|
Ajas Pasha
Ajas Pasha (? - Anatolia, 1486) was a Bosnian sanjak-bey and later pasha in Ottoman service. Career He was sanjak-bey of Bosnia, referred to as ''the Lord of the King's land'', from 1470 to 1475, 1477 to 1478 and in 1483, and ruled sanjak-bey of Herzegovina, also referred to as ''Herzegovina's Krajisnik'' or ''Duke of the Herzeg's land'', from 1478 to 1480 and 1481 to 1483. In 1472 he raided Croatian littoral, Istria and Friuli region. In November 1481 he besieged Herceg Novi, and on 14th December of 1481 he captured the city after Vlatko Hercegović gave up defending it and agreed surrender. For this he was awarded title of ''pasha''. Achievements He played a key role in the development of Visoko from a Bosnian medieval type of town to Ottoman styled urban organization. He legalized his waqf in 1477 hammam, shops, maktab, water supply system, bridge on river Bosna, madrasa Madrasa (, also , ; Arabic: مدرسة , pl. , ) is the Arabic word for any type of educationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasha
Pasha, Pacha or Paşa ( ota, پاشا; tr, paşa; sq, Pashë; ar, باشا), in older works sometimes anglicized as bashaw, was a higher rank in the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, generals, dignitary, dignitaries, and others. As an honorific, honorary title, ''Pasha'', in one of its various ranks, is similar to a British Peerage of the United Kingdom, peerage or knighthood, and was also one of the highest titles in the 20th-century Kingdom of Egypt. The title was also used in Morocco in the 20th century, where it denoted a regional official or governor of a district. Etymology The English word "pasha" comes from Turkish language, Turkish ('; also ()). The Oxford Dictionaries (website), Oxford Dictionaries attributes the origin of the English borrowing to the mid-17th century. The etymology of the Turkish word itself has been a matter of debate. Contrary to titles like emir (''amīr'') and bey (''beg''), which were es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herceg Novi
Herceg Novi ( cyrl, Херцег Нови, ) is a coastal town in Montenegro located at the Western entrance to the Bay of Kotor and at the foot of Mount Orjen. It is the administrative center of the Herceg Novi Municipality with around 33,000 inhabitants. Herceg Novi was known as Castelnuovo ("New castle" in Italian) between 1482 and 1797, when it was part of the Ottoman Empire and the Albania Veneta of the Republic of Venice. It was a Catholic bishopric and remains a Latin titular see as Novi. Herceg Novi has had a turbulent past, despite being one of the youngest settlements on the Adriatic. A History of Montenegro, history of varied occupations has created a blend of diverse and picturesque architectural style in the city. Names In Montenegrin language, Montenegrin, the town is known as ''Herceg Novi'' or Херцег Нови; in Italian language, Italian as ''Castelnuovo''; and in Greek language, Greek as ''Neòkastron'' (Νεοκαστρον), Turkish as Kala-i Novi, all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Generals
Ottoman is the Turkish spelling of the Arabic masculine given name Uthman ( ar, عُثْمان, ‘uthmān). It may refer to: Governments and dynasties * Ottoman Caliphate, an Islamic caliphate from 1517 to 1924 * Ottoman Empire, in existence from 1299 to 1922 ** Ottoman dynasty, ruling family of the Ottoman Empire *** Osmanoğlu family, modern members of the family * Ottoman architecture Ethnicities and languages * Ottoman Armenians, the Armenian ethnic group in the Ottoman Empire * Ottoman Greeks, the Greek ethnic group in the Ottoman Empire * Ottoman Serbs, the Serbian ethnic group in the Ottoman Empire * Ottoman Turks, the Turkic ethnic group in the Ottoman Empire ** Ottoman Turkish alphabet ** Ottoman Turkish language, the variety of the Turkish language that was used in the Ottoman Empire Products * Ottoman bed, a type of storage bed * Ottoman (furniture), padded stool or footstool * Ottoman (textile), fabric with a pronounced ribbed or corded effect, often made of silk or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bosnia And Herzegovina Generals
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and Herzegovina borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to the north and southwest. In the south it has a narrow coast on the Adriatic Sea within the Mediterranean, which is about long and surrounds the town of Neum. Bosnia, which is the inland region of the country, has a moderate continental climate with hot summers and cold, snowy winters. In the central and eastern regions of the country, the geography is mountainous, in the northwest it is moderately hilly, and in the northeast it is predominantly flat. Herzegovina, which is the smaller, southern region of the country, has a Mediterranean climate and is mostly mountainous. Sarajevo is the capital and the largest city of the country followed by Banja Luka, Tuzla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ottoman Governors Of Bosnia
Bosnia became part of the Ottoman Empire after 1454. The Ottoman government appointed sanjak-beys as governors of Bosnia. The following is a list of Ottoman governors of the Bosnian sanjak, eyalet, and vilayet within Ottoman Empire The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) .... References Sources * * {{Lists of Ottoman governors Bosnia Ottoman governors Bosnia, Ottoman Bosnia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanqah
A khanqah ( fa, خانقاه) or khangah ( fa, خانگاه; also transliterated as ''khankah'', ''khaneqa'', ''khanegah'' or ''khaneqah''; also Arabized ''hanegah'', ''hanikah'', ''hanekah'', ''khankan''), also known as a ribat (), is a building designed specifically for gatherings of a Sufi brotherhood or ''tariqa'' and is a place for spiritual practice and religious education. The khanqah is typically a large structure with a central hall and smaller rooms on either side. Traditionally, the kahnqah was state-sponsored housing for Sufis. Their primary function is to provide them with a space to practice social lives of asceticism. Buildings intended for public services, such as hospitals, kitchens, and lodging, are often attached to them. Khanqahs were funded by Ayyubid sultans in Syria, Zangid sultans in Egypt, and Delhi sultans in India in return for Sufi support of their regimes. Etymology The word khanqah is likely either Turkish or Persian in origin. In the Arab world, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naqshbandi
The Naqshbandi ( fa, نقشبندی)), Neqshebendi ( ku, نهقشهبهندی), and Nakşibendi (in Turkish) is a major Sunni order of Sufism. Its name is derived from Baha-ud-Din Naqshband Bukhari. Naqshbandi masters trace their lineage to the Islamic prophet Muhammad through Abu Bakr, the first Caliph of Sunni Islam and Ali, the fourth Caliph of Sunni Islam. It is because of this dual lineage through Ali and Abu Bakr through the 6th Imam Jafar al Sadiq that the order is also known as the "convergence of the two oceans" or "Sufi Order of Jafar al Sadiq". History The Naqshbandi order owes many insights to Yusuf Hamdani and Abdul Khaliq Gajadwani in the 12th century, the latter of whom is regarded as the organizer of the practices and is responsible for placing stress upon the purely silent ''invocation''. It was later associated with Baha-ud-Din Naqshband Bukhari in the 14th century, hence the name of the order. The name can be interpreted as "engraver (of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madrasa
Madrasa (, also , ; Arabic: مدرسة , pl. , ) is the Arabic word for any type of educational institution, secular or religious (of any religion), whether for elementary instruction or higher learning. The word is variously transliterated ''Madrasah arifah'', ''medresa'', ''madrassa'', ''madraza'', ''medrese'', etc. In countries outside the Arab world, the word usually refers to a specific type of religious school or college for the study of the religion of Islam, though this may not be the only subject studied. In an architectural and historical context, the term generally refers to a particular kind of institution in the historic Muslim world which primarily taught Islamic law and jurisprudence (''fiqh''), as well as other subjects on occasion. The origin of this type of institution is widely credited to Nizam al-Mulk, a vizier under the Seljuks in the 11th century, who was responsible for building the first network of official madrasas in Iran, Mesopotamia, and Khorasan. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bosna (river)
The Bosna () is the third longest river in Bosnia and Herzegovina, and is considered one of the country's three major internal rivers, along with the Neretva and the Vrbas. The other three major rivers of Bosnia and Herzegovina are the Una, to the northwest; the Sava, to the north, and the Drina, to the east. This river is the namesake of Bosnia. The river Bosna flows for . The river is possibly mentioned for the first time during the 1st century AD by Roman historian Marcus Velleius Paterculus under the name ''Bathinus flumen''. Another basic source that is associated with the hydronym ''Bathinus'' is the Salonitan inscription of the governor of Dalmatia, Publius Cornelius Dolabella, where it is said that the ''Bathinum'' river divides the Breuci from the Osseriates. And also by the name of Basante. There was also the name Bason on the map ''From Istanbul to Vienna'' along the Danube and the Black Sea — a river-centric map by the Venetian cartographer Stefano Scolari, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually something that is otherwise difficult or impossible to cross. There are many different designs of bridges, each serving a particular purpose and applicable to different situations. Designs of bridges vary depending on factors such as the function of the bridge, the nature of the terrain where the bridge is constructed and anchored, and the material used to make it, and the funds available to build it. The earliest bridges were likely made with fallen trees and stepping stones. The Neolithic people built boardwalk bridges across marshland. The Arkadiko Bridge (dating from the 13th century BC, in the Peloponnese) is one of the oldest arch bridges still in existence and use. Etymology The '' Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the origin of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
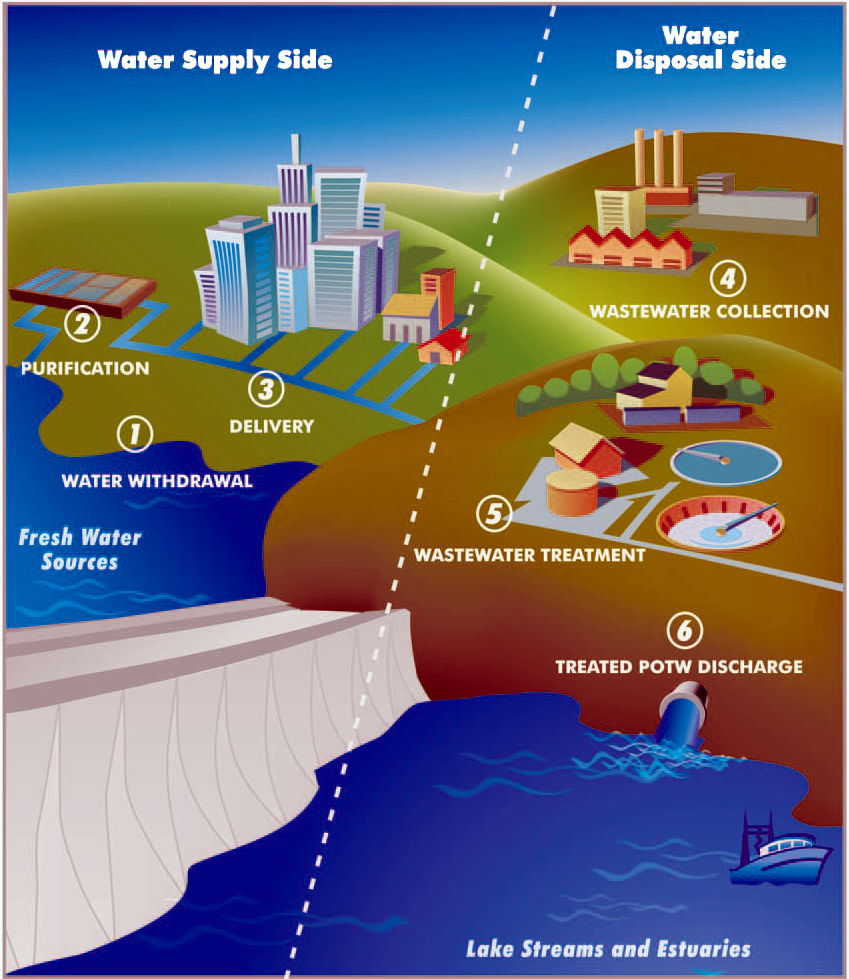
Water Supply Network
A water supply network or water supply system is a system of engineered hydrologic and hydraulic components that provide water supply. A water supply system typically includes the following: # A drainage basin (see water purification – sources of drinking water) # A raw water collection point (above or below ground) where the water accumulates, such as a lake, a river, or groundwater from an underground aquifer. Raw water may be transferred using uncovered ground-level aqueducts, covered tunnels, or underground water pipes to water purification facilities. # Water purification facilities. Treated water is transferred using water pipes (usually underground). # Water storage facilities such as reservoirs, water tanks, or water towers. Smaller water systems may store the water in cisterns or pressure vessels. Tall buildings may also need to store water locally in pressure vessels in order for the water to reach the upper floors. # Additional water pressurizing components such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maktab (education)
A kuttab ( ar, كُتَّاب ''kuttāb'', plural: ''kataatiib'', ) or maktab ( ar, مَكْتَب) is a type of elementary school in the Muslim world. Though the ''kuttab'' was primarily used for teaching children in reading, writing, grammar, and Islamic studies, such as memorizing and reciting the Qur'an (including ''Qira'at''), other practical and theoretical subjects were also often taught. The kuttāb represents an old-fashioned method of education in Muslim majority countries, in which a sheikh teaches a group of students who sit in front of him on the ground. Until the 20th century, when modern schools developed, kuttabs were the prevalent means of mass education in much of the Islamic world. Name Kuttab refers to only elementary schools in Arabic. This institution can also be called a ''maktab'' () or ''maktaba'' () in Arabic—with many transliterations. In common Modern Standard Arabic usage, ''maktab'' means "office" while ''maktabah'' means "library" or "(place of) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |