|
Alchemilla Erythropoda
''Alchemilla erythropoda'', the dwarf lady's mantle, is a species of flowering herbaceous perennial plant in the family Rosaceae, native to Eastern Europe. It forms a clump of hairy, palmate leaves up to high, with sprays of green-yellow flowers in early summer. The leaves of this and its relative '' A. mollis'' are noted for being highly water-repellent. It is smaller than ''A. mollis'', however, and its leaves may develop a reddish tinge if grown in full sun. This plant is valued as groundcover in cultivation in temperate regions. It tolerates a wide range of soil conditions, but is prone to self-seeding. It has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit. It grows best in full sun to partial sun conditions, and is relatively pest- and disease-free. In the US, it's suitable for hardiness zones A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Vasilievich Juzepczuk
Sergius is a male given name of Ancient Roman origin after the name of the Latin ''gens'' Sergia or Sergii of regal and republican ages. It is a common Christian name, in honor of Saint Sergius, or in Russia, of Saint Sergius of Radonezh, and has been the name of four popes. It has given rise to numerous variants, present today mainly in the Romance (Serge, Sergio, Sergi) and Slavic languages (Serhii, Sergey, Serguei). It is not common in English, although the Anglo-French name Sergeant is possibly related to it. Etymology The name originates from the Roman ''nomen'' (patrician family name) ''Sergius'', after the name of the Roman ''gens'' of Latin origins Sergia or Sergii from Alba Longa, Old Latium, counted by Theodor Mommsen as one of the oldest Roman families, one of the original 100 ''gentes originarie''. It has been speculated to derive from a more ancient Etruscan name but the etymology of the nomen Sergius is problematic. Chase hesitantly suggests a connection with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lotus Effect
The lotus effect refers to self-cleaning properties that are a result of ultrahydrophobicity as exhibited by the leaves of ''Nelumbo'', the lotus flower. Dirt particles are picked up by water droplets due to the micro- and nanoscopic architecture on the surface, which minimizes the droplet's adhesion to that surface. Ultrahydrophobicity and self-cleaning properties are also found in other plants, such as ''Tropaeolum'' (nasturtium), ''Opuntia'' (prickly pear), ''Alchemilla'', cane, and also on the wings of certain insects. The phenomenon of ultrahydrophobicity was first studied by Dettre and Johnson in 1964 using rough hydrophobic surfaces. Their work developed a theoretical model based on experiments with glass beads coated with paraffin or Polytetrafluoroethylene, PTFE fluorotelomer, telomer. The self-cleaning property of ultrahydrophobic micro-nanotechnology, nanostructured surfaces was studied by Wilhelm Barthlott and Ehler in 1977, who described such self-cleaning and ultr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
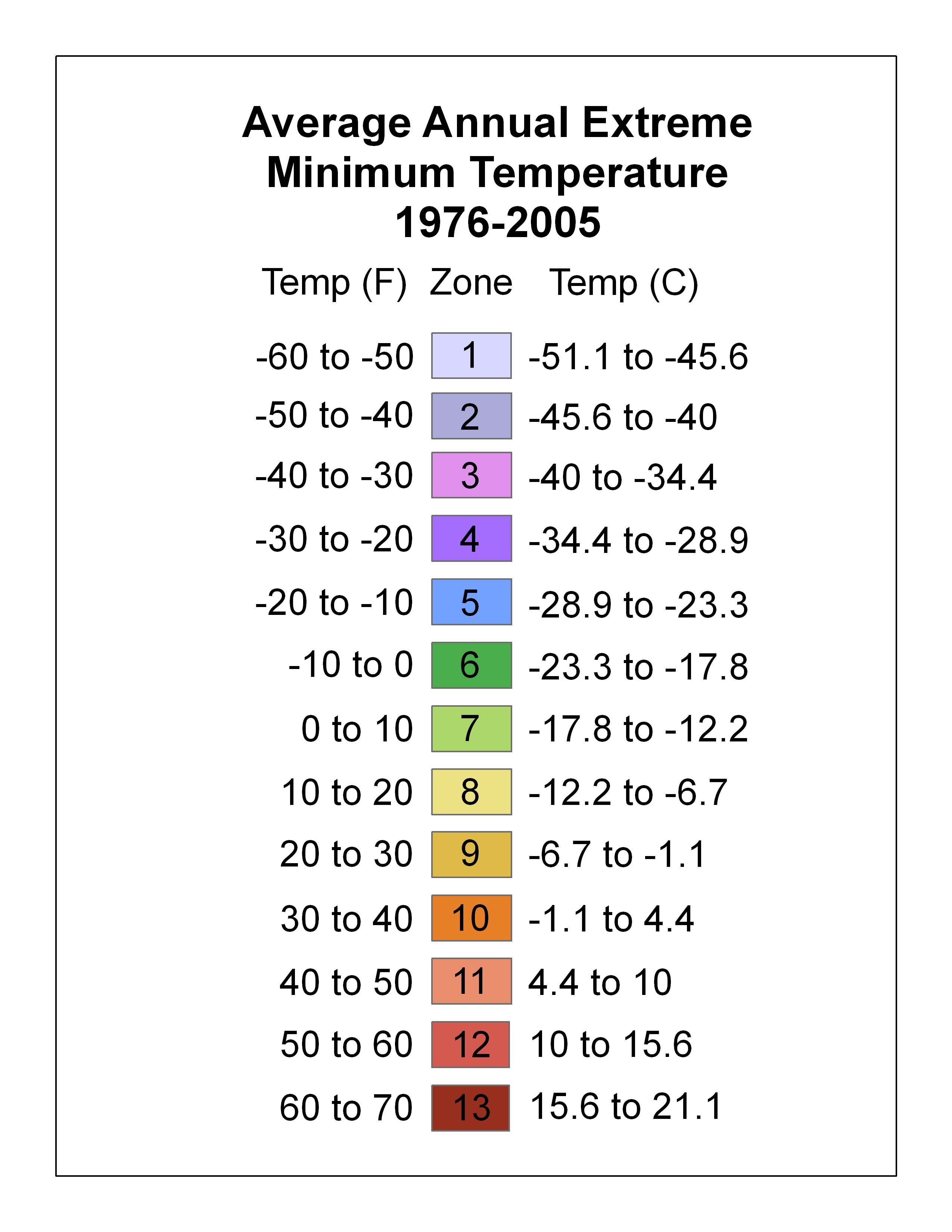
Hardiness Zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most widely used system, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as a rough guide for landscaping and gardening, defines 13 zones by long-term average annual extreme minimum temperatures. It has been adapted by and to other countries (such as Canada) in various forms. Unless otherwise specified, in American contexts "hardiness zone" or simply "zone" usually refers to the USDA scale. For example, a plant may be described as "hardy to zone 10": this means that the plant can withstand a minimum temperature of 30 °F (−1.1 °C) to 40 °F (4.4 °C). Other hardiness rating schemes have been developed as well, such as the UK Royal Horticultural Society and US Sunset Western Garden Book systems. A heat zone (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Award Of Garden Merit
The Award of Garden Merit (AGM) is a long-established annual award for plants by the British Royal Horticultural Society (RHS). It is based on assessment of the plants' performance under UK growing conditions. History The Award of Garden Merit is a mark of quality awarded, since 1922, to garden plants (including trees, vegetables and decorative plants) by the United Kingdom, Royal Horticultural Society (RHS). Awards are made annually after plant trials intended to judge the plants' performance under UK growing conditions. Trials may last for one or more years, depending on the type of plant being analyzed, and may be performed at Royal Horticulture Society Garden in Wisley and other gardens or after observation of plants in specialist collections. Trial reports are made available as booklets and on the website. Awards are reviewed annually in case plants have become unavailable horticulturally, or have been superseded by better cultivars. Similar awards The award should not be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Horticultural Society
The Royal Horticultural Society (RHS), founded in 1804 as the Horticultural Society of London, is the UK's leading gardening charity. The RHS promotes horticulture through its five gardens at Wisley (Surrey), Hyde Hall (Essex), Harlow Carr (North Yorkshire), Rosemoor (Devon) and Bridgewater (Greater Manchester); flower shows including the Chelsea Flower Show, Hampton Court Palace Flower Show, Tatton Park Flower Show and Cardiff Flower Show; community gardening schemes; Britain in Bloom and a vast educational programme. It also supports training for professional and amateur gardeners. the president was Keith Weed and the director general was Sue Biggs CBE. History Founders The creation of a British horticultural society was suggested by John Wedgwood (son of Josiah Wedgwood) in 1800. His aims were fairly modest: he wanted to hold regular meetings, allowing the society's members the opportunity to present papers on their horticultural activities and discoveries, to enc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosperm plants. Seeds are the product of the ripened ovule, after the embryo sac is fertilized by sperm from pollen, forming a zygote. The embryo within a seed develops from the zygote, and grows within the mother plant to a certain size before growth is halted. The seed coat arises from the integuments of the ovule. Seeds have been an important development in the reproduction and success of vegetable gymnosperm and angiosperm plants, relative to more primitive plants such as ferns, mosses and liverworts, which do not have seeds and use water-dependent means to propagate themselves. Seed plants now dominate biological niches on land, from forests to grasslands both in hot and cold climates. The term "seed" also has a general me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperateness
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout the year and more distinct seasonal changes compared to tropical climates, where such variations are often small and usually only have precipitation changes. In temperate climates, not only do latitudinal positions influence temperature changes, but sea currents, prevailing wind direction, continentality (how large a landmass is) and altitude also shape temperate climates. The Köppen climate classification defines a climate as "temperate" C, when the mean temperature is above but below in the coldest month to account for the persistency of frost. However, other climate classifications set the minimum at . Zones and climates The north temperate zone extends from the Tropic of Cancer (approximately 23.5° north latitude) to the Arctic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groundcover
Groundcover or ground cover is any plant that grows over an area of ground. Groundcover provides protection of the topsoil from erosion and drought. In an ecosystem, the ground cover forms the layer of vegetation below the shrub layer known as the herbaceous layer. The most widespread ground covers are grasses of various types. In ecology, groundcover is a difficult subject to address because it is known by several different names and is classified in several different ways. The term groundcover could also be referring to “the herbaceous layer,” “regenerative layer", “ground flora” or even "step over." In agriculture, ground cover refers to anything that lies on top of the soil and protects it from erosion and inhibits weeds. It can be anything from a low layer of grasses to a plastic material. The term ''ground cover'' can also specifically refer to landscaping fabric which is like a breathable tarp that allows water and gas exchange. In gardening jargon, however, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alchemilla Mollis
''Alchemilla mollis'', the garden lady's-mantle or lady's-mantle, is a species of flowering plant in the family Rosaceae. This herbaceous perennial plant is native to southern Europe and grown throughout the world as an ornamental garden plant. It grows tall, with leaves that are palmately veined, with a scalloped and serrated margin. The stipules are noteworthy in that they are fused together and leaf like. The chartreuse yellow flowers are held in dense clusters above the foliage. ''A. mollis'' has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit. The plant self-seeds freely and can become invasive. According to some accounts, lady's mantle has been used for centuries as a herbal remedy. According to other authorities, however, it has never been used medicinally, but has been confused with two species that have a history of medicinal use: '' A. alpina'' (Alpine lady's mantle) and ''A. xanthochlora''. The plant is often grown as groundcover, and is val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flower
A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants (plants of the division Angiospermae). The biological function of a flower is to facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs. Flowers may facilitate outcrossing (fusion of sperm and eggs from different individuals in a population) resulting from cross-pollination or allow selfing (fusion of sperm and egg from the same flower) when self-pollination occurs. There are two types of pollination: self-pollination and cross-pollination. Self-pollination occurs when the pollen from the anther is deposited on the stigma of the same flower, or another flower on the same plant. Cross-pollination is when pollen is transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on a different individual of the same species. Self-pollination happens in flowers where the stamen and carpel mature at the same time, and are positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |