|
Air Source Heat Pump
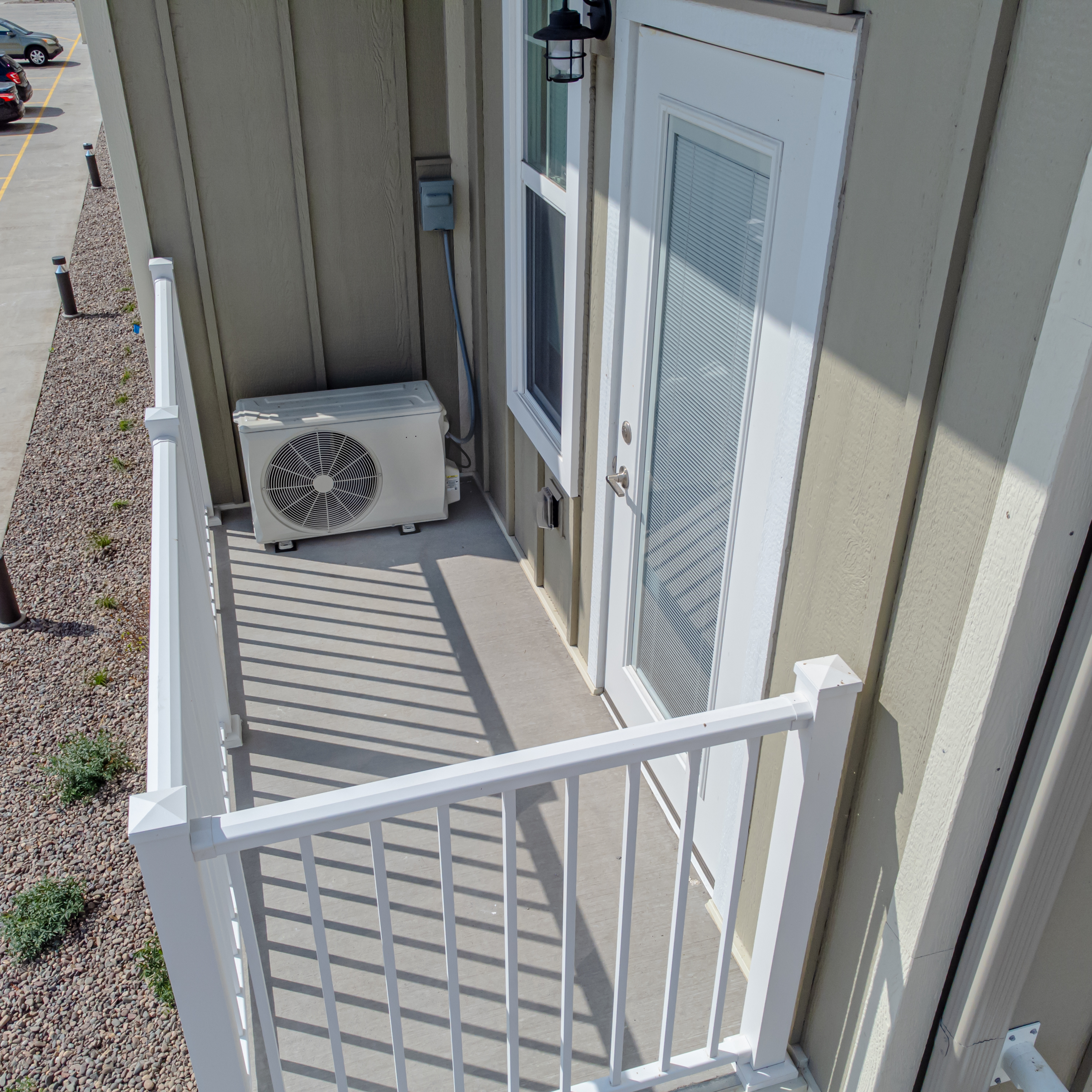
An air source heat pump (ASHP) is a heat pump that can absorb heat from air outside a building and release it inside; it uses the same vapor-compression refrigeration process and much the same equipment as an air conditioner, but in the opposite direction. ASHPs are the most common type of heat pump and, usually being smaller, tend to be used to heat individual houses or flats rather than blocks, districts or industrial processes. ''Air-to-air'' heat pumps provide hot or cold air directly to rooms, but do not usually provide hot water. ''Air-to-water'' heat pumps use radiators or underfloor heating to heat a whole house and are often also used to provide domestic hot water. An ASHP can typically gain 4 kWh thermal energy from 1 kWh electric energy. They are optimized for flow temperatures between , suitable for buildings with heat emitters sized for low flow temperatures. With losses in efficiency, an ASHP can even provide full central heating with a flow tempera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Pump
A heat pump is a device that uses electricity to transfer heat from a colder place to a warmer place. Specifically, the heat pump transfers thermal energy using a heat pump and refrigeration cycle, cooling the cool space and warming the warm space. In winter a heat pump can move heat from the cool outdoors to warm a house; the pump may also be designed to move heat from the house to the warmer outdoors in summer. As they transfer heat rather than generating heat, they are more energy-efficient than heating by gas boiler. A gaseous refrigerant is compressed so its pressure and temperature rise. When operating as a heater in cold weather, the warmed gas flows to a heat exchanger in the indoor space where some of its thermal energy is transferred to that indoor space, causing the gas to condense into a liquid. The liquified refrigerant flows to a heat exchanger in the outdoor space where the pressure falls, the liquid evaporates and the temperature of the gas falls. It is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Compressor
A compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. An air compressor is a specific type of gas compressor. Many compressors can be staged, that is, the gas is compressed several times in steps or stages, to increase discharge pressure. Often, the second stage is physically smaller than the primary stage, to accommodate the already compressed gas without reducing its pressure. Each stage further compresses the gas and increases its pressure and also temperature (if inter cooling between stages is not used). Types Compressors are similar to pumps: both increase the pressure on a fluid (such as a gas) and both can transport the fluid through a pipe (material), pipe. The main distinction is that the focus of a compressor is to change the density or volume of the fluid, which is mostly only achievable on gases. Gases are compressible, while liquids are relatively incompressible, so compressors are rarely used for liquids. The main actio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storage Heater
A storage heater or heat bank (Australia) is an electrical heater which stores thermal energy during the evening, or at night when electricity is available at lower cost, and releases the heat during the day as required. Alternatively, solar storage heaters are designed to store solar energy as heat, to be released during the night or other periods where it is required, often making it more cost effective than selling surplus electricity to the grid and buying it back at night. Principle of operation Storage heaters are typically composed of clay bricks or other ceramic material ( grog), of concrete walls, or of water containers. There are also special materials such as feolite. This material serves as a heat storage medium. There are electrical heating elements embedded in the material which can be switched on to heat the storage medium and thus to store energy. The stored heat is given off continuously (through thermal radiation and convection). To speed up the heat transf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Energy Storage
Thermal energy storage (TES) is the storage of thermal energy for later reuse. Employing widely different technologies, it allows surplus thermal energy to be stored for hours, days, or months. Scale both of storage and use vary from small to large – from individual processes to district, town, or region. Usage examples are the balancing of energy demand between daytime and nighttime, storing summer heat for winter heating, or winter cold for summer cooling (Seasonal thermal energy storage). Storage media include water or ice-slush tanks, masses of native earth or bedrock accessed with heat exchangers by means of boreholes, deep aquifers contained between impermeable strata; shallow, lined pits filled with gravel and water and insulated at the top, as well as eutectic solutions and phase-change materials. Other sources of thermal energy for storage include heat or cold produced with heat pumps from off-peak, lower cost electric power, a practice called peak shaving; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Panel
A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electricity by using photovoltaic (PV) cells. PV cells are made of materials that produce excited electrons when exposed to light. These electrons flow through a circuit and produce direct current (DC) electricity, which can be used to power various devices or be stored in battery (electricity), batteries. Solar panels are also known as solar cell panels, solar electric panels, or PV modules. Solar panels are usually arranged in groups called arrays or systems. A photovoltaic system consists of one or more solar panels, an solar inverter, inverter that converts DC electricity to alternating current (AC) electricity, and sometimes other components such as charge controller, controllers, Measuring instrument, meters, and solar tracker, trackers. Most panels are in solar farms or Rooftop solar power, rooftop solar panels which grid-connected photovoltaic system, supply the electricity grid. Some advantages of solar panels are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geothermal Heat Pump
A ground source heat pump (also geothermal heat pump) is a heating/cooling system for buildings that use a type of heat pump to transfer heat to or from the ground, taking advantage of the relative constancy of temperatures of the earth through the seasons. Ground-source heat pumps (GSHPs)or geothermal heat pumps (GHP), as they are commonly termed in North Americaare among the most energy-efficient technologies for providing HVAC and water heating, using less energy than can be achieved by use of resistive electric heaters. Efficiency is given as a coefficient of performance (CoP) which is typically in the range 3-6, meaning that the devices provide 3-6 units of heat for each unit of electricity used. Setup costs are higher than for other heating systems, due to the requirement of installing ground loops over large areas or of drilling bore holes, hence ground source is often installed when new blocks of flats are built. Air-source heat pumps have lower set-up costs but have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fan (mechanical)
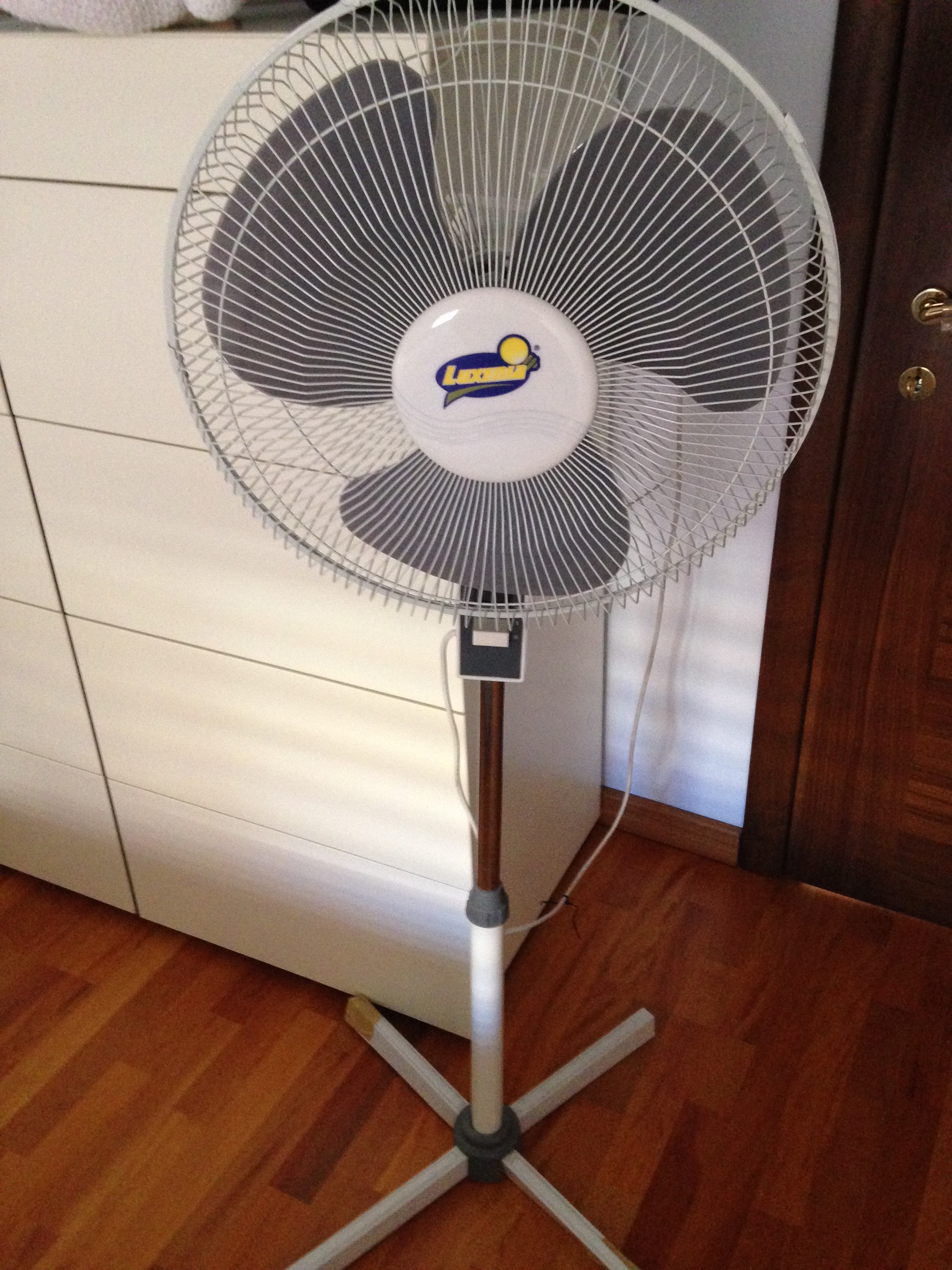
A fan is a powered machine that creates airflow. A fan consists of rotating vanes or blades, generally made of wood, plastic, or metal, which act on the air. The rotating assembly of blades and hub is known as an '' impeller'', '' rotor'', or ''runner''. Usually, it is contained within some form of housing, or case. This may direct the airflow, or increase safety by preventing objects from contacting the fan blades. Most fans are powered by electric motors, but other sources of power may be used, including hydraulic motors, handcranks, and internal combustion engines. Mechanically, a fan can be any revolving vane, or vanes used for producing currents of air. Fans produce air flows with high volume and low pressure (although higher than ambient pressure), as opposed to compressors which produce high pressures at a comparatively low volume. A fan blade will often rotate when exposed to an air-fluid stream, and devices that take advantage of this, such as anemometers and win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valve
A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid (gases, liquids, fluidized solids, or Slurry, slurries) by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically Piping and plumbing fitting, fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category. In an open valve, fluid flows in a direction from higher pressure to lower pressure. The word is derived from the Latin ''valva'', the moving part of a door, in turn from ''volvere'', to turn, roll. The simplest, and very ancient, valve is simply a freely hinged flap which swings down to obstruct fluid (gas or liquid) flow in one direction, but is pushed up by the flow itself when the flow is moving in the opposite direction. This is called a check valve, as it prevents or "checks" the flow in one direction. Modern control valves may regulate pressure or Fluid dynamics, flow downstream and operate on sophisticated Automation#Industrial automation, automat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Gas Law
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of the empirical Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. The ideal gas law is often written in an empirical form: pV = nRT where p, V and T are the pressure, volume and Thermodynamic temperature, temperature respectively; n is the amount of substance; and R is the ideal gas constant. It can also be derived from the microscopic kinetic theory of gases, kinetic theory, as was achieved (independently) by August Krönig in 1856 and Rudolf Clausius in 1857. Equation The state function, state of an amount of gas is determined by its pressure, volume, and temperature. The modern form of the equation relates these simply in two main forms. The temperature us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latent Heat
Latent heat (also known as latent energy or heat of transformation) is energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process—usually a first-order phase transition, like melting or condensation. Latent heat can be understood as hidden energy which is supplied or extracted to change the state of a substance without changing its temperature or pressure. This includes the latent heat of fusion (solid to liquid), the latent heat of vaporization (liquid to gas) and the latent heat of sublimation (solid to gas). The term was introduced around 1762 by Scottish chemist Joseph Black. Black used the term in the context of calorimetry where a heat transfer caused a volume change in a body while its temperature was constant. In contrast to latent heat, sensible heat is energy transferred as heat, with a resultant temperature change in a body. Usage The terms ''sensible heat'' and ''latent heat'' refer to energy transferred between a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vapor
In physics, a vapor (American English) or vapour (Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) is a substance in the gas phase at a temperature lower than its critical temperature,R. H. Petrucci, W. S. Harwood, and F. G. Herring, ''General Chemistry'', Prentice-Hall, 8th ed. 2002, p. 483–86. which means that the vapor can be condensation, condensed to a liquid by increasing the pressure on it without reducing the temperature of the vapor. A vapor is different from an aerosol. An aerosol is a suspension of tiny particles of liquid, solid, or both within a gas. For example, water has a critical temperature of , which is the highest temperature at which liquid water can exist at any pressure. In the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere at ordinary temperatures gaseous water (known as water vapor) will condense into a liquid if its partial pressure is increased sufficiently. A vapor may co-exist with a liquid (or a solid). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |