|
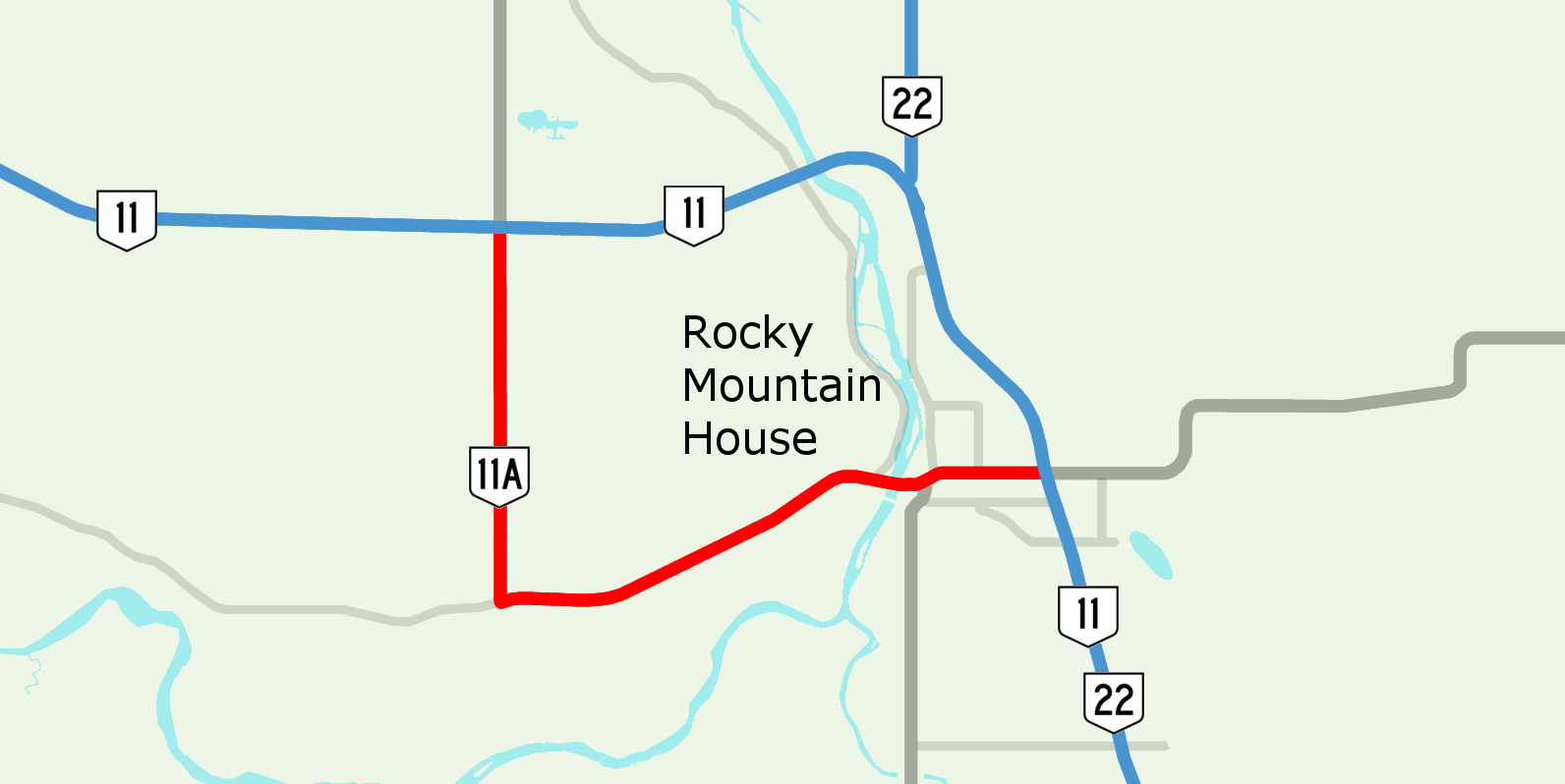
Alberta Highway 11A
Alberta Provincial Highway No. 11A is the designation of two routes that connect to Highway 11 (David Thompson Highway) in Alberta, Canada. The Rocky Mountain House section is referred to as 11A:02 by Alberta Transportation, while 11A:06 runs from Sylvan Lake to Red Deer. Rocky Mountain House Highway 11A:02 begins at the Range Road 80 junction with Highway 11. It follows Range Road 80 south to Township Road 393, where it heads east to Rocky Mountain House, providing an alternate crossing of the North Saskatchewan River than Highway 11. Within Rocky Mountain House it is also known as 52 Avenue, and runs concurrent with Highway 752. Extending north past Highway 11, Highway 11A becomes Highway 756 as an entrance to Crimson Lake Provincial Park, extending east past Highways 11 and 22, Highway 11A becomes Highway 598. Major intersections Starting from the north end of Highway 11A: Sylv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta Transportation
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Territories (NWT) to the north, and the U.S. state of Montana to the south. It is one of the only two landlocked provinces in Canada (Saskatchewan being the other). The eastern part of the province is occupied by the Great Plains, while the western part borders the Rocky Mountains. The province has a predominantly continental climate but experiences quick temperature changes due to air aridity. Seasonal temperature swings are less pronounced in western Alberta due to occasional Chinook winds. Alberta is the fourth largest province by area at , and the fourth most populous, being home to 4,262,635 people. Alberta's capital is Edmonton, while Calgary is its largest city. The two are Alberta's largest census metropolitan areas. More than half of Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta Highway 752
The Canadian province of Alberta has provincial highway network of nearly as of 2009, of which were paved. All of Alberta's provincial highways are maintained by Alberta Transportation (AT), a department of the Government of Alberta. The network includes two distinct series of numbered highways: * The 1–216 series (formerly known as primary highways), making up Alberta's core highway network—typically paved and with the highest traffic volume * The 500–986 series, providing more local access, with a higher proportion of gravel surfaces History In 1926, Alberta discontinued its system of marking highways with different colours in favour of a numbering system. By 1928, the year a gravel road stretched from Edmonton to the United States border, Alberta's provincial highway network comprised . Prior to 1973, the expanding highway system comprised one-digit and two-digit highways, with some numbers having letter suffixes (e.g., Highway 1X, Highway 26A). In 1973 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calgary And Edmonton Trail
The Calgary and Edmonton Trail was a land transport route between Fort Edmonton and Fort Calgary in the Northwest Territories. Prior to European contact, there was already a route through the area that local Indigenous peoples used to travel from the Shortgrass Prairies in the south to the Aspen Parkland in the north and back. After a fur trade post was established at Fort Edmonton, these trails became part of the massive fur-trading transportation network that European companies used to export furs from the interior to the coasts and on to Europe. The northern portion of trail to Fort Edmonton was traveled by David Thompson in 1800. The more modern trail was blazed by John McDougall in 1873 as far as Morley and extended to Calgary two years later. Development of the trail allowed mail service between Calgary and Edmonton in July 1883. Name and namesakes Alberta Highway 2 is now the main route from Edmonton to Calgary. Most of it bears the name " Queen Elizabeth II Highway" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta Highway 781
The Canadian province of Alberta has provincial highway network of nearly as of 2009, of which were paved. All of Alberta's provincial highways are maintained by Alberta Transportation (AT), a department of the Government of Alberta. The network includes two distinct series of numbered highways: * The 1–216 series (formerly known as primary highways), making up Alberta's core highway network—typically paved and with the highest traffic volume * The 500–986 series, providing more local access, with a higher proportion of gravel surfaces History In 1926, Alberta discontinued its system of marking highways with different colours in favour of a numbering system. By 1928, the year a gravel road stretched from Edmonton to the United States border, Alberta's provincial highway network comprised . Prior to 1973, the expanding highway system comprised one-digit and two-digit highways, with some numbers having letter suffixes (e.g., Highway 1X, Highway 26A). In 1973 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Deer County, Alberta
Red Deer County is a municipal district in central Alberta, Canada within Census Division No. 8 and surrounding the City of Red Deer. The neighbouring municipalities of Red Deer County are Clearwater County to the west, Lacombe County to the north, the County of Stettler No. 6 to the east, Kneehill County to the southeast and Mountain View County to the south. It is located approximately midway between Edmonton and Calgary, bisected by the Queen Elizabeth II Highway and bounded on the north and east by the Red Deer River. Geography Communities and localities The following urban municipalities are surrounded by Red Deer County. ;Cities *Red Deer ;Towns *Bowden * Innisfail *Penhold * Sylvan Lake ;Villages *Delburne * Elnora ; Summer villages * Jarvis Bay * Norglenwold The following hamlets are located within Red Deer County. ;Hamlets * Ardley * Benalto * Dickson *Gasoline Alley * Linn Valley * Lousana *Markerville *Springbrook * Spruce View The following localitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Deer River
The Red Deer River is a river in Alberta and a small portion of Saskatchewan, Canada. It is a major tributary of the South Saskatchewan River and is part of the larger Saskatchewan-Nelson system that empties into Hudson Bay. Red Deer River has a total length of and a drainage area of . Its mean discharge is . The river got its name from the translation of ''Was-ka-soo seepee'' which means "elk river" in the Cree language. "Red deer" was an alternative name for elk, referring to a closely related Eurasian species. Communities located along the Red Deer River include Sundre, Red Deer, Drumheller, and Empress, The city of Brooks, as well as Dinosaur Provincial Park, are also located in the Red Deer River Basin. A glacial flood about 18,000 years ago eroded out a portion of this basin and apparently all or most of the scenic badlands bearing the dinosaur and other Cretaceous fossils. History Joseph Tyrrell discovered a huge coal seam here in 1883, besides large dinosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
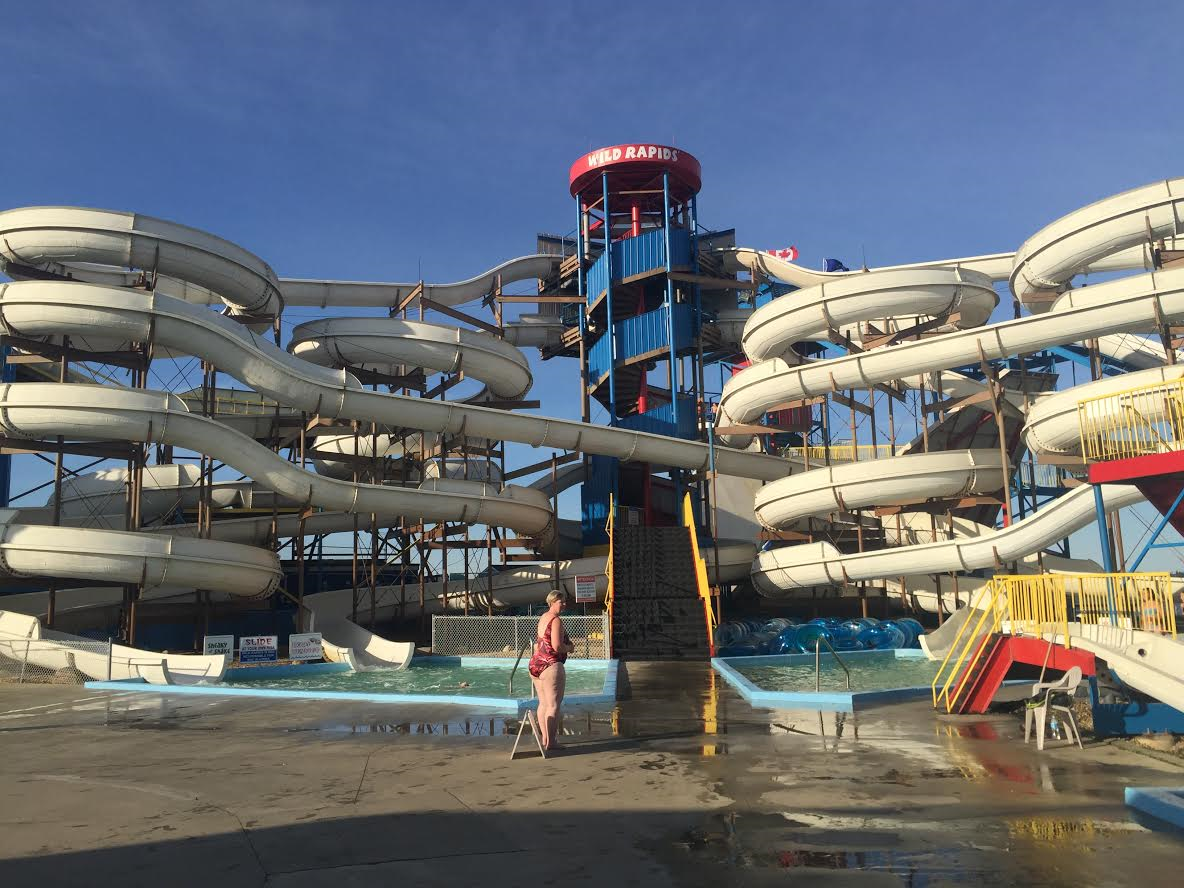
Wild Rapids Waterslides
Wild Rapids Waterslide Park was located on the shores of Sylvan Lake in the resort town of Sylvan Lake, Alberta, Canada. Wild Rapids opened to the public in 1982, and it was Alberta's second-largest water park after the World Waterpark in West Edmonton Mall. Wild Rapids Waterslide was one of five waterslide parks in Alberta, and the last outdoor water park to operate until it closed in 2016. The park contained 12 slides, many small pools, three hot tubs, and a children's water playground. The park closed at the end of the 2016 season, after operating for 34 years. The park was located near Red Deer, between Edmonton and Calgary, along Alberta Highway 11A. Wild Rapids was the largest water park of its kind in western Canada. History Wild Rapids Waterslide was founded in 1982 by Dave Dubeta and Garry Johnson, and opened just in time for its first full summer of operations. Wild Rapids Water Slide was built on the land previously owned by the Johnson Family, known as Sandy Cove Cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benalto, Alberta
Benalto is a hamlet in central Alberta, Canada within Red Deer County. It is located approximately west of the Town of Sylvan Lake. Benalto is also recognized by Statistics Canada as a designated place. Kountry Meadows, a manufactured home community and designated place recognized by Statistics Canada, is immediately adjacent to the Hamlet of Benalto. Although it forms part of the community, the hamlet's boundaries do not include the manufactured home park at this time. Demographics In the 2021 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada, Benalto had a population of 198 living in 65 of its 66 total private dwellings, a change of from its 2016 population of 177. With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2021. As a designated place in the 2016 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada, Benalto had a population of 177 living in 63 of its 66 total private dwellings, a change of from its 2011 population of 175. With a land area of , it ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternate Route
An official alternate route is a special route in the United States that provides an alternate alignment for a highway. They are loop roads and found in many road systems in the United States including the U.S. Highway system and various state and county route systems. Alternate routes were created as a means of connecting a town (or towns) desired to be on a route that had been routed differently to put another important town or city on the route, or, in the case of the U.S. Highway system, as a means to eliminate divided routes. The term "optional route" has also been used. In some cases, an additional business route exists as a third alignment, as with former U.S. Route 71 Alternate, which bypassed Joplin, Missouri. AASHTO defines and specifies that alternate routes of the US Route system should have the following behavior: An "Alternate Route" shall be considered a route which starts at a point where it branches off from the main numbered route, may pass through certain c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta Highway 598
The Canadian province of Alberta has provincial highway network of nearly as of 2009, of which were paved. All of Alberta's provincial highways are maintained by Alberta Transportation (AT), a department of the Government of Alberta. The network includes two distinct series of numbered highways: * The 1–216 series (formerly known as primary highways), making up Alberta's core highway network—typically paved and with the highest traffic volume * The 500–986 series, providing more local access, with a higher proportion of gravel surfaces History In 1926, Alberta discontinued its system of marking highways with different colours in favour of a numbering system. By 1928, the year a gravel road stretched from Edmonton to the United States border, Alberta's provincial highway network comprised . Prior to 1973, the expanding highway system comprised one-digit and two-digit highways, with some numbers having letter suffixes (e.g., Highway 1X, Highway 26A). In 1973 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta Highway 756
The Canadian province of Alberta has provincial highway network of nearly as of 2009, of which were paved. All of Alberta's provincial highways are maintained by Alberta Transportation (AT), a department of the Government of Alberta. The network includes two distinct series of numbered highways: * The 1–216 series (formerly known as primary highways), making up Alberta's core highway network—typically paved and with the highest traffic volume * The 500–986 series, providing more local access, with a higher proportion of gravel surfaces History In 1926, Alberta discontinued its system of marking highways with different colours in favour of a numbering system. By 1928, the year a gravel road stretched from Edmonton to the United States border, Alberta's provincial highway network comprised . Prior to 1973, the expanding highway system comprised one-digit and two-digit highways, with some numbers having letter suffixes (e.g., Highway 1X, Highway 26A). In 1973 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Saskatchewan River
The North Saskatchewan River is a glacier-fed river that flows from the Canadian Rockies continental divide east to central Saskatchewan, where it joins with the South Saskatchewan River to make up the Saskatchewan River. Its water flows eventually into the Hudson Bay. The Saskatchewan River system is the largest shared between the Canadian provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan. Its watershed includes most of southern and central Alberta and Saskatchewan. Course The North Saskatchewan River has a length of , and a drainage area of . At its end point at Saskatchewan River Forks it has a mean discharge of . The yearly discharge at the Alberta–Saskatchewan border is more than . The river begins above at the toe of the Saskatchewan Glacier in the Columbia Icefield, and flows southeast through Banff National Park alongside the Icefields Parkway. At the junction of the David Thompson Highway (Highway 11), it initially turns northeast for before switching to a more direct easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |