|
Alberta Highway 855
Alberta Provincial Highway No. 855 is a highway in the province of Alberta, Canada. It runs south-north from Highway 9 west of Hanna to Highway 55 and Highway 63 in Atmore. It provides access to rural areas, and is gravel at both its south and north ends. At it is the longest 500-986 series highway in Alberta. It is also known as Lougheed Avenue in Heisler, 45 Street in Daysland, 54 Street in Holden, Sawchuk Street in Mundare, and 50 Street in Andrew and Smoky Lake Smoky Lake is a town in central Alberta, Canada. It is located northeast of Edmonton at the junction of Highway 28 and Highway 855. It lies between the North Saskatchewan River, Smoky Creek and White Earth Creek, in a mainly agricultural area. .... Major intersections Starting from the south end of Highway 855: References 855 {{Alberta-road-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta Transportation
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Territories (NWT) to the north, and the U.S. state of Montana to the south. It is one of the only two landlocked provinces in Canada (Saskatchewan being the other). The eastern part of the province is occupied by the Great Plains, while the western part borders the Rocky Mountains. The province has a predominantly continental climate but experiences quick temperature changes due to air aridity. Seasonal temperature swings are less pronounced in western Alberta due to occasional Chinook winds. Alberta is the fourth largest province by area at , and the fourth most populous, being home to 4,262,635 people. Alberta's capital is Edmonton, while Calgary is its largest city. The two are Alberta's largest census metropolitan areas. More than half of Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoky Lake, Alberta
Smoky Lake is a town in central Alberta, Canada. It is located northeast of Edmonton at the junction of Highway 28 and Highway 855. It lies between the North Saskatchewan River, Smoky Creek and White Earth Creek, in a mainly agricultural area. The provincial historic site of Victoria Settlement is nearby. Long Lake Provincial Park is located north of the town. The Woods Cree, a First Nations people, named "Smoking Lake" for the smoke from ceremonies performed on the shore; the name Smoky Lake may also be based in the mist that rose from the lake in great quantities at sundown. One of its churches, the St. Onuphrius Ukrainian-Catholic, built in 1907, has been moved to the Canadian Museum of History in Gatineau, Quebec Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ....Borys G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Saskatchewan River
The North Saskatchewan River is a glacier-fed river that flows from the Canadian Rockies continental divide east to central Saskatchewan, where it joins with the South Saskatchewan River to make up the Saskatchewan River. Its water flows eventually into the Hudson Bay. The Saskatchewan River system is the largest shared between the Canadian provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan. Its watershed includes most of southern and central Alberta and Saskatchewan. Course The North Saskatchewan River has a length of , and a drainage area of . At its end point at Saskatchewan River Forks it has a mean discharge of . The yearly discharge at the Alberta–Saskatchewan border is more than . The river begins above at the toe of the Saskatchewan Glacier in the Columbia Icefield, and flows southeast through Banff National Park alongside the Icefields Parkway. At the junction of the David Thompson Highway (Highway 11), it initially turns northeast for before switching to a more direct easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta Highway 15
Alberta Provincial Highway No. 15, commonly referred to as Highway 15 or Manning Drive, is a highway in the Edmonton Region of Alberta, connecting northeast Edmonton to the City of Fort Saskatchewan and communities within Lamont County. It serves as an alternative to Highway 16 that bypasses Elk Island National Park. The highway follows the route of a railway line completed in 1905 by the Canadian Northern Railway. In Edmonton, the most southerly portion of the route is named Fort Road, followed by Manning Drive to the north, a developing freeway. Highway 15 is designated as a core route of Canada's National Highway System, between Highway 16 and the intersection with Highway 28A within Edmonton and is part of the Edmonton-Fort McMurray corridor. Route description The highway begins at the intersection of 50 Street and Highway 16 (Yellowhead Trail) in Edmonton. It proceeds north along 50 Street to Manning Drive, where it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elk Island National Park
Elk Island National Park is a national park in Alberta, Canada, that played an important part in the conservation of the Plains bison. The park is administered by the Parks Canada Agency. This "island of conservation" is east of Edmonton, along the Yellowhead Highway, which goes through the park. It is Canada's eighth smallest in area but largest fully enclosed national park, with an area of . The park is representative of the northern prairies plateau ecosystem and as such, the knob and kettle landscape is a mix of native fescue grassland that has been converted to forage land dominated by non-native grasses, aspen parkland and boreal forest. As well, Elk Island plays host to both the largest and the smallest terrestrial mammals in North America, the wood bison and pygmy shrew respectively. History Elk Island National Park is situated in the Beaverhills area, which with its aspen thickets and easy access to water, has provided shelter for wintering herds of elk, bison a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellowhead Blank
Yellowhead or Yellow Head may refer to: Places ;In Canada *Yellowhead Highway in Western Canada **Yellowhead Trail, Edmonton, Alberta *Yellowhead County, Alberta *Yellowhead (electoral district), Alberta *Grande Yellowhead Public School Division No. 77, Alberta *Rural Municipality of Yellowhead, Manitoba *Tête Jaune Cache, British Columbia * West Yellowhead (electoral district), Alberta *Yellowhead Centre, Neepawa, Manitoba * Yellowhead Lake, British Columbia *Yellowhead Mountain, Alberta and British Columbia *Yellowhead Pass mountain pass and National Historic Site, Alberta and British Columbia * Yellowhead Power Station, natural gas fired electrical station in Saskatchewan, Canada ;In the United States *Yellow Head, Maine, a village in Lincoln County, Maine *Yellowhead Township, Kankakee County, Illinois People * Ozaawindib, a 19th-century Ojibwa warrior * Ozaawindib (Chippewa chief), a 19th-century Ojibwa chief for the Prairie Rice Lake Band of Lake Superior Chippewa Indian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle River
Battle River is a river in central Alberta and western Saskatchewan. It is a major tributary of the North Saskatchewan River. The Battle River flows for and has a total drainage area of . The mean discharge is 10 m³/s at its mouth. History The river did not gain its current name until relatively recently. When Anthony Henday passed through the region in the 1750s, he did not mention a river with this name. But by 1793 Peter Fidler mentions arriving at the "Battle or Fighting River", likely so named because of the beginning of a period of rivalry between the Iron Confederacy (Cree and Assiniboine) and the Blackfoot Confederacy. Course The headwaters of Battle River is Battle Lake in west-central Alberta, east of Winfield. The river meanders through Alberta eastward into Saskatchewan, where it discharges into the North Saskatchewan River at Battleford. Over its course, the river flows through Ponoka and by Hardisty and Fabyan within Alberta. Big Knife Provincial Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Knife Provincial Park
Big Knife Provincial Park is a small provincial park in central Alberta, Canada. It was established in 1962 on the Battle River, at the confluence with Big Knife Creek, and is located between the villages of Donalda and Forestburg, 10 km south of Highway 53, 88 km from the city of Camrose. According to tradition, Big Knife Creek's name commemorates a battle between two Aboriginal Canadians, namely Big Man and Knife. Activities Many activities in the park are water related and include canoeing, kayaking, swimming, fishing and power boating. Birdwatching and camping at the ''Big Knife Campground'' are also popular. The park is open during the summer (from May to September), with only limited access during the winter months. See also *List of provincial parks in Alberta *List of Canadian provincial parks This is a list of all provincial/territorial parks and other provincial/territorial protected areas in Canada. Alberta Alberta's provincial parks and protected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta Highway 589
The Canadian province of Alberta has provincial highway network of nearly as of 2009, of which were paved. All of Alberta's provincial highways are maintained by Alberta Transportation (AT), a department of the Government of Alberta. The network includes two distinct series of numbered highways: * The 1–216 series (formerly known as primary highways), making up Alberta's core highway network—typically paved and with the highest traffic volume * The 500–986 series, providing more local access, with a higher proportion of gravel surfaces History In 1926, Alberta discontinued its system of marking highways with different colours in favour of a numbering system. By 1928, the year a gravel road stretched from Edmonton to the United States border, Alberta's provincial highway network comprised . Prior to 1973, the expanding highway system comprised one-digit and two-digit highways, with some numbers having letter suffixes (e.g., Highway 1X, Highway 26A). In 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
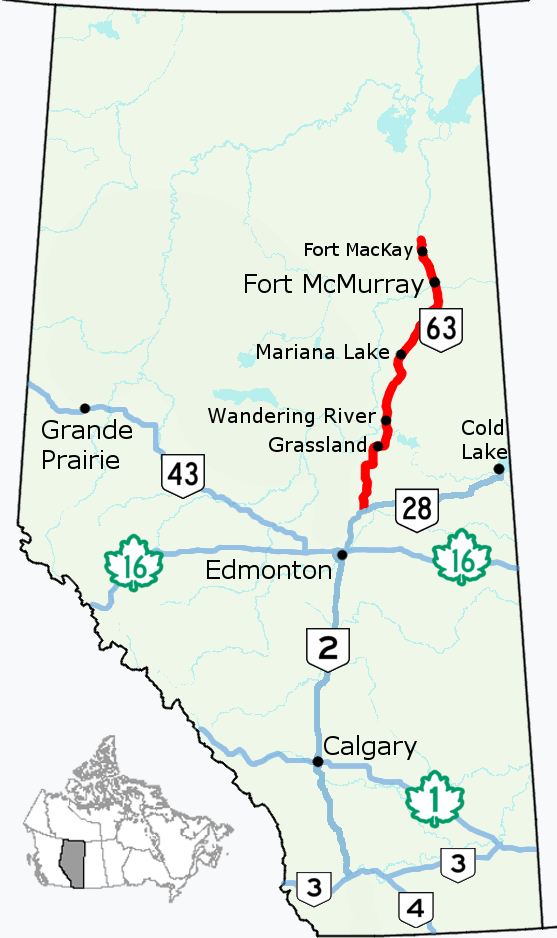
Alberta Highway 63
Alberta Provincial Highway No. 63, commonly referred to as Highway 63, is a highway in northern Alberta, Canada that connects the Athabasca oil sands and Fort McMurray to Edmonton via Highway 28. It begins as a two-lane road near the hamlet of Radway where it splits from Highway 28, running north through aspen parkland and farmland of north central Alberta. North of Boyle, it curves east to pass through the hamlet of Grassland and becomes divided west of Atmore where it again turns north, this time through heavy boreal forest and muskeg, particularly beyond Wandering River. Traffic levels significantly increase as Highway 63 bends through Fort McMurray, crossing the Athabasca River before connecting the city to the Syncrude and Suncor Energy plants further north. It ends approximately beyond a second crossing of the Athabasca River northeast of Fort McKay. The southern segment of Highway 63 from Radway to Atmore was built before the mid- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta Highway 55
Alberta Provincial Highway No. 55, commonly referred to as Highway 55, is a long east–west highway in northeast Alberta, Canada. It extends from the Saskatchewan border in the east through the Cold Lake, Lac La Biche, and Athabasca where it ends at Highway 2. In Saskatchewan, it continues as Saskatchewan Highway 55. The entire length of Highway 55 comprises the easternmost segment of Alberta's portion of the Northern Woods and Water Route (NWWR). West of Athabasca, the Northern Woods and Water Route continues westward along Highway 2 and then Highway 49. History The original designation Highway 55 was a long north-south highway that appeared on maps in the mid-1950s and connected Fort Saskatchewan with Highway 16, just east of Edmonton. In 1973, Alberta established its secondary highway system along mostly existing unimproved roads, with '' Secondary Highway 662'' running between Highway 36 and Cold Lake, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta Highway 9
Alberta Provincial Highway No. 9, commonly referred to as Highway 9, is a highway in south-central Alberta, Canada, which together with Saskatchewan Highway 7 connects Calgary to Saskatoon, Saskatchewan via Drumheller. It is designated as a core route of the National Highway System, forming a portion of an interprovincial corridor. Highway 9 spans approximately from the Trans-Canada Highway ( Highway 1) east of Calgary to Alberta's border with Saskatchewan. Route description Highway 9 begins at its interchange with Highway 1 approximately east of Chestermere and west of Strathmore, and approximately north of Langdon via Highway 797. For its first , Highway 9 generally runs in a north/south direction to Beiseker, where it meets Highways 72 and 806. At Beiseker, Highway 9 runs in an east-west direction for to Drumheller, where it meets Highways 10 and 56. Highways 9 and 56 then run in a north/south concurrence for from Drumhel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |