|
Al-Jammasin Al-Sharqi
Al-Jammasin al-Sharqi was a Palestinian Arab village in the Jaffa Subdistrict. It was depopulated during the 1948 Palestine War on March 17, 1948. It was located 9 km northeast of Jaffa. History Al-Jammasin's inhabitants were known to be descendants of nomads from the Jordan Valley. In 1596, a Jammasin (Masra'at Hasana) tribe appear in the Ottoman census, located in the ''Nahiya'' of Bani Sa'b of the '' Liwa'' of Nablus, paying taxes on goats, beehives and water buffalos. Khalidi writes that judging from the absence of taxes on any crops, this ''Masra'at'' (farm) probably specialised in short-distance herding and semi-nomadic tasks. The tribe was known to have settled in the area by the 18th century. British Mandate era In the 1922 census of Palestine conducted by the British Mandate authorities, the tribal area of Jammasin had a population of 200 Muslims,Barron, 1923, Table VII, Sub-district of Jaffa, p 20/ref> while in the 1931 census ''Jammasin esh-Sharqiya'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 in the region of Palestine under the terms of the League of Nations Mandate for Palestine. During the First World War (1914–1918), an Arab uprising against Ottoman rule and the British Empire's Egyptian Expeditionary Force under General Edmund Allenby drove the Ottoman Turks out of the Levant during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign. The United Kingdom had agreed in the McMahon–Hussein Correspondence that it would honour Arab independence if the Arabs revolted against the Ottoman Turks, but the two sides had different interpretations of this agreement, and in the end, the United Kingdom and France divided the area under the Sykes–Picot Agreementan act of betrayal in the eyes of the Arabs. Further complicating the issue was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraham (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices of Muhammad ('' sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts (''hadith''). With an estimated population of almost 1.9 billion followers as of 2020 year estimation, Muslims comprise more than 24.9% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each continental landmass stands at: 45% of Africa, 25% of Asia and Oceania (collectively), 6% of Europe, and 1% of the Americas. Additionally, in subdivided geographical regions, the figure stands at: 91% of the Middle East–North Africa, 90% of Central Asia, 65% of the Caucasus, 42% of Southeast As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petah Tikva
Petah Tikva ( he, פֶּתַח תִּקְוָה, , ), also known as ''Em HaMoshavot'' (), is a city in the Central District (Israel), Central District of Israel, east of Tel Aviv. It was founded in 1878, mainly by Haredi Judaism, Haredi Jews of the Old Yishuv, and became a permanent settlement in 1883 with the financial help of Edmond James de Rothschild, Baron Edmond de Rothschild. In , the city had a population of . Its population density is approximately . Its jurisdiction covers 35,868 dunams (~35.9 km2 or 15 sq mi). Petah Tikva is part of the Tel Aviv Metropolitan Area. Etymology Petah Tikva takes its name (meaning "Door of Hope") from the biblical allusion in Hosea 2:15: "... and make the valley of Achor a door of hope." The Achor Valley, near Jericho, was the original proposed location for the town. The city and its inhabitants are sometimes known by the nickname "Mlabes" after the Arab village preceding the town. (See "Ottoman era" under "History" below.) Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haganah
Haganah ( he, הַהֲגָנָה, lit. ''The Defence'') was the main Zionist paramilitary organization of the Jewish population ("Yishuv") in Mandatory Palestine between 1920 and its disestablishment in 1948, when it became the core of the Israel Defense Forces (IDF). Formed out of previous existing militias, its original purpose was to defend Jewish settlements from Arab attacks, such as the riots of 1920, 1921, 1929 and during the 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine. It was under the control of the Jewish Agency, the official governmental body in charge of Palestine's Jewish community during the British Mandate. Until the end of the Second World War, Haganah's activities were moderate, in accordance with the policy of havlaga ("self-restraint"), which caused the splitting of the more radical Irgun and Lehi. The group received clandestine military support from Poland. Haganah sought cooperation with the British in the event of an Axis invasion of Palestine through N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
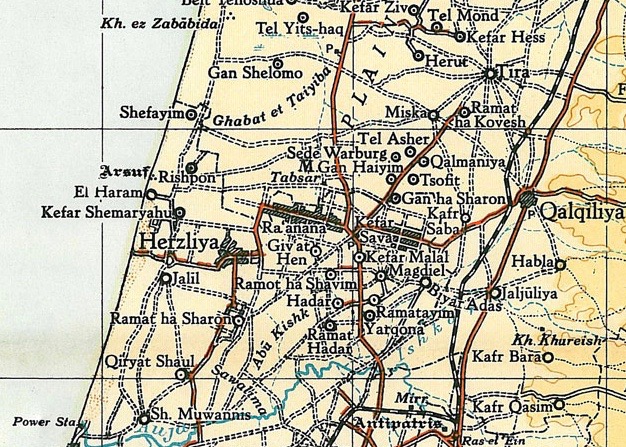
Abu Kishk
Abu Kishk (Arabic: ) was a Palestinian village in the Jaffa Subdistrict located 12 km northeast of Jaffa, situated 2 km northwest of the Yarkon River. The village was depopulated during the 1947–1948 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine on 30 March 1948 by the Irgun. In 1945 the population of the village was about 1,900, about 300 of them lived in the area of the future Herzliya. Location The village was situated about northwest of the Yarkon River. Secondary roads linked it to the Jaffa-Haifa highway and to neighboring villages.Khalidi, 1992, p. 235 History British Mandate of Palestine In 1925 the village school was founded. By the mid-1940s it had 108 students, including 9 girls. At the time of the 1931 census, Abu Kishk had a population of 1007 residents, all Muslims.Mills, 1932, p16/ref> In the 1945 statistics Abu Kishk had 1,900 Muslim residents, who owned a total of 17,121 dunams of land. A total of 2,486 dunums of village land was used for citrus or ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ijlil Al-Shamaliyya
Ijlil al-Shamaliyya ( ar, إجليل الشمالية ''Ijlīl aš-Šamāliyya'') was a Palestinian Arab village in the Jaffa Subdistrict. It was depopulated during the 1947–1948 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine on April 3, 1948. Location Ijlil al-Shamaliyya, (meaning "Northern Ijlil"), was located on a hilltop, northeast of Jaffa, and about 100 meters north of its sister village, Ijlil al-Qibliyya ("Southern Jilil"). History During the late Ottoman period, in June 1870, the French explorer Victor Guérin visited both villages. He described them as one unit called ''Edjlil'', situated on a hill and divided into two districts. Together, they had 380 inhabitants. The houses were built of rammed earth or with different small aggregates mixed in with kneaded and dried silt. In 1882, the PEF's ''Survey of Western Palestine'' described the two villages, named ''El Jelil'', as "a mud village, with a well to the south and a second to the north. .A small olive-grove exis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ijlil Al-Qibliyya
Ijlil al-Qibliyya, also al-Jalil, was a Palestinian Arab village in the Jaffa Subdistrict. It was depopulated during the 1947–1948 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine on April 3, 1948. In 1945 the village has a population of 680, 210 of which were Jewish. Ijlil al-Qibliya was named after al-Shaykh Salih 'Abd al-Jalil, whose maqam was located in the village. Location Ijlil al-Qibliyya, (meaning "Southern Ijlil"), was located on a hilltop, northeast of Jaffa, and about 100 meters southwest of its sister village, Ijlil al-Shamaliyya ("Northern Jilil"). History During the late Ottoman period, in June 1870, the French explorer Victor Guérin visited both villages. He described them as one village, called ''Edjlil'', situated on a hill and divided into two districts. Together, they had 380 inhabitants. The houses were built of rammed earth or with different small aggregates mixed in with kneaded and dried silt. In 1882, the PEF's ''Survey of Western Palestine'' described ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mukhtar
A mukhtar ( ar, مختار, mukhtār, chosen one; el, μουχτάρης) is a village chief in the Levant: "an old institution that goes back to the time of the Ottoman rule". According to Amir S. Cheshin, Bill Hutman and Avi Melamed, the mukhtar "for centuries were the central figures". They "were not restricted to Muslim communities" where even non-Arab "Christian and Jewish communities in the Arab world also had mukhtars." Quoting Tore Björgo: "The mukhtar was, among other things, responsible for collecting taxes and ensuring that law and order was prevailing in his village". See also * Kodjabashi The kodjabashis ( el, κοτζαμπάσηδες, kotzabasides; singular κοτζάμπασης, ''kotzabasis''; sh, kodžobaša, kodžabaša; from tr, kocabaṣı, hocabaṣı) were local Christian notables in parts of the Ottoman Balkans, most ... References External links * Arabic words and phrases Ottoman Empire {{Ottoman-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Jammasin Al-Gharbi
Al-Jammasin al-Gharbi was a Palestinian people, Palestinian Arab village in the Jaffa Subdistrict, Mandatory Palestine, Jaffa Subdistrict. It was depopulated during the 1947–48 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine on March 17, 1948. It was located 6.5 km northeast of Jaffa. History Al-Jammasin's inhabitants were known to be descendants of nomads from the Jordan Valley (Middle East), Jordan Valley. In 1596, a Jammasin tribe appear in the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman daftar, census, located in the ''Nahiya'' of Bani Sa'b of the ''Liwa (Arabic), Liwa'' of Sanjak of Nablus, Nablus, paying taxes on water buffalos. Walid Khalidi, Khalidi writes that it is not certain that this was the same tribe that settled the two Jammasin villages. The tribe was known to have settled in the area by the 18th century. British Mandate era In the 1922 census of Palestine conducted by the Mandatory Palestine, British Mandate authorities, the tribal area of Jammasin had a population of 200 Muslims,Barr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Mas'udiyya
Al-Mas'udiyya (also known as ''Summayl''), was a Palestinian Arab village in the Jaffa Subdistrict. It was depopulated during the 1947–1948 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine on December 25, 1947. It was located 5 km northeast of Jaffa, situated 1.5 km south of the al-'Awja River. The village used to be known as Summayl. History In 1799, it was noted as an unnamed village on the map that Pierre Jacotin compiled that year. An Ottoman village list from about 1870 showed that ''Samwil'' had 23 houses and a population of 62, though the population count included men, only. It was noted as a Bedouin camp, 4,5 km north of Jaffa centre, and 1 km from the sea.Socin, 1879, p160/ref> In 1882, the PEF's ''Survey of Western Palestine'' (SWP) described Summeil as an ordinary adobe village, which had a large well, and a cave.Conder and Kitchener, 1882, SWP II, p. 275/ref> British Mandate era In the 1922 census of Palestine, conducted by the British Mandate au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Shaykh Muwannis
Al-Shaykh Muwannis ( ar, الشيخ مونّس), also Sheikh Munis, was a small Palestinian Arab village in the Jaffa Subdistrict of Mandatory Palestine, located approximately 8.5 kilometers from the center of Jaffa city in territory earmarked for Jewish statehood under the UN Partition Plan. The village was abandoned in March 1948 due to the threats of Jewish militias, two months before the 1948 Arab–Israeli war. Today, Tel Aviv University lies on part of the village land. History According to local legend, the village was named for a local religious figure, al-Shaykh Muwannis, whose maqam was in the village. Ottoman era During the Ottoman era, Pierre Jacotin named the village ''Dahr'' on his map from 1799. Al-Shaykh Muwannis was noted in December 1821, as being "located on a hill surrounded by muddy land that was flooded with water despite the moderate winter". In 1856 the village was named ''Sheikh Muennis'' on Kiepert's map of Palestine published that year. In 1870, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Shaykh Muwannis
Al-Shaykh Muwannis ( ar, الشيخ مونّس), also Sheikh Munis, was a small Palestinian Arab village in the Jaffa Subdistrict of Mandatory Palestine, located approximately 8.5 kilometers from the center of Jaffa city in territory earmarked for Jewish statehood under the UN Partition Plan. The village was abandoned in March 1948 due to the threats of Jewish militias, two months before the 1948 Arab–Israeli war. Today, Tel Aviv University lies on part of the village land. History According to local legend, the village was named for a local religious figure, al-Shaykh Muwannis, whose maqam was in the village. Ottoman era During the Ottoman era, Pierre Jacotin named the village ''Dahr'' on his map from 1799. Al-Shaykh Muwannis was noted in December 1821, as being "located on a hill surrounded by muddy land that was flooded with water despite the moderate winter". In 1856 the village was named ''Sheikh Muennis'' on Kiepert's map of Palestine published that year. In 1870, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |