|
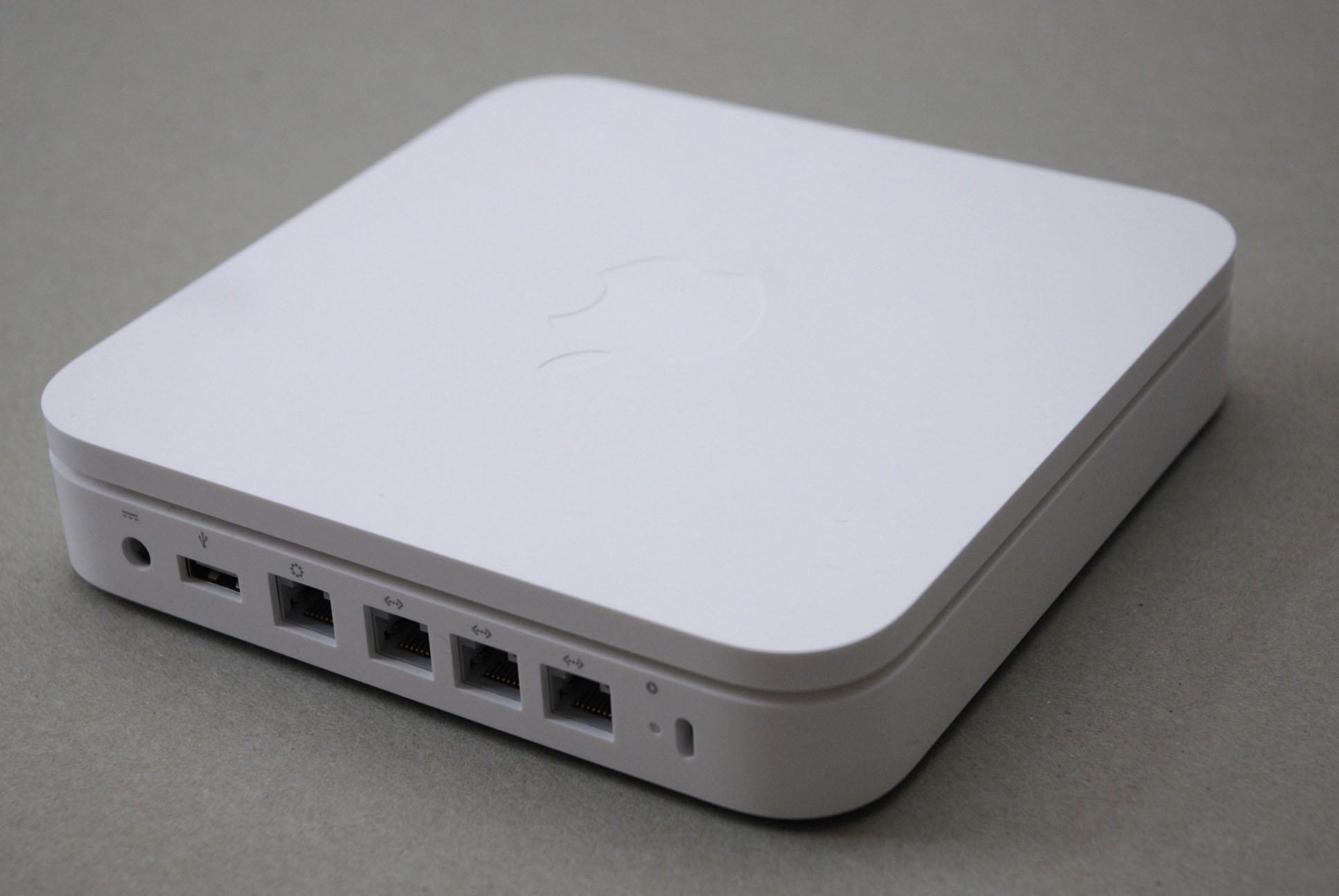
AirPort Extreme
The AirPort Extreme is a residential gateway combining the functions of a router, network switch, wireless access point and NAS as well as varied other functions, and one of Apple's former AirPort products. The latest model, the 6th generation, supports 802.11ac networking in addition to older standards. Versions of the same system with a built-in network-accessible hard drive are known as the AirPort Time Capsule. Apple discontinued developing its lineup of wireless routers in 2016, but continues limited hardware and software support. History The name "AirPort Extreme" originally referred to any one of Apple's AirPort products that implemented the (then) newly introduced 802.11g Wi-Fi standard, differentiating it from earlier devices that ran the slower 802.11a and b standards. At that time the gateway part of this lineup was known as the AirPort Extreme Base Station. With the addition of the even faster Draft-N standards in early 2009 this naming was dropped, and from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep Proxy Service
Apple's Bonjour Sleep Proxy service is an open source component of zero-configuration networking, designed to assist in reducing power consumption of networked electronic devices. A device acting as a sleep proxy server will respond to Multicast DNS queries for another compatible device which has gone into low power mode. The ''low-power-mode'' device remains ''asleep'' while the sleep proxy server responds to Multicast DNS queries. When the sleep proxy server sees a query which requires the ''low-power-mode'' device to ''wake up'', the sleep proxy server sends a special wake-up-packet ("magic packet") to the low-power-mode device. Finally, communication parameters are updated via Multicast DNS, and normal communications proceed. Apple refers to the service as Bonjour Sleep Proxy in its support documents. The service supports the Wake on Demand feature, first offered in Mac OS X Snow Leopard. Details Address resolution protocol The sleep proxy service responds to addre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet
Ethernet () is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 1983 as IEEE 802.3. Ethernet has since been refined to support higher bit rates, a greater number of nodes, and longer link distances, but retains much backward compatibility. Over time, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies such as Token Ring, FDDI and ARCNET. The original 10BASE5 Ethernet uses coaxial cable as a shared medium, while the newer Ethernet variants use twisted pair and fiber optic links in conjunction with switches. Over the course of its history, Ethernet data transfer rates have been increased from the original to the latest , with rates up to under development. The Ethernet standards include several wiring and signaling variants of the OSI physical layer. Systems communicating over Ethernet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AirPort Express
The AirPort Express is a Wi-Fi base station product from Apple Inc., part of the AirPort product line. While more compact and in some ways simpler than another Apple Wi-Fi base station, the AirPort Extreme, the Express offers audio output capability the Extreme lacks. The AirPort Express was the first AirPlay device to receive streamed audio from a computer running iTunes on the local network. AirPort Express outperforms the stringent requirements of the ENERGY STAR Program Requirements for Small Network Equipment (SNE) Version 1.0. Apple discontinued developing its wireless routers in 2018, but continues limited support of later models. Description When connected to an Ethernet network, the Express can function as a wireless access point. The latest model allows up to 50 networked users. It can be used as an Ethernet-to-wireless bridge under certain wireless configurations. It can be used to extend the range of a network, including functioning as a printer and audio server. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Router Firmware Projects
List of software created and maintained by people other than the manufacturer of the product. The extent of support for (and testing on) particular hardware varies from project to project. Embedded Notable custom-firmware projects for wireless routers. Many of these will run on various brands such as Linksys, Asus, Netgear, etc. * OpenWrt – Customizable FOSS firmware written from scratch; features a combined SquashFS/JFFS2 file system and the package manager opkg with over 3000 available packages (Linux/GPL); now merged with LEDE. ** LEDE – A fork of the OpenWrt project that shared many of the same goals; merged back into OpenWrt as of v. 18.06 (2018). ** Commotion Wireless – FOSS mesh networking. ** DD-WRT – Based on OpenWrt kernel since v. 23 (Dec. 2005), paid and free versions available. ** Gargoyle – A free OpenWrt-based Linux distribution for a range of Broadcom and Atheros chipset based wireless routers. ** LibreCMC – An FSF-endorsed derivation of OpenWRT with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple Community
The Apple community is a group of people interested in Apple Inc. and its products, who report information in various media. Generally this has evolved into a proliferation of websites, but latterly has also expanded into podcasts (both audio and video), either speculating on rumors about future product releases, simply report Apple-related news stories, or have discussions about Apple's products and how to use them. Such stories and discussions may include topics related to physical products like the Macintosh and iOS devices (e.g., the iPhone, iPod, and iPad); software and operating systems, like Final Cut Pro, Logic Pro X, iWork, iOS, and macOS; or even services Apple offers like iCloud, iTunes Store, or Apple Music. Apple enjoys a cult-like following for its platforms, especially following the massive increase in popularity for the brand brought about by the huge increase in sales for all its products that started around the time the company introduced the original iPod in la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point-to-point Protocol Over Ethernet
The Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) is a network protocol for encapsulating Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) frames inside Ethernet frames. It appeared in 1999, in the context of the boom of DSL as the solution for tunneling packets over the DSL connection to the ISP's IP network, and from there to the rest of the Internet. A 2005 networking book noted that "Most DSL providers use PPPoE, which provides authentication, encryption, and compression." Typical use of PPPoE involves leveraging the PPP facilities for authenticating the user with a username and password, predominately via the PAP protocol and less often via CHAP. Around 2000, PPPoE was also starting to become a replacement method for talking to a modem connected to a computer or router over an Ethernet LAN displacing the older method, which had been USB. This use-case, connecting routers to modems over Ethernet is still extremely common today. On the customer-premises equipment, PPPoE may be implemente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Machine (macOS)
Time Machine is the backup mechanism of macOS, the desktop operating system developed by Apple. The software is designed to work with both local storage devices and network-attached disks, and is most commonly used with external disk drives connected using either USB or Thunderbolt. It was first introduced in Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard, which appeared in October 2007 and incrementally refined in subsequent releases of macOS. Time Machine was revamped in macOS 11 Big Sur to support APFS, thereby enabling "faster, more compact, and more reliable backups" than were possible previously. Overview Time Machine creates incremental backups of files that can be restored at a later date. It allows the user to restore the whole system or specific files. It also works within a number of applications such as Mail and iWork, making it possible to restore individual objects (e.g. emails, contacts, text documents, presentations) without leaving the application. According to an Apple support sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NTFS
New Technology File System (NTFS) is a proprietary journaling file system developed by Microsoft. Starting with Windows NT 3.1, it is the default file system of the Windows NT family. It superseded File Allocation Table (FAT) as the preferred filesystem on Windows and is supported in Linux and BSD as well. NTFS reading and writing support is provided using a free and open-source kernel implementation known as NTFS3 in Linux and the NTFS-3G driver in BSD. By using the convert command, Windows can convert FAT32/16/12 into NTFS without the need to rewrite all files. NTFS uses several files typically hidden from the user to store metadata about other files stored on the drive which can help improve speed and performance when reading data. Unlike FAT and High Performance File System (HPFS), NTFS supports access control lists (ACLs), filesystem encryption, transparent compression, sparse files and file system journaling. NTFS also supports shadow copy to allow backups of a system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NetBSD
NetBSD is a free and open-source Unix operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). It was the first open-source BSD descendant officially released after 386BSD was forked. It continues to be actively developed and is available for many platforms, including servers, desktops, handheld devices, and embedded systems. The NetBSD project focuses on code clarity, careful design, and portability across many computer architectures. Its source code is publicly available and permissively licensed. History NetBSD was originally derived from the 4.3BSD-Reno release of the Berkeley Software Distribution from the Computer Systems Research Group of the University of California, Berkeley, via their Net/2 source code release and the 386BSD project. The NetBSD project began as a result of frustration within the 386BSD developer community with the pace and direction of the operating system's development. The four founders of the NetBSD project, Chris Demetriou, Theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VxWorks
VxWorks is a real-time operating system (or RTOS) developed as proprietary software by Wind River Systems, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Aptiv. First released in 1987, VxWorks is designed for use in embedded systems requiring real-time, deterministic performance and, in many cases, safety and security certification for industries such as aerospace and defense, medical devices, industrial equipment, robotics, energy, transportation, network infrastructure, automotive, and consumer electronics.VxWorks Goes 64-bit", Electronic Design, March 25, 2011 VxWorks supports AMD/Intel architecture, POWER architecture, ARM architectures and RISC-V. The RTOS can be used in multicore |
Server Message Block
Server Message Block (SMB) is a communication protocol originally developed in 1983 by Barry A. Feigenbaum at IBM and intended to provide shared access to files and printers across nodes on a network of systems running IBM's OS/2. It also provides an authenticated inter-process communication (IPC) mechanism. In 1987, Microsoft and 3Com implemented SMB in LAN Manager for OS/2, at which time SMB used the NetBIOS service atop the NetBIOS Frames protocol as its underlying transport. Later, Microsoft implemented SMB in Windows NT 3.1 and has been updating it ever since, adapting it to work with newer underlying transports: TCP/IP and NetBT. SMB implementation consists of two vaguely named Windows services: "Server" (ID: LanmanServer) and "Workstation" (ID: LanmanWorkstation). It uses NTLM or Kerberos protocols for user authentication. In 1996, Microsoft published a version of SMB 1.0 with minor modifications under the Common Internet File System (CIFS ) moniker. CIFS was compatible w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple Filing Protocol
The Apple Filing Protocol (AFP), formerly AppleTalk Filing Protocol, is a proprietary network protocol, and part of the Apple File Service (AFS), that offers file services for macOS and the classic Mac OS. In Mac OS 9 and earlier, AFP was the primary protocol for file services. The protocol was deprecated starting in OS X 10.9 Mavericks, and AFP Server support was removed in macOS 11 Big Sur. In macOS 10.x, AFP is one of several file services supported, with others including Server Message Block (SMB), Network File System (NFS), File Transfer Protocol (FTP), and WebDAV. AFP currently supports Unicode file names, POSIX and access control list permissions, resource forks, named extended attributes, and advanced file locking. Compatibility AFP versions 3.0 and greater rely exclusively on TCP/IP (port 548) for establishing communication, supporting AppleTalk only as a service discovery protocol. The AFP 2.x family supports both TCP/IP (using Data Stream Interface) and AppleTalk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)