|
Al-Nu'man Ibn Humaydah
An-Nu'man ibn Humaydah al-Bariqi (; died 600 CE) was a philosopher in Classical Arab. In addition, he was knight and the leader of the Bariq tribe, located in Bariq of Azd, Yemen and was famous for its glory. Lineage His full name was al-Nu'man b. Humaydah b. al-Harith b. Awf b. Amr b. Sa`d b. Thailbh b. Kinanah al-Bariqi Ibn Bariq Ibn Uday Ibn Haritha Ibn Amr Mazikiee Ibn Aamr bin Haritha Algtarif bin Imru al-Qais Thailb bin Mazen Ibn Al-Azd Ibn Al-Ghoth Ibn Nabit Ibn Malik bin Zaid Ibn Kahlan Ibn Saba'a (Sheba) Ibn Yashjub Ibn Yarab Ibn Qahtan Ibn Hud (Eber Eber ( he, , ʿĒḇer; grc-x-biblical, Ἔβερ, Éber; ar, عٰابِر, ʿĀbir) is an ancestor of the Ishmaelites and the Israelites according to the "Table of Nations" in the Book of Genesis () and the Books of Chronicles (). Lineage ...). * Humaydah b. al-Harith ( ar, حميضة بن الحارث), was his father. * Humaydah b. al-Nu'man b. Humaydah al-Bariqi ( ar, حميضة بن النعمان بن ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the western Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas, Western Europe, Turkey, Indonesia, and Iran. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims (the remainder consisted mostly of Arab Christians), while Arab Muslims are only 20 percent of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
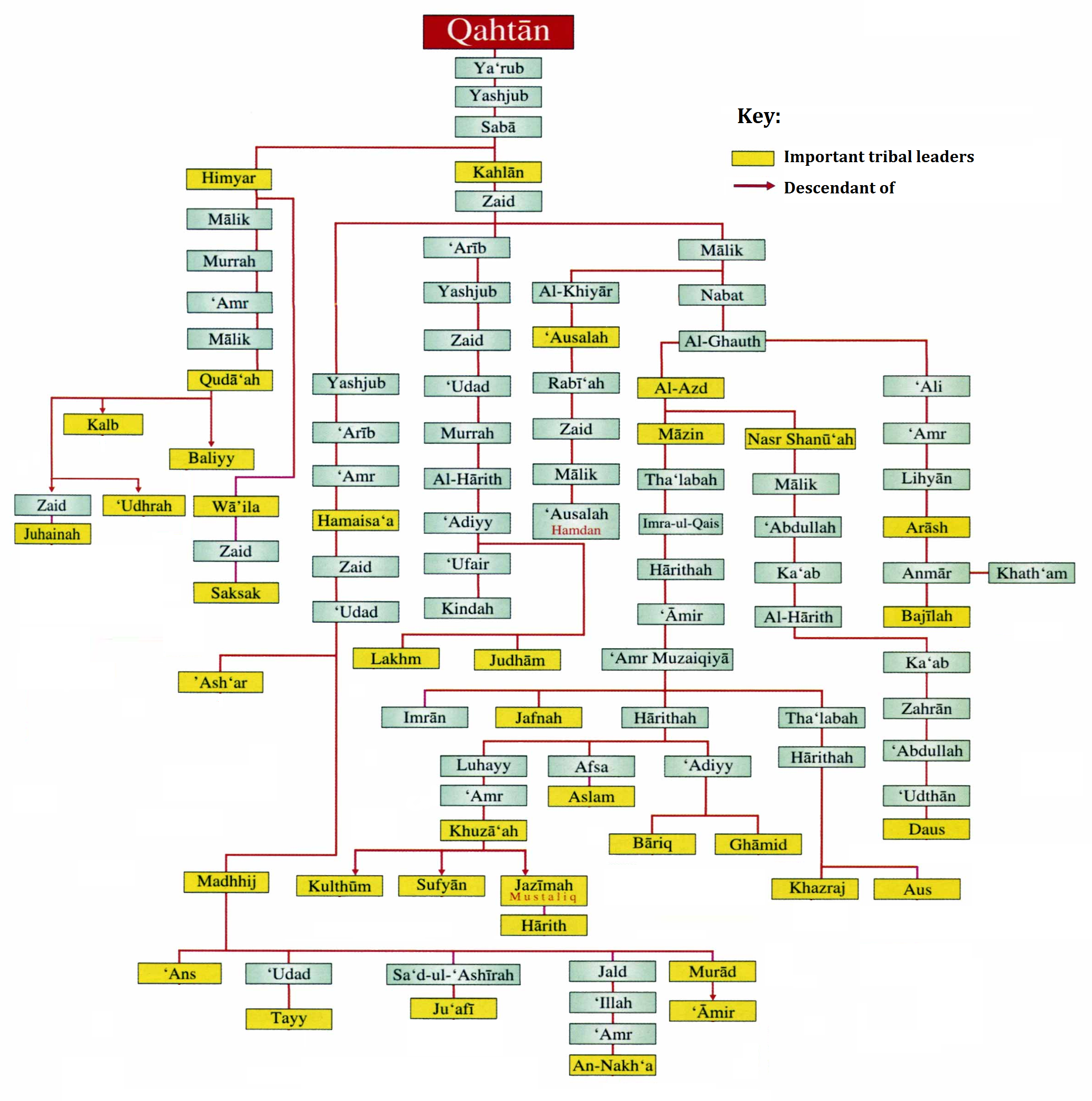
Qahtan
The terms Qahtanite and Qahtani ( ar, قَحْطَانِي; transliterated: Qaḥṭānī) refer to Arabs who originate from South Arabia. The term "Qahtan" is mentioned in multiple ancient Arabian inscriptions found in Yemen. Arab traditions believe that they are the original Arabs. Traditional Arab genealogy According to Arab tradition, the Qahtanites are from South Arabia, unlike the Adnanites who are from the north of Arabia descended from Ishmael through Adnan. "The 'arabized or arabizing Arabs', on the contrary, are believed to be the descendants of Ishmael through Adnan, but in this case the genealogy does not match the Biblical line exactly. The label 'arabized' is due to the belief that Ishmael spoke Hebrew until he got to Mecca, where he married a Yemeni woman and learnt Arabic. Both genealogical lines go back to Sem, son of Noah, but only Adnanites can claim Abraham as their ascendant, and the lineage of Mohammed, the Seal of Prophets (khatim al-anbiya'), can therefor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banu Bariq
Bariq (also transliterated as Barik or Bareq, ar, بارق) is a tribe from Bareq in south-west Saudi Arabia. It belongs to the ancient Al-Azd tribe which has many clans linked to it. As far as ancestry goes, Aws, Khazraj, Ghassān and Banu Khuza'a, and others all belong to Al-Azd. They were one of the tribes of Arabia during Muhammad's era. This tribe consists of four divisions: Al-Humaydah, Al-Musa ibn 'Ali, Al-Isba' and Al-Jibali. Their homes are located 15 miles north of Mahayil. They stretch 20 miles north and south and 30 miles east and west, and are bounded by "Banu Shihr" to the east, "Khath'm" and "Balqarn" to the north, "Al-Raysh" and "Al-Durayb" to the south and "Rabi'at al-Maqatirah" to the west. Most of them live in the villages scattered across this region. History They were a branch of the Al-Azd tribe, which was one of the two branches of Kahlan the other being Himyar. In ancient times, they inhabited Ma'rib, the capital city of the Sabaean Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century Arabic Poets
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. In its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
600 Deaths
6 (six) is the natural number following 5 and preceding 7. It is a composite number and the smallest perfect number. In mathematics Six is the smallest positive integer which is neither a square number nor a prime number; it is the second smallest composite number, behind 4; its proper divisors are , and . Since 6 equals the sum of its proper divisors, it is a perfect number; 6 is the smallest of the perfect numbers. It is also the smallest Granville number, or \mathcal-perfect number. As a perfect number: *6 is related to the Mersenne prime 3, since . (The next perfect number is 28.) *6 is the only even perfect number that is not the sum of successive odd cubes. *6 is the root of the 6-aliquot tree, and is itself the aliquot sum of only one other number; the square number, . Six is the only number that is both the sum and the product of three consecutive positive numbers. Unrelated to 6's being a perfect number, a Golomb ruler of length 6 is a "perfect ruler". Six is a con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humaydah Al-Bariqi
Humaydah ibn an-Nu'man al-Bariqi ( ar, حميضة بن النعمان البارقي), was a companion of Muhammad. He was the leader of the tribe of Bariq and an extremely successful military general during the reign of Rashidun Caliph Umar. Humaydah also fought under Sa`d's command against the Sassanid army at the Battle of al-Qādisiyyah. Lineage His full name was Humaydah b. al-Nu'man b. Humaydah b. al-Harith b. Awf b. Amr b. Sa`d b. Thailbh b. Kinanah al-Bariqi Ibn Bariq Ibn Uday Ibn Haritha Ibn Amr Mazikiee Ibn Aamr bin Haritha Algtarif bin Imru al-Qais Thailb bin Mazen Ibn Al-Azd Ibn Al-Ghoth Ibn Nabit Ibn Malik bin Zaid Ibn Kahlan Ibn Saba'a (Sheba) Ibn Yashjub Ibn Yarab Ibn Qahtan Ibn Hud (Eber). Nu'man b. Humaydah al-Bariqi ( ar, النعمان بن حميضة البارقي) was his father. References {{Reflist Further reading * History of the Prophets and Kings (1/2218 2258, 2259 and 2334) *The Complete History ''The Complete History'' (, ''al-Kāmil fit-T� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eber
Eber ( he, , ʿĒḇer; grc-x-biblical, Ἔβερ, Éber; ar, عٰابِر, ʿĀbir) is an ancestor of the Ishmaelites and the Israelites according to the "Table of Nations" in the Book of Genesis () and the Books of Chronicles (). Lineage Eber was a great-grandson of Noah's son Shem and the father of Peleg, born when Eber was 34 years old, and of Joktan. He was the son of Shelah, a distant ancestor of Abraham. According to the Hebrew Bible, Eber died at the age of 464. In the Septuagint, the name is written as Heber/Eber (), and his father is called Sala (). His son is called Phaleg/Phalek (), born when Heber was 134 years old, and he had other sons and daughters. Heber lived to an age of 464 years. Name The Aramaic/Hebrew root () is connected with crossing over and the beyond. Considering that other names for descendants of Shem also stand for places, Eber can also be considered the name of an area, perhaps near Assyria. A number of mediaeval scholars such as Mich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hud (prophet)
), but this is disputed , image = Prophet Hud Name.svg , image_size = 150px , alt = , caption = The name ''Hud'' written in Islamic calligraphy, followed by "Peace be upon him". , birth_name = , birth_date = , birth_place = , death_date = , death_place = , resting_place = Possibly Qabr An-Nabi Hud in Hadhramaut, South Arabia , title = Prophet , predecessor = Nuh , successor = Salih , children = , parents = , relatives = Hud (; ar, هُوْد, Hūd) was a prophet of ancient Arabia mentioned in the Quran. The eleventh chapter of the Quran, ''Hud'', is named after him, though the narrative of Hud comprises only a small portion of the chapter. Historical context Hud has sometimes been identified with Eber, an ancestor of the Ishmaelites and the Israelites who is mentioned in the Old Testament. He is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarab
Ya'rub ( ar, يعرب, also spelled ''Yarob'',''Ya'rob'', ''Yarrob'', ''Yarab'' or ''Yaarub'') is an ancient Arabic personal name. He is the grandson of Abir being the son of Qahtan and the ancestor of the Himyarite and Sabaean kings of Yemen.van Donzel, 1994, p. 483. A similar account places Ya'rub as Qahtan's grandson (Ya'rub bin Yashjub bin Qahtan) and holds that he is the forefather of ''al-'Arab al-'Ariba'' ("the arab arabs" or "pure arabs"), who are generally identified with the Qahtanites and its two main tribes, the Himyar and the Kahlan.Prentiss, 2003, p. 172. Some legendary accounts relate that Ya'rub was the first to speak Arabic and that the language was named for him.Crosby, 2007, pp. 74-75.Sperl, 1989, p. 209. Shams-i Qais Razi, writing in the 12-13th century CE, traced the origins of Arabic poetry to Ya'rub and he is also credited with having invented the Kufic script.Sperl et al., 1996, p. 138.Thackston, 2001, p. 7. Ancestor of kings Ya'rub was said to be one of g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bariq
Bariq (also transliterated as Barik or Bareq, ar, بارق) is a tribe from Bareq in south-west Saudi Arabia. It belongs to the ancient Al-Azd tribe which has many clans linked to it. As far as ancestry goes, Aws, Khazraj, Ghassān and Banu Khuza'a, and others all belong to Al-Azd. They were one of the tribes of Arabia during Muhammad's era. This tribe consists of four divisions: Al-Humaydah, Al-Musa ibn 'Ali, Al-Isba' and Al-Jibali. Their homes are located 15 miles north of Mahayil. They stretch 20 miles north and south and 30 miles east and west, and are bounded by "Banu Shihr" to the east, "Khath'm" and "Balqarn" to the north, "Al-Raysh" and "Al-Durayb" to the south and "Rabi'at al-Maqatirah" to the west. Most of them live in the villages scattered across this region. History They were a branch of the Al-Azd tribe, which was one of the two branches of Kahlan the other being Himyar. In ancient times, they inhabited Ma'rib, the capital city of the Sabaean Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheba
Sheba (; he, ''Šəḇāʾ''; ar, سبأ ''Sabaʾ''; Ge'ez: ሳባ ''Saba'') is a kingdom mentioned in the Hebrew Bible ( Old Testament) and the Quran. Sheba features in Jewish, Muslim, and Christian traditions, particularly the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo tradition. It was the home of the biblical "Queen of Sheba", who is left unnamed in the Bible, but receives the names ''Makeda'' in Ethiopian and ''Bilqīs'' in Arabic tradition. According to Josephus it was also the home of the biblical " Princess Tharbis" said to have been the first wife of Moses when he was still a prince of Egypt. There are competing theories of where this kingdom was, with some placing it in either South Arabia or the Horn of Africa. Encyclopedia Britannica posits that the biblical narrative about the kingdom of Sheba was based on the ancient civilization of Saba (Old South Arabian: 𐩪𐩨𐩱 ''S-b-ʾ'') in South Arabia. This view is echoed by Israel Finkelstein and Neil Asher Silberman who w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saba'a
The Sabaeans or Sabeans (Sabaean:, ; ar, ٱلسَّبَئِيُّوْن, ''as-Sabaʾiyyūn''; he, סְבָאִים, Səḇāʾīm) were an ancient group of South Arabians. They spoke the Sabaean language, one of the Old South Arabian languages.Stuart Munro-Hay, ''Aksum: An African Civilization of Late Antiquity'', 1991. They founded the kingdom of Sabaʾ ( ar, سَبَأ, links=no) in modern-day Yemen, Quran 27:6-93 Quran 34:15-18 which was believed to be the biblical land of Sheba and "the oldest and most important of the South Arabian kingdoms". The exact date of the foundation of Sabaʾ is a point of disagreement among scholars. Kenneth Kitchen dates the kingdom to between 1200 BCE and 275 CE, with its capital at Maʾrib, in what is now Yemen.Kenneth A. Kitchen ''The World of "Ancient Arabia" Series''. Documentation for Ancient Arabia. Part I. Chronological Framework and Historical Sources p.110 On the other hand, Israel Finkelstein and Neil Asher Silberman believe that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |