|
Alain Goriely
Alain Goriely FRS is a Belgian mathematician, currently holding the statutory professorship (chair) of mathematical modelling at the University of Oxford, Mathematical Institute. He is director of the Oxford Centre for Industrial Mathematics (OCIAM), of the International Brain and Mechanics Lab (IBMTL) and Professorial Fellow at St Catherine's College, Oxford. At the Mathematical Institute, he was the director of external relations and public engagement, from 2013 until 2022, initiating the Oxford Mathematics series of public lectures. In 2022, he was elected to the Royal Society. Biography Born and raised in Brussels, Alain Goriely obtained his B.Sc. in 1989 and Ph.D. in 1994 from the Université Libre de Bruxelles where he became lecturer in the Mathematics Department. Shortly after, he moved to the University of Arizona to take the positions of Research Associate (1994-1997), Assistant Professor (1998-2002), Associate Professor (2002-2007) and Professor (2007-2010). In Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium-ion Batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also sees significant use for grid-scale energy storage and military and aerospace applications. Compared to other rechargeable battery technologies, Li-ion batteries have high energy densities, low self-discharge, and no memory effect (although a small memory effect reported in LFP cells has been traced to poorly made cells). Chemistry, performance, cost and safety characteristics vary across types of lithium-ion batteries. Most commercial Li-ion cells use intercalation compounds as the active materials. The anode or negative electrode is usually graphite, although silicon-carbon is also being increasingly used. Cells can be manufactured to prioritize either energy or power density. Handheld electronics mostly use lithium polymer batteries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercapacitors
A supercapacitor (SC), also called an ultracapacitor, is a high-capacity capacitor, with a capacitance value much higher than other capacitors but with lower voltage limits. It bridges the gap between electrolytic capacitors and Rechargeable battery, rechargeable batteries. It typically stores 10 to 100 times more specific energy, energy per unit volume or mass than electrolytic capacitors, can accept and deliver charge much faster than batteries, and tolerates many more charge and discharge cycles than Rechargeable battery, rechargeable batteries. Supercapacitors are used in applications requiring many rapid charge/discharge cycles, rather than long-term compact energy storage — in automobiles, buses, trains, cranes and elevators, where they are used for Regenerative brake, regenerative braking, short-term energy storage, or burst-mode power delivery. Smaller units are used as power backup for static random-access memory (SRAM). Unlike ordinary capacitors, supercapacito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
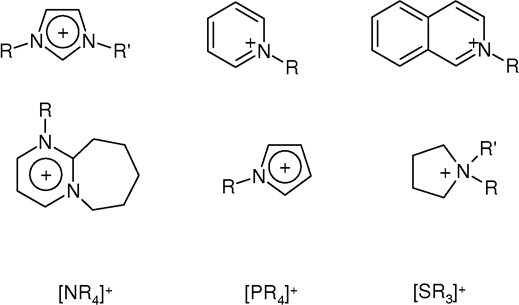
Ionic Liquids
An ionic liquid (IL) is a salt in the liquid state. In some contexts, the term has been restricted to salts whose melting point is below a specific temperature, such as . While ordinary liquids such as water and gasoline are predominantly made of electrically neutral molecules, ionic liquids are largely made of ions. These substances are variously called liquid electrolytes, ionic melts, ionic fluids, fused salts, liquid salts, or ionic glasses. Ionic liquids have many potential applications. They are powerful solvents and can be used as electrolytes. Salts that are liquid at near-ambient temperature are important for electric battery applications, and have been considered as sealants due to their very low vapor pressure. Any salt that melts without decomposing or vaporizing usually yields an ionic liquid. Sodium chloride (NaCl), for example, melts at into a liquid that consists largely of sodium cations () and chloride anions (). Conversely, when an ionic liquid is cooled, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tendril Perversion
Tendril perversion is a geometric phenomenon sometimes observed in helical structures in which the direction of the helix transitions between left-handed and right-handed. Such a reversal of chirality is commonly seen in helical plant tendrils and telephone handset cords. The phenomenon was known to Charles Darwin, who wrote in 1865, The term "tendril perversion" was coined by Alain Goriely and Michael Tabor in 1998 based on the word ''perversion'' found in the 19th century science literature. "Perversion" is a transition from one chirality to another and was known to James Clerk Maxwell, who attributed it to topologist J. B. Listing. Tendril perversion can be viewed as an example of spontaneous symmetry breaking, in which the strained structure of the tendril adopts a configuration of minimum energy while preserving zero overall twist. Tendril perversion has been studied both experimentally and theoretically. Gerbode et al. have made experimental studies of the coiling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homoclinic Connection
{{unreferenced, date=December 2010 In dynamical systems, a branch of mathematics, a structure formed from the stable manifold and unstable manifold of a fixed point. Definition for maps Let f:M\to M be a map defined on a manifold M, with a fixed point p. Let W^s(f,p) and W^u(f,p) be the stable manifold and the unstable manifold of the fixed point p, respectively. Let V be a connected invariant manifold such that : V\subseteq W^s(f,p)\cap W^u(f,p) Then V is called a homoclinic connection. Heteroclinic connection It is a similar notion, but it refers to two fixed points, p and q. The condition satisfied by V is replaced with: :V\subseteq W^s(f,p)\cap W^u(f,q) This notion is not symmetric with respect to p and q. Homoclinic and heteroclinic intersections When the invariant manifolds W^s(f,p) and W^u(f,q), possibly with p=q, intersect but there is no homoclinic/heteroclinic connection, a different structure is formed by the two manifolds, sometimes referred to as the homoclini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melnikov Distance
In mathematics, the Melnikov method is a tool to identify the existence of chaos in a class of dynamical systems under periodic perturbation. Introduction The Melnikov method is used in many cases to predict the occurrence of chaotic orbits in non-autonomous smooth nonlinear systems under periodic perturbation. According to the method, it is possible to construct a function called the "Melnikov function" which can be used to predict either regular or chaotic behavior of a dynamical system. Thus, the Melnikov function will be used to determine a measure of distance between stable and unstable manifolds in the Poincaré map. Moreover, when this measure is equal to zero, by the method, those manifolds crossed each other transversally and from that crossing the system will become chaotic. This method appeared in 1890 by H. Poincaré and by V. Melnikov in 1963 and could be called the "Poincaré-Melnikov Method". Moreover, it was described by several textbooks as Guckenheimer & Holme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Newton Institute
The Isaac Newton Institute for Mathematical Sciences is an international research institute for mathematics and its many applications at the University of Cambridge. It is named after one of the university's most illustrious figures, the mathematician and natural philosopher Sir Isaac Newton and occupies one of the buildings in the Cambridge Centre for Mathematical Sciences. History After a national competition run by SERC, the Science and Engineering Research Council (now known as EPSRC Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council), this institute was chosen to be the national research institute for mathematical sciences in the UK. It opened in 1992 with support from St John's College and Trinity College. St. John's provided the land and a purpose-built building, Trinity provided running costs for the first five years and the London Mathematical Society provided other support. Shortly afterwards at the institute, the British mathematician Andrew Wiles announced hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is considered among the most prestigious universities in the world. Stanford was founded in 1885 by Leland and Jane Stanford in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford Jr., who had died of typhoid fever at age 15 the previous year. Leland Stanford was a U.S. senator and former governor of California who made his fortune as a railroad tycoon. The school admitted its first students on October 1, 1891, as a coeducational and non-denominational institution. Stanford University struggled financially after the death of Leland Stanford in 1893 and again after much of the campus was damaged by the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. Following World War II, provost of Stanford Frederick Terman inspired and supported faculty and graduates' entrepreneu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre And Marie Curie University
Pierre and Marie Curie University (french: link=no, Université Pierre-et-Marie-Curie, UPMC), also known as Paris 6, was a public university, public research university in Paris, France, from 1971 to 2017. The university was located on the Jussieu Campus in the Latin Quarter of the 5th arrondissement of Paris, France. UPMC merged with Paris-Sorbonne University into a new combined Sorbonne University. It was ranked as the best university in France in medicine and health sciences by ''Times Higher Education'' in 2018. History Paris VI was one of the inheritors of the faculty of Sciences of the University of Paris, which was divided into several universities in 1970 after the student protests of May 1968 events in France, May 1968. In 1971, the five faculties of the former University of Paris (Paris VI as the Faculty of Sciences) were split and then re-formed into thirteen universities by the Edgar Faure, Faure Law. The campus of Paris VI was built in the 1950s and 1960s, on a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |