|
Agrochola Lychnidis
''Agrochola lychnidis'', the beaded chestnut, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Michael Denis and Ignaz Schiffermüller in 1775. It is distributed throughout the whole of Europe from Ireland to the Urals. It also occurs in western North Africa and Asia Minor. The wingspan is 30–35 mm. Forewing bright rufous or reddish ochreous with the veins paler, often dusted with darker; inner and outer lines double, dark, with the centre rufous, often very faint, but always marked by black spots on costa; submarginal line preceded by a row of dark lunules between the veins and by a dark bar at costa; median shade distinct; stigmata blackish, distinct, especially the narrow oblique orbicular; hindwing dark grey, the fringe rufous. This species varies in colour exceedingly; the brighter rufous specimens, with pale veins, represent typical ''lychnidis'' F.; the duller brownish forms, also with pale veins, are ''pistacina'' F.; - ''rubetra'' Esper the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Denis
Johann Nepomuk Cosmas Michael Denis, also: ''Sined the Bard'', (27 September 1729 – 29 September 1800) was an Austrian Catholic priest and Jesuit, who is best known as a poet, bibliographer, and lepidopterist. Life Denis was born at Schärding, located on the Inn (river), Inn River, then ruled by the Electorate of Bavaria, in 1729, the son of Johann Rudolph Denis, who taught him Latin at an early age. At the age of ten, he was enrolled to be educated by the Society of Jesus, Jesuits at their college in Passau. After completing his studies in 1747, he entered the novitiate of the Society of Jesus in Vienna. In 1749, following this initial formation period, Denis was sent to carry his period of regency (Jesuit), Regency at Jesuit colleges in Graz and Klagenfurt. He was Holy Orders, ordained a Catholic priest, priest in 1757. Two years later, he was appointed professor at the Theresianum in Vienna, a Jesuit college. After the suppression of the Jesuits in 1773, and the subsequent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History Museum, London
The Natural History Museum in London is a museum that exhibits a vast range of specimens from various segments of natural history. It is one of three major museums on Exhibition Road in South Kensington, the others being the Science Museum and the Victoria and Albert Museum. The Natural History Museum's main frontage, however, is on Cromwell Road. The museum is home to life and earth science specimens comprising some 80 million items within five main collections: botany, entomology, mineralogy, palaeontology and zoology. The museum is a centre of research specialising in taxonomy, identification and conservation. Given the age of the institution, many of the collections have great historical as well as scientific value, such as specimens collected by Charles Darwin. The museum is particularly famous for its exhibition of dinosaur skeletons and ornate architecture—sometimes dubbed a ''cathedral of nature''—both exemplified by the large ''Diplodocus'' cast that domina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moths Of Asia
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species. Differences between butterflies and moths While the butterflies form a monophyletic group, the moths, comprising the rest of the Lepidoptera, do not. Many attempts have been made to group the superfamilies of the Lepidoptera into natural groups, most of which fail because one of the two groups is not monophyletic: Microlepidoptera and Macrolepidoptera, Heterocera Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of w ... and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moths Described In 1775
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species. Differences between butterflies and moths While the butterflies form a monophyletic group, the moths, comprising the rest of the Lepidoptera, do not. Many attempts have been made to group the superfamilies of the Lepidoptera into natural groups, most of which fail because one of the two groups is not monophyletic: Microlepidoptera and Macrolepidoptera, Heterocera and Rhopalocera, Jugatae and Frenatae, Monotrysia and Ditrysia.Scoble, MJ 1995. The Lepidoptera: Form, function and diversity. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 404 p. Although the rules for distinguishing moths from butterflies are not well establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moths Of Europe
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species. Differences between butterflies and moths While the butterflies form a monophyletic group, the moths, comprising the rest of the Lepidoptera, do not. Many attempts have been made to group the superfamilies of the Lepidoptera into natural groups, most of which fail because one of the two groups is not monophyletic: Microlepidoptera and Macrolepidoptera, Heterocera and Rhopalocera, Jugatae and Frenatae, Monotrysia and Ditrysia.Scoble, MJ 1995. The Lepidoptera: Form, function and diversity. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 404 p. Although the rules for distinguishing moths from butterflies are not well establis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moths Of Africa
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species. Differences between butterflies and moths While the butterflies form a monophyletic group, the moths, comprising the rest of the Lepidoptera, do not. Many attempts have been made to group the superfamilies of the Lepidoptera into natural groups, most of which fail because one of the two groups is not monophyletic: Microlepidoptera and Macrolepidoptera, Heterocera and Rhopalocera, Jugatae and Frenatae, Monotrysia and Ditrysia.Scoble, MJ 1995. The Lepidoptera: Form, function and diversity. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 404 p. Although the rules for distinguishing moths from butterflies are not well establis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agrochola
''Agrochola'' is a genus of moths of the family Noctuidae. The genus was erected by Jacob Hübner in 1821. Species * '' Agrochola agnorista'' Boursin, 1955 * '' Agrochola albimacula'' Kononenko, 1978 * '' Agrochola albirena'' Boursin, 1956 * '' Agrochola antiqua'' (Hacker, 1993) * '' Agrochola approximata'' (Hampson, 1906) * '' Agrochola attila'' Hreblay & Ronkay, 1999 * '' Agrochola azerica'' Ronkay & Gyulai, 1997 * '' Agrochola blidaensis'' (Stertz, 1915) * ''Agrochola circellaris'' (Hufnagel, 1766) – the brick * '' Agrochola deleta'' (Staudinger, 1881) * '' Agrochola disrupta'' Wiltshire, 1952 * '' Agrochola dubatolovi'' Varga & Ronkay, 1991 * '' Agrochola egorovi'' (Bang-Haas, 1934) * '' Agrochola evelina'' (Butler, 1879) * '' Agrochola fibigeri'' Hacker & Moberg, 1989 * '' Agrochola flavirena'' (Moore, 1881) * '' Agrochola gorza'' Hreblay & Ronkay, 1999 * '' Agrochola gratiosa'' (Staudinger, 1881) * '' Agrochola haematidea'' (Duponchel, 1827) – southern chestnut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
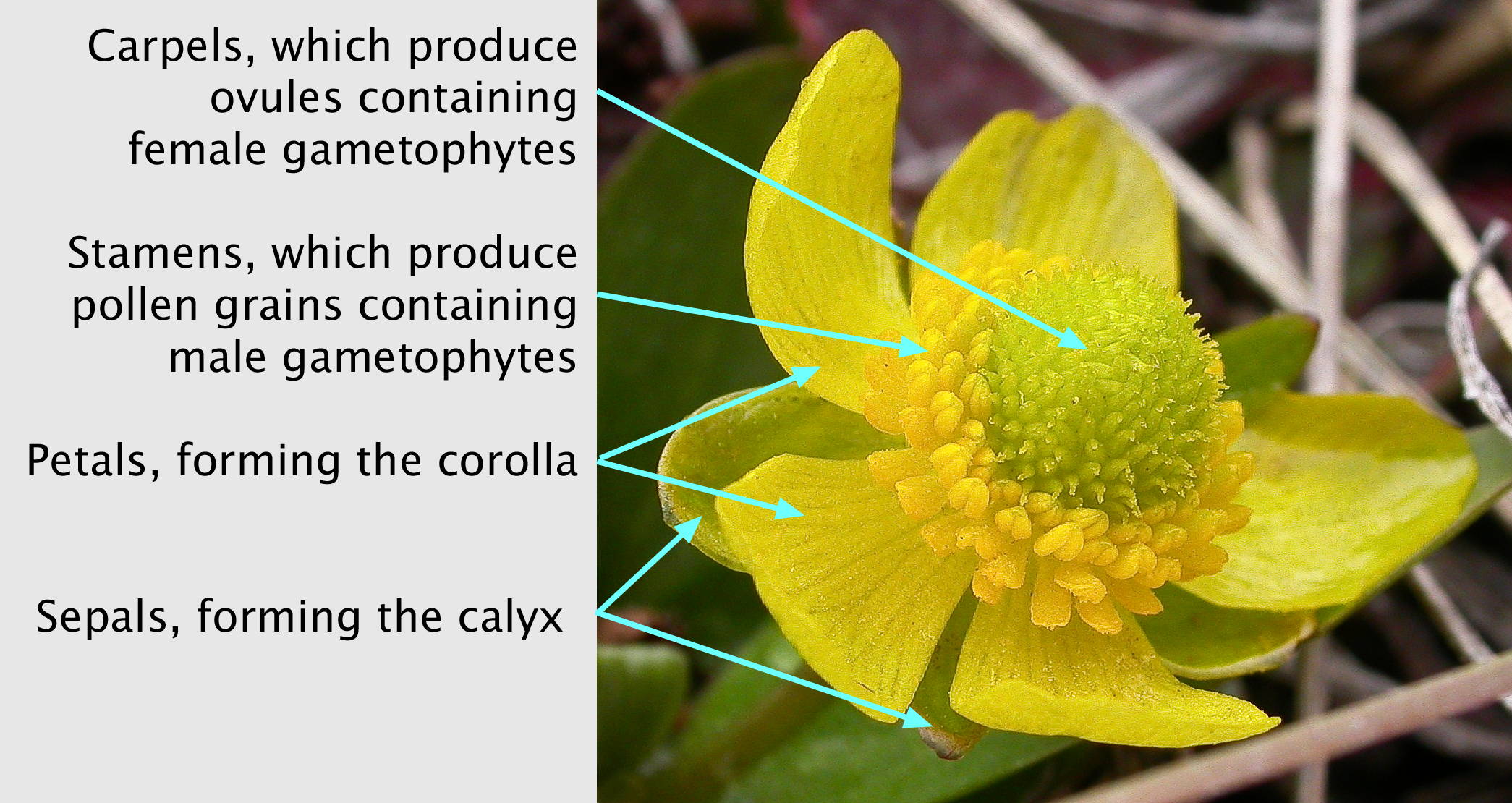
Ranunculus
''Ranunculus'' is a large genus of about almost 1700 to more than 1800 species of flowering plants in the family Ranunculaceae. Members of the genus are known as buttercups, spearworts and water crowfoots. The genus is distributed in Europe, North America and South America. The familiar and widespread buttercup of gardens throughout Northern Europe (and introduced elsewhere) is the creeping buttercup ''Ranunculus repens'', which has extremely tough and tenacious roots. Two other species are also widespread, the bulbous buttercup ''Ranunculus bulbosus'' and the much taller meadow buttercup ''Ranunculus acris''. In ornamental gardens, all three are often regarded as weeds. Buttercups usually flower in the spring, but flowers may be found throughout the summer, especially where the plants are growing as opportunistic colonizers, as in the case of garden weeds. The water crowfoots (''Ranunculus'' subgenus ''Batrachium''), which grow in still or running water, are sometimes tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achillea
''Achillea'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, known colloquially as yarrows. The plants typically have frilly leaves. The common name "yarrow" usually refers to '' A. millefolium''. The genus was named after the Greek mythological character Achilles, whose soldiers were said to have used yarrow to treat their wounds; this is reflected by common names such as allheal and bloodwort. The genus is native primarily to Eurasia and North America. Description These plants typically have frilly, hairy, aromatic leaves. The plants show large, flat clusters of small flowers at the top of the stem. The flowers can be white, yellow, orange, pink or red and are generally visited by many insects, and are thus characterised by a generalised pollination system. Taxonomy Carl Linnaeus described the genus in 1753. The common name "yarrow" is usually applied to ''Achillea millefolium'', but may also be used for other species within the genus. Selected species Near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salix
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions. Most species are known as willow, but some narrow-leaved shrub species are called osier, and some broader-leaved species are referred to as sallow (from Old English ''sealh'', related to the Latin word ''salix'', willow). Some willows (particularly arctic and alpine species) are low-growing or creeping shrubs; for example, the dwarf willow (''Salix herbacea'') rarely exceeds in height, though it spreads widely across the ground. Description Willows all have abundant watery bark sap, which is heavily charged with salicylic acid, soft, usually pliant, tough wood, slender branches, and large, fibrous, often stoloniferous roots. The roots are remarkable for their toughness, size, and tenacity to live, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prunus
''Prunus'' is a genus of trees and shrubs, which includes (among many others) the fruits plums, cherries, peaches, nectarines, apricots, and almonds. Native to the North American temperate regions, the neotropics of South America, and the paleotropics of Asia and Africa, 430 different species are classified under ''Prunus''. Many members of the genus are widely cultivated for their fruit and for decorative purposes. ''Prunus'' fruit are drupes, or stone fruits. The fleshy mesocarp surrounding the endocarp is edible while the endocarp itself forms a hard, inedible shell called the pyrena ("stone" or "pit"). This shell encloses the seed (or "kernel") which is edible in many species (such as almonds) but poisonous in others (such as apricots). Besides being eaten off the hand, most ''Prunus'' fruit are also commonly used in processing, such as jam production, canning, drying, and seeds for roasting. Botany Members of the genus can be deciduous or evergreen. A few species ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)