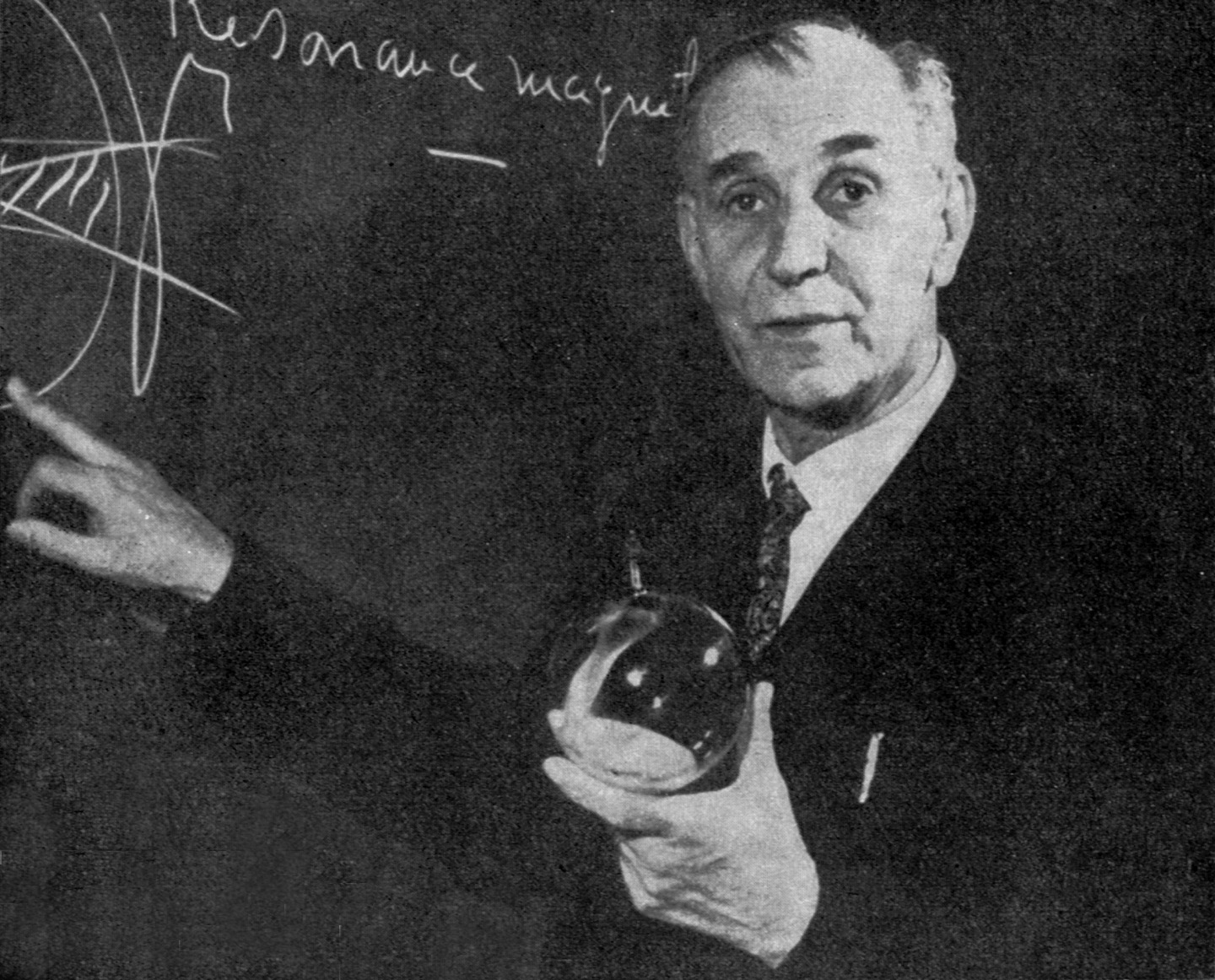|
Albert Fert
Albert Fert (; born 7 March 1938) is a French physicist and one of the discoverers of giant magnetoresistance which brought about a breakthrough in gigabyte hard disks. Currently, he is an emeritus professor at Paris-Saclay University in Orsay, scientific director of a joint laboratory (''Unité mixte de recherche'') between the Centre national de la recherche scientifique (National Scientific Research Centre) and Thales Group, and adjunct professor at Michigan State University. He was awarded the 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics together with Peter Grünberg. Biography In 1962 Albert Fert graduated from the École Normale Supérieure in Paris, where he attended courses by the physicists Alfred Kastler and Jacques Friedel. (As an undergraduate he had strong interests in photography and cinema, and was a great admirer of the work of Ingmar Bergman).) After the École Normale Supérieure, Fert attended the University of Grenoble and in 1963 received his Ph.D. (''doctorat de troisiè ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcassonne, Aude
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department. Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the Aude between historic trade routes, linking the Atlantic to the Mediterranean Sea and the Massif Central to the Pyrénées. Its strategic importance was quickly recognized by the Romans, who occupied its hilltop until the demise of the Western Roman Empire. In the fifth century, it was taken over by the Visigoths, who founded the city. Within three centuries, it briefly came under Islamic rule. Its strategic location led successive rulers to expand its fortifications until the Treaty of the Pyrenees in 1659. Its citadel, known as the Cité de Carcassonne, is a medieval fortress dating back to the Gallo-Roman period and restored by the theorist and architect Eugène Viollet-le-Duc in 1853. It was added to the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris-Saclay University
Paris-Saclay University (french: Université Paris-Saclay) is a public research university based in Paris, France. It is one of the 13 prestigious universities that emerged from the division of the University of Paris, also known as the Sorbonne. Paris-Saclay is ranked 1st in France and 13th in the world in the Academic Ranking of World Universities (ARWU) ranking. In subject rankings, it is placed 1st in the world for Mathematics and 9th in the world for Physics, as well as being in the top 15 for Medicine and Agriculture. It is part of the Paris-Saclay project, which is a research-intensive academic campus, and is the main center for training and research within the technology cluster of Paris-Saclay. The University integrates several leading ''grandes écoles'', faculties, colleges and research centers that are part of the world's top research organizations in various fields. Paris-Saclay has achieved particular renown in mathematics. As of 2021, 11 Fields Medalists have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Université Paris-Sud
Paris-Sud University (French: ''Université Paris-Sud''), also known as University of Paris — XI (or as Université d'Orsay before 1971), was a French research university distributed among several campuses in the southern suburbs of Paris, including Orsay, Cachan, Châtenay-Malabry, Sceaux, and Kremlin-Bicêtre campuses. The main campus was located in Orsay. Starting from 2020, University Paris Sud has been replaced by the University of Paris-Saclay in The League of European Research Universities (LERU). Paris-Sud was one of the largest and most prestigious universities in France, particularly in science and mathematics. The university was ranked 1st in France, 9th in Europe and 37th worldwide by 2019 Academic Ranking of World Universities (ARWU) in particular it was ranked as 1st in Europe for physics and 2nd in Europe for mathematics. Five Fields Medalists and two Nobel Prize Winners have been affiliated to the university. On 16 January 2019, Alain Sarfati was electe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Paris XI
Paris-Sud University (French: ''Université Paris-Sud''), also known as University of Paris — XI (or as Université d'Orsay before 1971), was a French research university distributed among several campuses in the southern suburbs of Paris, including Orsay, Cachan, Châtenay-Malabry, Sceaux, and Kremlin-Bicêtre campuses. The main campus was located in Orsay. Starting from 2020, University Paris Sud has been replaced by the University of Paris-Saclay in The League of European Research Universities (LERU). Paris-Sud was one of the largest and most prestigious universities in France, particularly in science and mathematics. The university was ranked 1st in France, 9th in Europe and 37th worldwide by 2019 Academic Ranking of World Universities (ARWU) in particular it was ranked as 1st in Europe for physics and 2nd in Europe for mathematics. Five Fields Medalists and two Nobel Prize Winners have been affiliated to the university. On 16 January 2019, Alain Sarfati was elected P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris-Saclay Faculty Of Sciences
The Paris-Saclay Faculty of Sciences or Orsay Faculty of Sciences, in French : ''Faculté des sciences d'Orsay'', is the mathematics and physics school within Paris-Saclay University, founded in 1956. It offers undergraduate and graduate degrees in mathematics, physics and chemistry (though its undergraduates are officially enrolled in Paris-Saclay Undergraduate School). Previously the Paris-Sud Faculty of Sciences, the School assumed its current structure in 2019. Christine Paulin-Mohring has been the School's dean since 2016. Recent investments as part of the Paris-Saclay cluster have enlarged the School's faculty and upgraded its facilities. In July 2020, Paris-Saclay was ranked first worldwide for Mathematics by ''Academic Ranking of World Universities (ARWU)'' and 9th worldwide for Physics (1st in Europe). The Faculty has produced numerous research discoveries and many distinguished alumni and professors. History Established in 1956, the Paris-Saclay Faculty of Scienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Grenoble
The Université Grenoble Alpes (UGA, French: meaning "''Grenoble Alps University''") is a public research university in Grenoble, France. Founded in 1339, it is the third largest university in France with about 60,000 students and over 3,000 researchers. Established as the University of Grenoble by Humbert II of Viennois, it split in 1970 following the wide-spread civil unrest of May 1968. Three of the University of Grenoble's successors—Joseph Fourier University, Pierre Mendès-France University, and Stendhal University—merged in 2016 to restore the original institution under the name Université Grenoble Alpes. In 2020, the Grenoble Institute of Technology, the Grenoble Institute of Political Studies, and the Grenoble School of Architecture also merged with the original university. The university is organized around two closely located urban campuses: Domaine Universitaire, which straddles Saint-Martin-d'Hères and Gières, and Campus GIANT in Grenoble. UGA also owns and op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingmar Bergman
Ernst Ingmar Bergman (14 July 1918 – 30 July 2007) was a Swedish film director, screenwriter, Film producer, producer and playwright. Widely considered one of the greatest and most influential filmmakers of all time, his films are known as "profoundly personal meditations into the myriad struggles facing the psyche and the soul." Some of his most acclaimed work includes ''The Seventh Seal'' (1957), ''Wild Strawberries (film), Wild Strawberries'' (1957), ''The Virgin Spring'' (1960), ''Through a Glass Darkly (film), Through a Glass Darkly'' (1961), ''Persona (1966 film), Persona'' (1966), and ''Fanny and Alexander'' (1982). Bergman directed more than 60 films and documentaries for cinematic release and for television screenings, most of which he also wrote. His theatrical career continued in parallel and included periods as Leading Director of the Royal Dramatic Theatre in Stockholm and of the Residenztheater in Munich. He directed more than 170 plays. He forged a creativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Friedel
Jacques Friedel ForMemRS (; 11 February 1921 – 27 August 2014) was a French physicist and material scientist. Education Friedel attended the Cours Hattemer, a private school. He studied at the École Polytechnique from 1944 to 1946, and the École nationale supérieure des mines de Paris from 1946 to 1948. He graduated from the University of Paris with a Licence ès sciences degree in 1948, then studied at the Metallurgy Laboratory of the School of Mines with Charles Crussard. He graduated from the University of Bristol with a PhD in 1952, where he studied with Nevill Francis Mott, and a Doctorat d'Etat in Paris in 1954. Career He was assistant professor at Paris-Sorbonne University in 1956, then full professor of Solid State Physics (from 1959 to 1989) at the University of Paris-Sud where he co-founded the Laboratory of Solid State Physics. He authored more than 200 journal articles. He was the president of the Société française de physique, the European Physical Society ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Kastler
Alfred Kastler (; 3 May 1902 – 7 January 1984) was a French physicist, and Nobel Prize laureate. Biography Kastler was born in Guebwiller (Alsace, German Empire) and later attended the Lycée Bartholdi in Colmar, Alsace, and École Normale Supérieure in Paris in 1921. After his studies, in 1926 he began teaching physics at the Lycée of Mulhouse, and then taught at the University of Bordeaux, where he was a university professor until 1941. Georges Bruhat asked him to come back to the École Normale Supérieure, where he finally obtained a chair in 1952. Collaborating with Jean Brossel, he researched quantum mechanics, the interaction between light and atoms, and spectroscopy. Kastler, working on combination of optical resonance and magnetic resonance, developed the technique of "optical pumping". Those works led to the completion of the theory of lasers and masers. He won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1966 "for the discovery and development of optical methods for studying He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economist Intelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
École Normale Supérieure , a Japanese video-games developer/publisher
{{disambiguation, geo ...
École may refer to: * an elementary school in the French educational stages normally followed by secondary education establishments (collège and lycée) * École (river), a tributary of the Seine flowing in région Île-de-France * École, Savoie, a French commune * École-Valentin, a French commune in the Doubs département * Grandes écoles, higher education establishments in France * The École, a French-American bilingual school in New York City Ecole may refer to: * Ecole Software This is a list of Notability, notable video game companies that have made games for either computers (like PC or Mac), video game consoles, handheld or mobile devices, and includes companies that currently exist as well as now-defunct companies. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Grünberg
Peter Andreas Grünberg (; 18 May 1939 – 7 April 2018) was a German physicist, and Nobel Prize in Physics laureate for his discovery with Albert Fert of giant magnetoresistance which brought about a breakthrough in gigabyte hard disk drives. Life and career Grünberg was born in Pilsen, Bohemia—which at the time was in the German-occupied Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia (now the Czech Republic)—to the Sudeten German family of Anna and Feodor A. Grünberg which first lived in Dysina (Dýšina) to the east of Pilsen. Grünberg was a Catholic. After the war, the family was interned; the parents were brought to a camp. His father, a Russia-born engineer who since 1928 had worked for Škoda, died on 27 November 1945 in Czech imprisonment and is buried in a mass grave in Pilsen which is also inscribed with ''Grünberg Theodor † 27. November 1945''. His mother Anna (who died in 2002 aged 100) had to work in agriculture and stayed with her parents in the Petermann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |