may also refer to: Chemicals * Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life ** Alcoholic beverage, sometimes referred to as "alcohol", any drink containing ethanol ** Surrogate alcohol, any substance containing ethanol that is intentionally consumed by humans but is not meant for human consumption * Methanol, a commodity chemical that can serve as a precursor to other chemicals * Alcohol fuel, a fuel containing alcohols * Alcohol powder, a powdered form of alcohol * Fusel alcohol, a mixture of several alcohols (chiefly amyl alcohol) produced as a by-product of alcoholic fermentation. * Alcohols (medicine), the use of alcohols in medicine ** Rubbing alcohol, a solution of denatured or isopropyl alcohol used in medicine Music * "Alcohol" (Barenaked Ladies so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (drug)
Alcohol, sometimes referred to by the chemical name ''ethanol'', is a depressant, depressant drug that is the active ingredient in alcoholic drink, drinks such as beer, wine, and distilled spirits (hard liquor). It is one of the oldest and most commonly consumed recreational drugs, causing the characteristic effects of alcohol intoxication ("drunkenness"). Among other effects, alcohol produces happiness and euphoria, anxiolytic, decreased anxiety, increased sociability, sedation, impairment of cognitive, memory, motor control, motor, and sense, sensory function, and generalized depression of central nervous system (CNS) function. Ethanol is only one of several types of Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, but it is the only type of alcohol that is found in alcoholic beverages or commonly used for recreational purposes; other alcohols such as methanol and isopropyl alcohol are significantly more toxicity, toxic. A mild, brief exposure to isopropanol, being only moderately more toxic tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcoholic Liver Disease
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD), also called alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), is a term that encompasses the liver manifestations of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis with liver fibrosis or cirrhosis. It is the major cause of liver disease in Western countries. Although steatosis (fatty liver disease) will develop in any individual who consumes a large quantity of alcoholic beverages over a long period of time, this process is transient and reversible. More than 90% of all heavy drinkers develop fatty liver whilst about 25% develop the more severe alcoholic hepatitis, and 15% liver cirrhosis. Risk factors Risk factors known as of 2010 are: * Quantity of alcohol taken: Consumption of 60–80 g per day (14 g is considered one standard drink in the US, i.e., 1.5 fl oz hard liquor, 5 fl oz wine, 12 fl oz beer; drinking a six-pack of 5% ABV beer daily would be 84 g and just over the upper limit) for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath may occur with exertion or while lying down, and may wake people up during the night. Chest pain, including angina, is not usually caused by heart failure, but may occur if the heart failure was caused by a heart attack. The severity of the heart failure is measured by the severity of symptoms during exercise. Other conditions that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by altering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol And Cancer
Alcohol causes cancers of the oesophagus, liver, breast, colon, oral cavity, rectum, pharynx and laryngeal cancers, and probably causes cancers of the pancreas. Consumption of alcohol in any quantity can cause cancer. The more alcohol is consumed, the higher the cancer risk. Alcoholic beverages were classified as a Group 1 carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) in 1988. 3.6% of all cancer cases and 3.5% of cancer deaths worldwide are attributable to consumption of alcohol (more specifically, acetaldehyde, a derivative of ethanol). 740,000 cases of cancer in 2020 or 4.1% of new cancer cases were attributed to alcohol. Alcohol is thought to cause cancer through three main mechanisms: # DNA methylation # Oxidative stress # Hormonal alteration as well as secondary mechanisms of liver cirrhosis, microbiome dysbiosis, reduced immune system function, retinoid metabolism, increased levels of inflammation, 1-Carbon metabolism and disruption of fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abstainer
Abstentionism is standing for election to a deliberative assembly while refusing to take up any seats won or otherwise participate in the assembly's business. Abstentionism differs from an election boycott in that abstentionists participate in the election itself. Abstentionism has been used by Irish republican political movements in the United Kingdom and Ireland since the early 19th century. It was also used by Hungarian and Czech nationalists in the Austrian Imperial Council in the 1860s. In Hungary When suppressing the Hungarian Revolution of 1848, the Austrian Empire abolished the Diet of Hungary. Austria's 1861 February Patent reserved places for Hungary in the indirectly-elected Imperial Council, but the Hungarians did not send representatives, arguing the council was usurping authority properly belonging to the Diet. Emulating the Hungarians, the Czech delegates for Bohemia withdrew in 1863, and those from Moravia in 1864. Hungarian demands were met by the Compromise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Paradox
The French paradox is an apparently paradoxical epidemiological observation that French people have a relatively low incidence of coronary heart disease (CHD), while having a diet relatively rich in saturated fats, in apparent contradiction to the widely held belief that the high consumption of such fats is a risk factor for CHD. The paradox is that if the thesis linking saturated fats to CHD is valid, the French ought to have a higher rate of CHD than comparable countries where the per capita consumption of such fats is lower. It has also been suggested that the French paradox is an illusion, created in part by differences in the way that French authorities collect health statistics, as compared to other countries, and in part by the long-term effects, in the coronary health of French citizens, of changes in dietary patterns which were adopted years earlier. Identifying and quantifying the French paradox In 1991, Serge Renaud, a scientist from Bordeaux University, Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-term Effects Of Alcohol Consumption
The long-term heavy consumption of alcohol (alcohol use disorder) can cause severe detrimental effects. Health effects associated with alcohol intake in large amounts include an increased risk of developing an alcohol use disorder, malnutrition, chronic pancreatitis, erectile dysfunction, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, gastritis, stomach ulcers, alcoholic liver disease, certain types of dementia, and several types of cancer. In addition, damage to the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system (e.g., painful peripheral neuropathy) can occur from chronic heavy alcohol consumption. There is also an increased risk for accidental injuries, for example, those sustained in traffic accidents and falls. Studies show that individuals with heavy substance use have a much higher risk of having other disorders. A cross-sectional observational study found evidence that people who used substances had the highest risk for five of the disorders studied. However, even light and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johns Hopkins School Of Medicine
The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine (JHUSOM) is the medical school of Johns Hopkins University, a private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1893, the School of Medicine shares a campus with the Johns Hopkins Hospital and Johns Hopkins Children's Center, established in 1889. It has consistently ranked among the top medical schools in the United States in terms of the number/amount of research grants/funding awarded by the National Institutes of Health, among other measures. History The founding physicians (the "Four Doctors") of the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine included pathologist William Henry Welch (1850–1934), the first dean of the school and a mentor to generations of research scientists; a Canadian, internist Sir William Osler (1849–1919), regarded as the ''Father of Modern Medicine'', having been perhaps the most influential physician of the late 19th and early 20th centuries as author of '' The Principles and Practice of Medicine'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, abnormal heart rhythms, congenital heart disease, valvular heart disease, carditis, aortic aneurysms, peripheral artery disease, thromboembolic disease, and venous thrombosis. The underlying mechanisms vary depending on the disease. It is estimated that dietary risk factors are associated with 53% of CVD deaths. Coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease involve atherosclerosis. This may be caused by high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes mellitus, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor sleep, among other things. High blood pressure is estimated to account for appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |