|
Agápē
In Christianity, agape (; ) is "the highest form of love, charity" and "the love of God for man and of man for God". This is in contrast to philia, brotherly love, or philautia, self-love, as it embraces a deep and profound sacrificial love that transcends and persists regardless of circumstance. The verb form goes as far back as Homer, translated literally as affection, as in "greet with affection" and "show affection for the dead". Other ancient authors have used forms of the word to denote love of a spouse or family, or affection for a particular activity, in contrast to eros (an affection of a sexual nature). In the New Testament, it allegedly refers to the covenant love of God for humans, as well as the human reciprocal love for God; the term necessarily extends to the love of one's fellow human beings. Some contemporary writers have sought to extend the use of ''agape'' into non-religious contexts. The concept of ''agape'' has been widely examined within its Christian co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
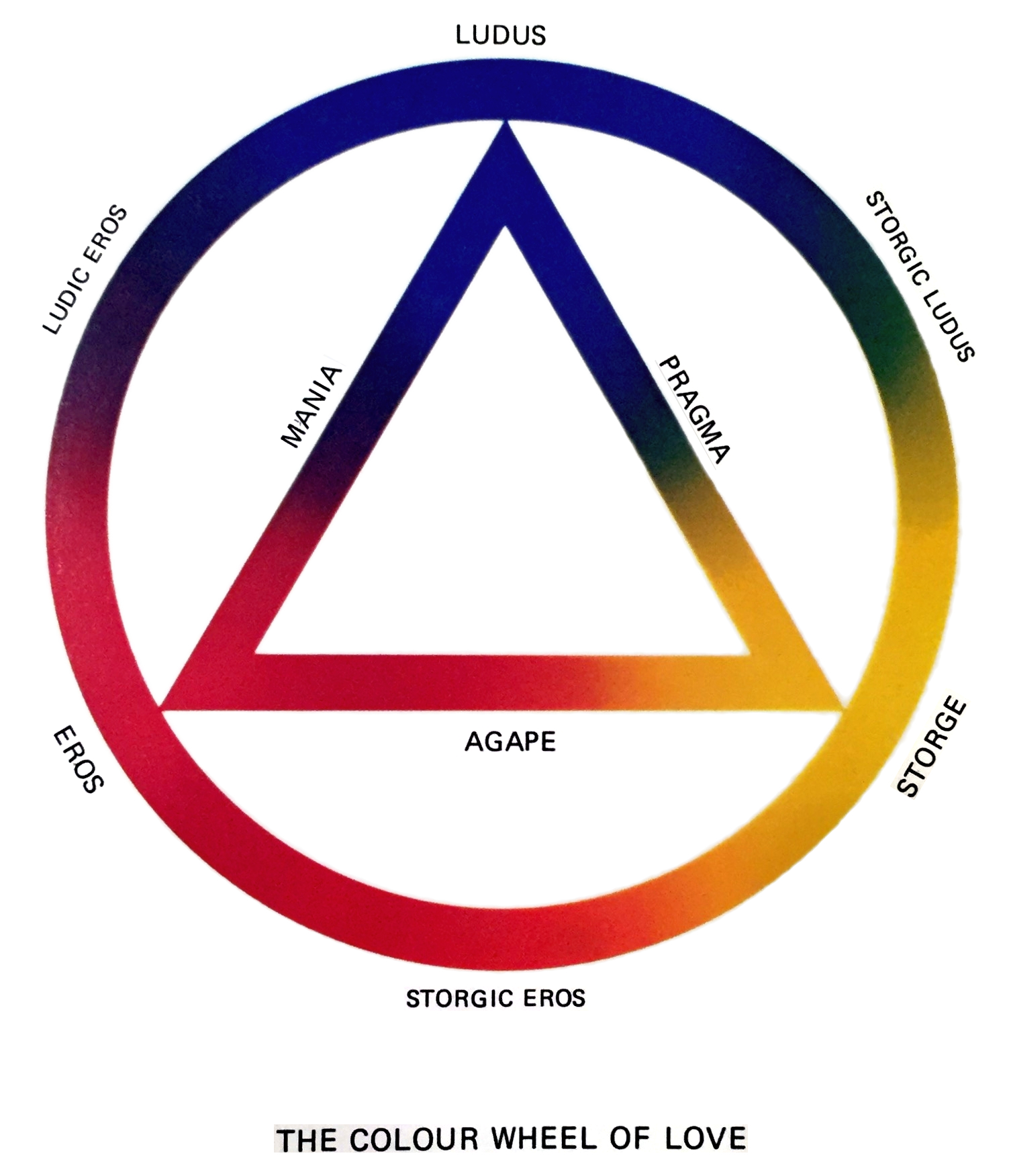
Greek Words For Love
Ancient Greek philosophy differentiates main conceptual forms and distinct words for the Modern English word love: ''agápē'', ''érōs'', ''philía'', ''philautía'', ''storgē'', and ''xenía''. List of concepts Though there are more Greek words for love, variants and possibly subcategories, a general summary considering these Ancient Greek concepts is as follows: * '' Agápe'' ( grc, ἀγάπη, agápē, label=none) means "love: esp. brotherly love, charity; the love of God for person and of person for God". ''Agape'' is used in ancient texts to denote feelings for one's children and the feelings for a spouse, and it was also used to refer to a love feast. Agape is used by Christians to express the unconditional love of God for His children. This type of love was further explained by Thomas Aquinas as "to will the good of another". * '' Éros'' ( grc, ἔρως, érōs, label=none) means "love, mostly of the sexual passion". The Modern Greek word "''erotas''" means "inti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Four Loves
''The Four Loves'' is a 1960 book by C. S. Lewis which explores the nature of love from a Christian and philosophical perspective through thought experiments. The book was based on a set of radio talks from 1958 which had been criticised in the U.S. at the time for their frankness about sex. Need/gift love Taking his start from St. John's words "God is Love", Lewis initially thought to contrast "Need-love" (such as the love of a child for its mother) and "Gift-love" (epitomized by God's love for humanity), to the disparagement of the former. However, he swiftly happened on the insight that the natures of even these basic categorizations of love are more complicated than they at first seemed: a child's need for parental comfort is a necessity, not a selfish indulgence, while conversely parental Gift-love in excessive form can be a perversion of its own. Pleasures Lewis continues his examination by exploring the nature of pleasure, distinguishing Need-pleasures (such as wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus is the Son of God, whose coming as the messiah was prophesied in the Hebrew Bible (called the Old Testament in Christianity) and chronicled in the New Testament. Christianity began as a Second Temple Judaic sect in the 1st century Hellenistic Judaism in the Roman province of Judea. Jesus' apostles and their followers spread around the Levant, Europe, Anatolia, Mesopotamia, the South Caucasus, Ancient Carthage, Egypt, and Ethiopia, despite significant initial persecution. It soon attracted gentile God-fearers, which led to a departure from Jewish customs, and, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bauer's Lexicon
''Bauer's Lexicon'' (also ''Bauer Lexicon'', ''Bauer's Greek Lexicon'', and ''Bauer, Arndt and Gingrich'') is among the most highly respected dictionaries of Biblical Greek. The producers of the German forerunner are Erwin Preuschen and Walter Bauer. The English edition is ''A Greek-English Lexicon of the New Testament and Other Early Christian Literature'' (the 3rd edition was published in 2001 by the University of Chicago Press, ). History ''The origin'' may be traced to Erwin Preuschen's ''Vollständiges Griechisch-Deutsches Handwörterbuch zu den Schriften des Neuen Testaments und der übrigen urchristlichen Literatur'' (1910). Walter Bauer extensively revised this work, as ''Griechisch-deutsches Wörterbuch zu den Schriften des Neuen Testaments und der übrigen urchristlichen Literatur''. ''The first English edition'' was published in 1957. It is based on the fourth German edition (1949-1952) of Walter Bauer’s Greek-German lexicon (Bauer lexicon). The project began in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shema Yisrael
''Shema Yisrael'' (''Shema Israel'' or ''Sh'ma Yisrael''; he , שְׁמַע יִשְׂרָאֵל ''Šəmaʿ Yīsrāʾēl'', "Hear, O Israel") is a Jewish prayer (known as the Shema) that serves as a centerpiece of the morning and evening Jewish prayer, Jewish prayer services. Its first verse encapsulates the Monotheism , monotheistic essence of Judaism: "Hear, O Israel: YHWH is our God, YHWH is one" (), found in . The first part can be translated as either "The our God" or "The is our God", and the second part as either "the is one" or as "the one " (in the sense of "the alone"), since Biblical Hebrew, Hebrew does not normally use a Copula (linguistics), copula in the present tense, so translators must decide by inference whether one is appropriate in English. The word used for "the " is the tetragrammaton YHWH. Observant Jews consider the ''Shema'' to be the most important part of the prayer service in Judaism, and its twice-daily recitation as a ''mitzvah'' (religious co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions. Judaism is considered by religious Jews to be the expression of the covenant that God established with the Israelites, their ancestors. It encompasses a wide body of texts, practices, theological positions, and forms of organization. The Torah, as it is commonly understood by Jews, is part of the larger text known as the ''Tanakh''. The ''Tanakh'' is also known to secular scholars of religion as the Hebrew Bible, and to Christians as the " Old Testament". The Torah's supplemental oral tradition is represented by later texts s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Commandment
The Great Commandment (or Greatest Commandment) is a name used in the New Testament to describe the first of two commandments cited by Jesus in , , and in answer to him in : Most Christian denominations consider these two commandments as, together, forming the core of the Christian religion. New Testament accounts Gospel of Matthew Gospel of Mark In the Gospel of Mark, the Shema is included: Gospel of Luke Old Testament references Leviticus 19:18 Deuteronomy Love the Lord thy God Matthew Henry sums up the question of which is the great commandment: Adam Clarke, in his ''Commentary on the Bible'', wrote: "Thou shalt love the Lord thy God" is explained to mean "Act in such a manner that God will be beloved by all His creatures." Consequently, Israel, being, as the priest-people, enjoined like the Aaronite priest to sanctify the name of God and avoid whatever tends to desecrate it (Lev. xxii. 32), is not only obliged to give his life as witness or martyr for the mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious leader; he is the central figure of Christianity, the world's largest religion. Most Christians believe he is the incarnation of God the Son and the awaited Messiah (the Christ) prophesied in the Hebrew Bible. Virtually all modern scholars of antiquity agree that Jesus existed historically. Research into the historical Jesus has yielded some uncertainty on the historical reliability of the Gospels and on how closely the Jesus portrayed in the New Testament reflects the historical Jesus, as the only detailed records of Jesus' life are contained in the Gospels. Jesus was a Galilean Jew who was circumcised, was baptized by John the Baptist, began his own ministry and was often referred to as "rabbi". Jesus debated with fellow Jews on ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christian message ("the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words and deeds of Jesus, culminating in his trial and death and concluding with various reports of his post-resurrection appearances. Modern scholars are cautious of relying on the gospels uncritically, but nevertheless, they provide a good idea of the public career of Jesus, and critical study can attempt to distinguish the original ideas of Jesus from those of the later authors. The four canonical gospels were probably written between AD 66 and 110. All four were anonymous (with the modern names added in the 2nd century), almost certainly none were by eyewitnesses, and all are the end-products of long oral and written transmission. Mark was the first to be written, using a variety of sources. The authors of Matthew and Luke both independently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chesed
( he, חֶסֶד, also Romanized: ) is a Hebrew word that means 'kindness or love between people', specifically of the devotional piety of people towards God as well as of love or mercy of God towards humanity. It is frequently used in Psalms in the latter sense, where it is traditionally translated "loving kindness" in English translations. In Jewish theology it is likewise used of God's love for the Children of Israel, and in Jewish ethics it is used for love or charity between people. in this latter sense of 'charity' is considered a virtue on its own, and also for its contribution to ''tikkun olam'' (repairing the world). It is also considered the foundation of many religious commandments practiced by traditional Jews, especially interpersonal commandments. is also one of the ten Sephirot on the Kabbalistic Tree of Life. It is given the association of kindness and love, and is the first of the emotive attributes of the . Etymology and translations The root has a prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenosis
In Christian theology, ''kenosis'' () is the 'self-emptying' of Jesus. The word () is used in Philippians 2:7: " made himself nothing" (NIV), or " eemptied himself" (NRSV), using the verb form (), meaning "to empty". The exact meaning varies among theologians. The less controversial meaning is that he emptied his own desires and becoming entirely receptive to God's divine will, "obedient to the point of death— even death on a cross." Philippians encourages other Christians to be similarly willing to submit to divine will, even if it comes at great personal cost. The phrase is also used to explain the human side of Jesus: that Jesus, to truly live as a mortal, had to have voluntarily bound use of his divine powers in some way, emptying himself. Philippians says that "though esuswas in the form of God, edid not regard equality with God as something to be exploited," suggesting that Jesus was not "abusing" his divine status to avoid the implications of a mortal life. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |