|
Agathe De Rambaud
Agathe de Rambaud was born in Versailles as Agathe-Rosalie Mottet and was baptized in the future cathedral Saint-Louis of Versailles, on 10 December 1764. She died in Aramon, in the ''département'' of Gard, on 19 October 1853. She was the official nurse of the royal children, and particularly in charge of the '' Dauphin'' from 1785 to 1792. Before the French Revolution Rambaud was born the daughter of Louis Melchior Mottet, '' Haut Commissaire'' of the French colonies, and of Jeanne Agathe Le Proux de La Rivière, who was the daughter of a First Commissioner of the French Navy . She was the granddaughter of the Baron Claude Nicolas Louis Mottet de La Motte, officer of the Royal Fox hunt, and the niece of Baron Benoît Mottet de La Fontaine, the last French Governor of Pondicherry. She was also related to Pierre-Jean-Baptiste Chaussard. She was sometimes given the courtesy title of Countess of Ribécourt. She married André Rambaud, a member of the ''bourgeoisie of Marsei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agathe De Rambaud
Agathe de Rambaud was born in Versailles as Agathe-Rosalie Mottet and was baptized in the future cathedral Saint-Louis of Versailles, on 10 December 1764. She died in Aramon, in the ''département'' of Gard, on 19 October 1853. She was the official nurse of the royal children, and particularly in charge of the '' Dauphin'' from 1785 to 1792. Before the French Revolution Rambaud was born the daughter of Louis Melchior Mottet, '' Haut Commissaire'' of the French colonies, and of Jeanne Agathe Le Proux de La Rivière, who was the daughter of a First Commissioner of the French Navy . She was the granddaughter of the Baron Claude Nicolas Louis Mottet de La Motte, officer of the Royal Fox hunt, and the niece of Baron Benoît Mottet de La Fontaine, the last French Governor of Pondicherry. She was also related to Pierre-Jean-Baptiste Chaussard. She was sometimes given the courtesy title of Countess of Ribécourt. She married André Rambaud, a member of the ''bourgeoisie of Marsei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alain Decaux
Alain Decaux (23 July 1925 − 27 March 2016) was a French historian. He was elected to the Académie française on 15 February 1979. In 2005, he was, with others authors as Frédéric Beigbeder, Mohamed Kacimi, Richard Millet and Jean-Pierre Thiollet, among the Beirut Book Fair's main guests in the Beirut International Exhibition & Leisure Center, commonly (BIEL).''Improvisation ''so'' piano'', Jean-Pierre Thiollet, Neva Ed., 2017, p. 277. Bibliography * 1947 ' (Librairie académique Perrin) * 1949 ' (Librairie académique Perrin) * 1951 ' (in collaboration with André Castelot, J.-C. Simard, and J.-F. Chiappe) * 1952 ' (Librairie académique Perrin) * 1952 ' (Librairie académique Perrin) * 1953 ' (Librairie académique Perrin) * 1954 ' (Librairie académique Perrin) * 1954 ' (Librairie académique Perrin) * 1956-1957 ' (in collaboration with Stellio Lorenzi and André Castelot) * 1957 ' (Librairie académique Perrin) * 1957-1966 ' (in collaboration with St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis-Joseph, Dauphin Of France
Louis Joseph Xavier François (22 October 1781 – 4 June 1789) was Dauphin of France as the second child and first son of King Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette. As son of a king of France, he was a '' fils de France'' ("Child of France"). Louis Joseph died at the age of seven from tuberculosis and was succeeded as Dauphin (and thus heir-apparent) by his four-year-old brother Louis Charles. Biography Louis Joseph Xavier François de France was born at the Palace of Versailles on 22 October 1781. He was named after his maternal uncle, Joseph II. The new-born was the long-awaited ''Dauphin'', his father's heir to the throne of France, as the Salic Law, which excluded women from acceding the throne, applied to his elder sister, Marie Thérèse Charlotte, ''Madame Royale''. The birth of Louis Joseph ruined the hopes of his uncle, the ''comte de Provence'', of succeeding his brother Louis XVI. His private household was created upon his birth. He was under the care of Victoire d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Normandy
In the Middle Ages, the duke of Normandy was the ruler of the Duchy of Normandy in north-western Kingdom of France, France. The duchy arose out of a grant of land to the Viking leader Rollo by the French king Charles the Simple, Charles III in 911. In 924 and again in 933, Normandy was expanded by royal grant. Rollo's male-line descendants continued to rule it until 1135. In 1202 the French king Philip Augustus, Philip II declared Normandy a forfeited fief and by 1204 his army had conquered it. It remained a French Province of France, royal province thereafter, still called the Duchy of Normandy, but only occasionally granted to a duke of the royal house as an apanage. Despite both the 13th century loss of mainland Normandy, and the extinction of the duchy itself in modern-day, republican France, in the Channel Islands the monarch of the United Kingdom is regardless still referred to by the title "Duke of Normandy". This is the title used whether the monarch is a king or a queen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis XVII Of France
Louis XVII (born Louis Charles, Duke of Normandy; 27 March 1785 – 8 June 1795) was the younger son of King Louis XVI of France and Queen Marie Antoinette. His older brother, Louis Joseph, Dauphin of France, died in June 1789, a little over a month before the start of the French Revolution. At his brother's death he became the new Dauphin (heir apparent to the throne), a title he held until 1791, when the new constitution accorded the heir apparent the title of Prince Royal. When his father was executed on 21 January 1793, during the middle period of the French Revolution, he automatically succeeded as the king of France, Louis XVII, in the eyes of the royalists. France was by then a republic and since Louis-Charles was imprisoned and died in captivity in June 1795, he never actually ruled. Nevertheless, in 1814 after the Bourbon Restoration, his uncle acceded to the throne and was proclaimed Louis XVIII. Biography Louis-Charles de France was born at the Palace of Ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie Antoinette
Marie Antoinette Josèphe Jeanne (; ; née Maria Antonia Josepha Johanna; 2 November 1755 – 16 October 1793) was the last queen of France before the French Revolution. She was born an archduchess of Austria, and was the penultimate child and youngest daughter of Empress Maria Theresa and Emperor Francis I. She became dauphine of France in May 1770 at age 14 upon her marriage to Louis-Auguste, heir apparent to the French throne. On 10 May 1774, her husband ascended the throne as Louis XVI and she became queen. Marie Antoinette's position at court improved when, after eight years of marriage, she started having children. She became increasingly unpopular among the people, however, with the French ''libelles'' accusing her of being profligate, promiscuous, allegedly having illegitimate children, and harboring sympathies for France's perceived enemies—particularly her native Austria. The false accusations of the Affair of the Diamond Necklace damaged her reputation further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
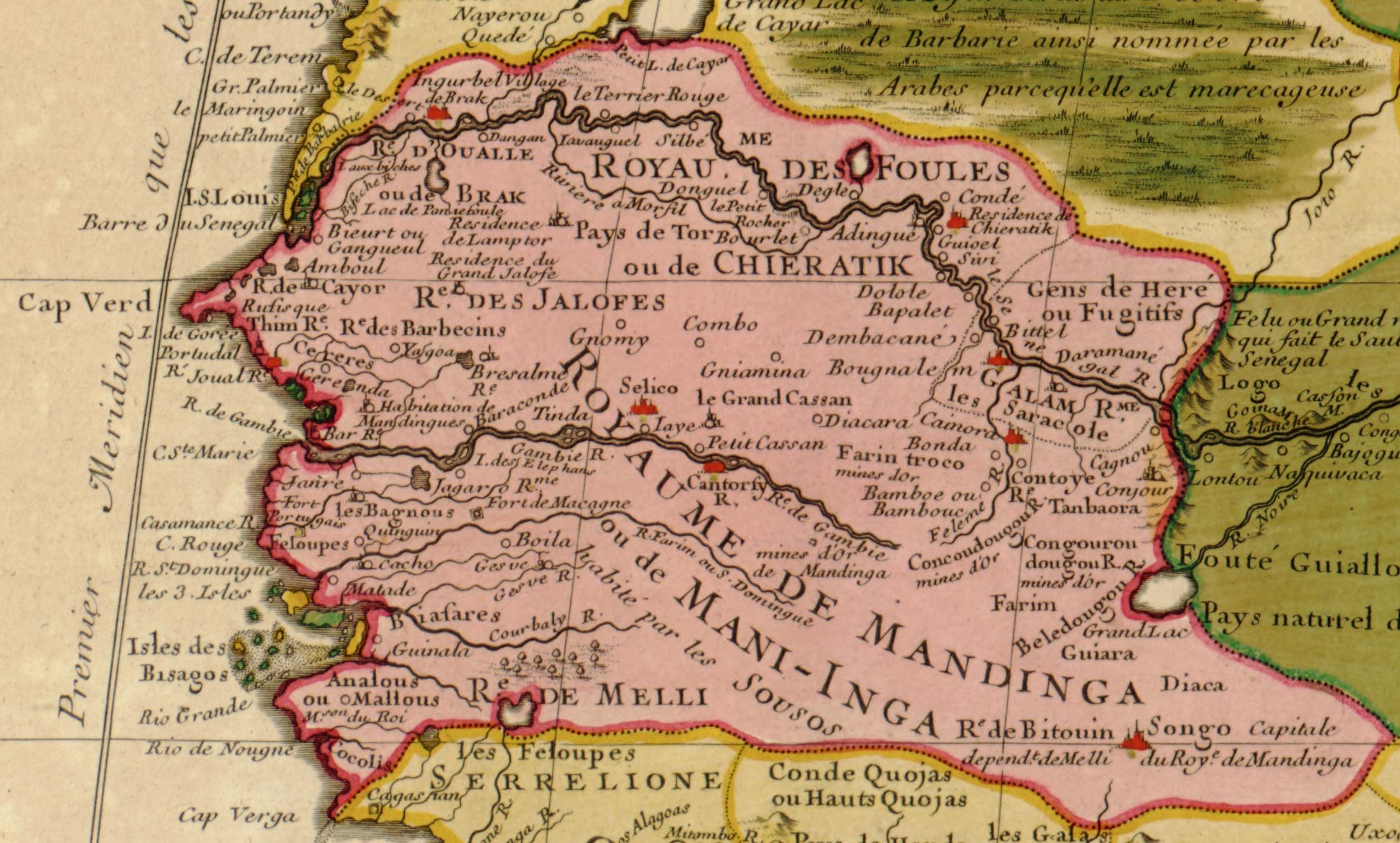
Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Renndaandi Senegaali); Arabic: جمهورية السنغال ''Jumhuriat As-Sinighal'') is a country in West Africa, on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. Senegal is bordered by Mauritania to the north, Mali to the east, Guinea to the southeast and Guinea-Bissau to the southwest. Senegal nearly surrounds the Gambia, a country occupying a narrow sliver of land along the banks of the Gambia River, which separates Senegal's southern region of Casamance from the rest of the country. Senegal also shares a maritime border with Cape Verde. Senegal's economic and political capital is Dakar. Senegal is notably the westernmost country in the mainland of the Old World, or Afro-Eurasia. It owes its name to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Senegal
The history of Senegal is commonly divided into a number of periods, encompassing the prehistoric era, the precolonial period, colonialism, and the contemporary era. Paleolithic The earliest evidence of human life is found in the valley of the Falémé in the south-east. The presence of man in the Lower Paleolithic is attested by the discovery of stone tools characteristic of Acheulean such as hand axes reported by Théodore Monod at the tip of Fann in the peninsula of Cap-Vert in 1938, or cleavers found in the south-east. There were also found stones shaped by the Levallois technique, characteristic of the Middle Paleolithic. Mousterian Industry is represented mainly by scrapers found in the peninsula of Cap-Vert, as well in the low and middle valleys of the Senegal and the Falémé. Some pieces are explicitly linked to hunting, like those found in Tiémassass, near M'Bour, a controversial site that some claim belongs to the Upper Paleolithic, while other argue in favor of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directoire
The Directory (also called Directorate, ) was the governing five-member committee in the French First Republic from 2 November 1795 until 9 November 1799, when it was overthrown by Napoleon Bonaparte in the Coup of 18 Brumaire and replaced by the Consulate. ''Directoire'' is the name of the final four years of the French Revolution. Mainstream historiography also uses the term in reference to the period from the dissolution of the National Convention on 26 October 1795 (4 Brumaire) to Napoleon's coup d’état. The Directory was continually at war with foreign coalitions, including Britain, Austria, Prussia, the Kingdom of Naples, Russia and the Ottoman Empire. It annexed Belgium and the left bank of the Rhine, while Bonaparte conquered a large part of Italy. The Directory established 196 short-lived sister republics in Italy, Switzerland and the Netherlands. The conquered cities and states were required to send France huge amounts of money, as well as art treasures, which we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French First Republic
In the history of France, the First Republic (french: Première République), sometimes referred to in historiography as Revolutionary France, and officially the French Republic (french: République française), was founded on 21 September 1792 during the French Revolution. The First Republic lasted until the declaration of the First Empire on 18 May 1804 under Napoléon Bonaparte, although the form of the government changed several times. This period was characterized by the fall of the monarchy, the establishment of the National Convention and the Reign of Terror, the Thermidorian Reaction and the founding of the Directory, and, finally, the creation Creation may refer to: Religion *''Creatio ex nihilo'', the concept that matter was created by God out of nothing * Creation myth, a religious story of the origin of the world and how people first came to inhabit it * Creationism, the belief tha ... of the French Consulate, Consulate and Napoleon's rise to power. End of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges René Le Peley De Pléville
Georges-René Le Peley de Pléville (29 June 1726 in Granville – 2 October 1805 in Paris) was the governor of the port of Marseilles, a French admiral, minister for the navy and the colonies from 15 July 1797 to 27 April 1798, a senator, a knight of the Order of St Louis and the Order of Cincinnatus, and one of the first Grand officiers of the Légion d'honneur. Life Origins and youth His father was Hervé Le Peley, seigneur de Pléville, a captain in the merchant navy, and his mother was the daughter of the seigneur du Saussey in the parish of Lingreville. Thus de Pléville was attracted to the sea and ships early in his life. Orphaned whilst very young, he ran away from the collège at Coutances to get himself engaged on a ship to Newfoundland in 1738. His uncle - intending him for the priesthood - asked the ship's captain to put de Pléville off life at sea. His first voyage as a pilotin was therefore particularly hard. At Newfoundland an old friend of his father wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |