|
Aichi Atsuta
The Aichi AE1A Atsuta (Japanese: or ) was a Japanese licensed version of the German Daimler-Benz DB 601A 12-cylinder liquid-cooled inverted-vee aircraft engine. The Atsuta powered only two models of Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service (IJNAS) aircraft in World War II. The Imperial Japanese Army Air Service (IJAAS) used the same engine (manufactured by Kawasaki as the Kawasaki Ha40) to power its Kawasaki Ki-61 ''Hien'' (Allied reporting name "Tony") fighter. The IJNAS's Atsuta and its IJAAS cousin, the Ha-40 were based on the engine that powered Germany's Messerschmitt Bf 109E fighter.Monogram Close-Up 13 Design and development Aichi receives Daimler-Benz DB 600 license Daimler-Benz granted Aichi Kokuki KK, a part of the Aichi Clock and Electric Co. (Aichi Tokei Denki KK), a license to manufacture the DB 600A through D models in November, 1936. At that time the Aichi Aircraft Company was building only the Nakajima Kotobuki 9-cylinder air-cooled radial engine at its Atsuta Engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tight by piston rings. In an engine, its purpose is to transfer force from expanding gas in the cylinder to the crankshaft via a piston rod and/or connecting rod. In a pump, the function is reversed and force is transferred from the crankshaft to the piston for the purpose of compressing or ejecting the fluid in the cylinder. In some engines, the piston also acts as a valve by covering and uncovering ports in the cylinder. __TOC__ Piston engines Internal combustion engines An internal combustion engine is acted upon by the pressure of the expanding combustion gases in the combustion chamber space at the top of the cylinder. This force then acts downwards through the connecting rod and onto the crankshaft. The connecting rod is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagoya
is the largest city in the Chūbu region, the fourth-most populous city and third most populous urban area in Japan, with a population of 2.3million in 2020. Located on the Pacific coast in central Honshu, it is the capital and the most populous city of Aichi Prefecture, and is one of Japan's major ports along with those of Tokyo, Osaka, Kobe, Yokohama, and Chiba. It is the principal city of the Chūkyō metropolitan area, which is the third-most populous metropolitan area in Japan with a population of 10.11million in 2020. In 1610, the warlord Tokugawa Ieyasu, a retainer of Oda Nobunaga, moved the capital of Owari Province from Kiyosu to Nagoya. This period saw the renovation of Nagoya Castle. The arrival of the 20th century brought a convergence of economic factors that fueled rapid growth in Nagoya, during the Meiji Restoration, and became a major industrial hub for Japan. The traditional manufactures of timepieces, bicycles, and sewing machines were followed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature, and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been leached by the action of water from the Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in soap manufacture, and sodium chloride (edible salt) is a de-icing agent and a nutrient for animals inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yokosuka R2Y
The Yokosuka R2Y ''Keiun'' (景雲 - "Cirrus Cloud") was a prototype reconnaissance aircraft built in Japan late in World War II. Design and development Commissioned for the Imperial Japanese Navy after the R1Y design was cancelled due to its disappointing performance estimates, the R2Y used coupled engines driving a single propeller and also featured a tricycle undercarriage. Completed in April 1945, the prototype made a short flight on 8 May, but was destroyed in a US air raid only a few days later, thus ending development. A proposal was also made to develop the R2Y into a turbojet-powered light bomber by replacing its piston engines with two Mitsubishi Ne-330 The is a group of autonomous Japanese multinational companies in a variety of industries. Founded by Yatarō Iwasaki in 1870, the Mitsubishi Group historically descended from the Mitsubishi zaibatsu, a unified company which existed from 1870 ...s. Designated the R2Y2 ''Keiun Kai'', was not constructed before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Aircraft Engine Identification Systems
Japanese aero-engines for military aircraft were given a wide variety of designations depending on the customer. This led to much confusion, particularly among the Allied forces, where a single engine type could have up to six different designations. This situation emerged because of the almost total lack of co-operation in weapons procurement between the IJAAS (大日本帝國陸軍航空隊 - Dai-Nippon Teikoku Rikugun Kokutai - Imperial Japanese Army Air Service) and the IJNAS (大日本帝國海軍航空隊 - Dai-Nippon Teikoku Kaigun Koukuu-tai - Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service). Engines could have designations in any or all of these designation systems: ;Army Hatsudoki experimental designation: (''Kawasaki Ha40'') ;Army long designation: (e.g. ''Army Type 99 900hp Air Cooled Radial'') ;Navy experimental designation: (''Nakajima NK9B'') ;Navy Name designation: ( ''Nakajima Homare 11'') ;Manufacturers designation: (''Nakajima NBA'') ;Unified system introduced by the Ministry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawasaki Ha-40
The Kawasaki Ha40, also known as the Army Type 2 1,100 hp Liquid Cooled In-line and Ha-60, was a license-built Daimler-Benz DB 601Aa 12-cylinder liquid-cooled inverted-vee aircraft engine. The Imperial Japanese Army Air Service (IJAAS) selected the engine to power its Kawasaki Ki-61 fighter. Design and development The Daimler-Benz DB 601Aa was a development of the earlier DB 600, with direct fuel injection replacing the carburetor. Like all DB 601s, it had a 33.9-litre displacement. The first prototype with the direct fuel injection was test run in 1935, and an order for 150 engines was placed in February 1937. A manufacturing license was granted to Aichi for the production of this engine for the Imperial Japanese Navy as the Atsuta and to Kawasaki for production of this engine for the IJAAS as the Ha40. Under the 1944 Unified System, this engine was re-designated as the Kawasaki Ha-60. The Kawasaki Ha40 and the Aichi Atsuta were based on the engine that powered Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freeman Army Airfield
: ''For the civil use of this facility after 1946, see Freeman Municipal Airport '' Freeman Army Airfield is an inactive United States Army Air Forces base. It is located south-southwest of Seymour, Indiana. The base was established in 1942 as a pilot training airfield. It was also the first military helicopter pilot training airfield. In 1944, black bomber pilots were trained at Freeman, and it was the scene of a racial incident that outraged many Americans and led to the military re-evaluating its racial policies. After the war, captured German, Italian and Japanese aircraft were brought to the base for evaluation and testing. It was closed in 1946. History Freeman Army Airfield was named in honor of Captain Richard S. Freeman. A native of Indiana and 1930 graduate of West Point, he was awarded the Distinguished Flying Cross, was awarded the Mackay Trophy, and was one of the pioneers of the Army Air Mail Service. Captain Freeman was killed on 6 February 1941 in the cra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright Field
Wilbur Wright Field was a military installation and an airfield used as a World War I pilot, mechanic, and armorer training facility and, under different designations, conducted United States Army Air Corps and Air Forces flight testing. Located near Riverside, Ohio, the site is officially "Area B" of Wright-Patterson Air Force Base and includes the National Museum of the United States Air Force built on the airfield. History World War I Wilbur Wright Field was established in 1917 for World War I on of land adjacent to the Mad River which included the 1910 Wright Brothers' Huffman Prairie Flying Field and that was leased to the Army by the Miami Conservancy District. Logistics support to Wilbur Wright Field was by the adjacent Fairfield Aviation General Supply Depot established in January 1918 and which also supplied three other Midwest Signal Corps aviation schools. A Signal Corps Aviation School began in June 1917 for providing combat pilots to the Western Front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Materiel Command
Air Materiel Command (AMC) was a United States Army Air Forces and United States Air Force command. Its headquarters was located at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio. In 1961, the command was redesignated the Air Force Logistics Command with some of its functions transferred to the new Air Force Systems Command. History The logistics function can be traced before the earliest days of the Air Service, when the Equipment Division of the U.S. Army Signal Corps established a headquarters for its new Airplane Engineering Department at McCook Field, Dayton, Ohio. Airplane Engineering Department The Airplane Engineering Department was established by the Equipment Division of the U.S. Army Signal Corps in 1917 for World War I experimental engineering. The department had a 1917 Foreign Data Section, and the Airplane Engineering Department was on McCook Field at Dayton, Ohio. McCook Field established the Air School of Application in 1919 and after WW I, the department was re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
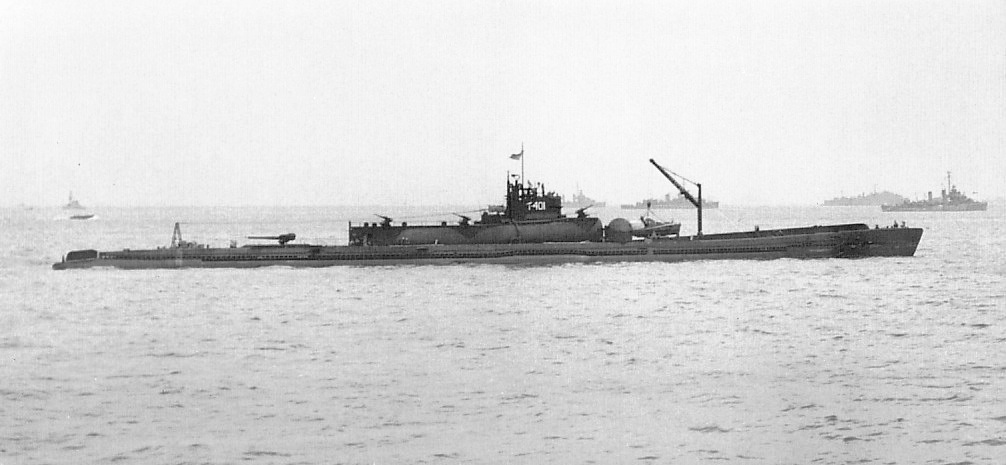
I-400-class Submarine
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) submarines were the largest submarines of World War II and remained the largest ever built until the construction of nuclear ballistic missile submarines in the 1960s. The IJN called this type of submarine . The type name was shortened to . They were submarine aircraft carriers able to carry three Aichi M6A ''Seiran'' aircraft underwater to their destinations. They were designed to surface, launch their planes, then quickly dive again before they were discovered. They also carried torpedoes for close-range combat. The ''I-400'' class was designed with the range to travel anywhere in the world and return. A fleet of 18 boats was planned in 1942, and work started on the first in January 1943 at the Kure, Hiroshima arsenal. Within a year the plan was scaled back to five, of which only three ( I-400 at Kure, and and I-402 at Sasebo) were completed. Origins The ''I-400'' class was the brainchild of Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto, Commander-in-Chief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawasaki Ki-100
The Kawasaki Ki-100 (''キ100'') is a single-seat single-engine monoplane fighter aircraft used by the Imperial Japanese Army Air Service during World War II. The Japanese Army designation was . It was not assigned an Allied code name. 275 Ki-100s were modified from Ki-61s as an emergency measure to accept a 14-cylinder Mitsubishi Ha-112-II radial engine in place of the original Kawasaki Ha-40 inverted V-12 inline engine which resulted in one of the best interceptors used by the Army during the war. It combined excellent power and maneuverability,Ethell, 1995, p.83 and from the first operational missions in March 1945 until the end of the war, it performed better than most IJAAF fighters against both United States Army Air Forces Boeing B-29 Superfortress bombers and North American P-51 Mustang fighters as well as U.S. Navy Grumman F6F Hellcat carrier fighters.Picarella, 2005, pp.76–77 A newly built variant, the Ki-100-Ib, was produced with a cut down rear fuselage during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |