|
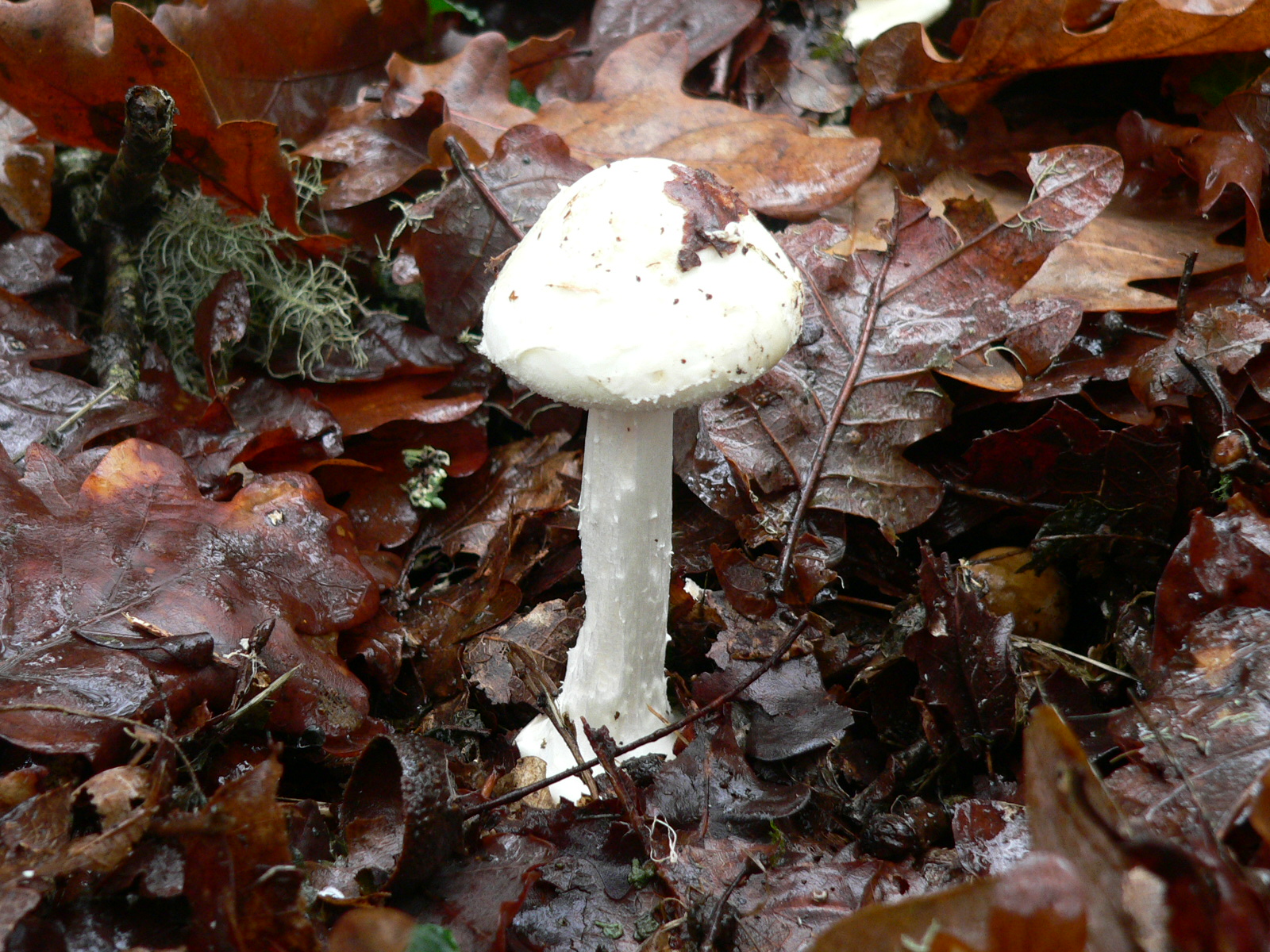
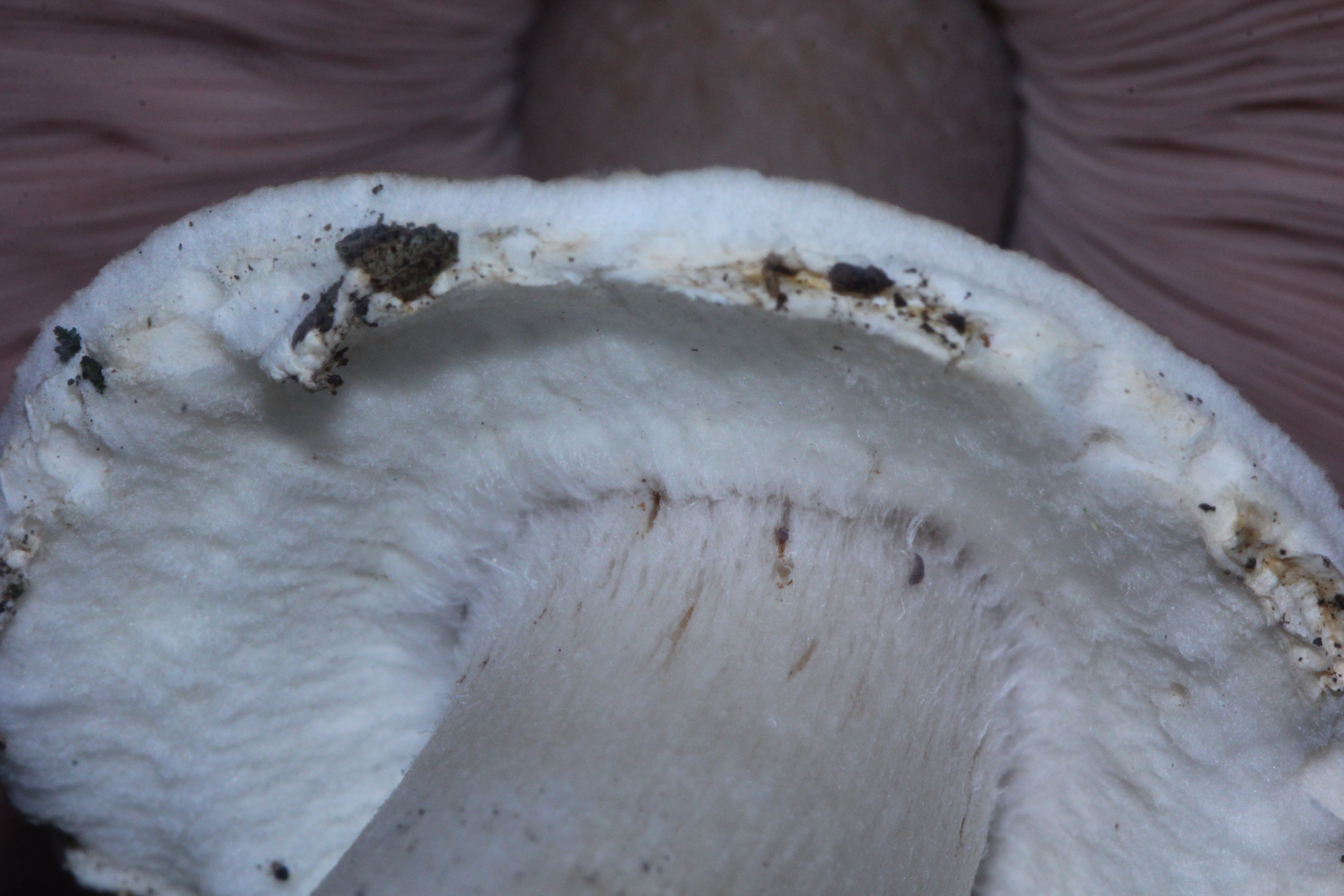
Agaricus Freirei
''Agaricus freirei'' is a species of fungus in the family Agaricaceae. ''Agaricus freirei'' closely resembles '' A. hondensis'', and, based on similarities in DNA sequence DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. Th ...s, is a close relative. Described as new to science in 2001, ''A. freirei'' is found in coastal regions of Spain. See also * List of ''Agaricus'' species References External links * freirei Fungi described in 2001 Fungi of Europe {{Agaricaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricaceae
The Agaricaceae are a family of basidiomycete fungi and include the genus ''Agaricus'', as well as basidiomycetes previously classified in the families Tulostomataceae, Lepiotaceae, and Lycoperdaceae. Taxonomy The family Agaricaceae was published by French botanist François Fulgis Chevallier in 1826. It is named after the type genus ''Agaricus'', originally circumscribed by Carl Linnaeus in his 1753 work ''Species Plantarum''. In his authoritative 1986 classification of the Agaricales, Rolf Singer divided the Agaricaceae into four tribes distinguished largely by spore color: ''Leucocoprineae'', ''Agariceae'', ''Lepioteae'', and ''Cystodermateae''. Genera once classified in the families Tulostomataceae, Battarreaceae, Lycoperdaceae, and Mycenastraceae have since been moved to the Agaricaceae based on molecular phylogenetics studies. According to a standard reference text, the Agaricaceae contains 85 genera and 1340 species. Description Agaricaceae species use a wide variety o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
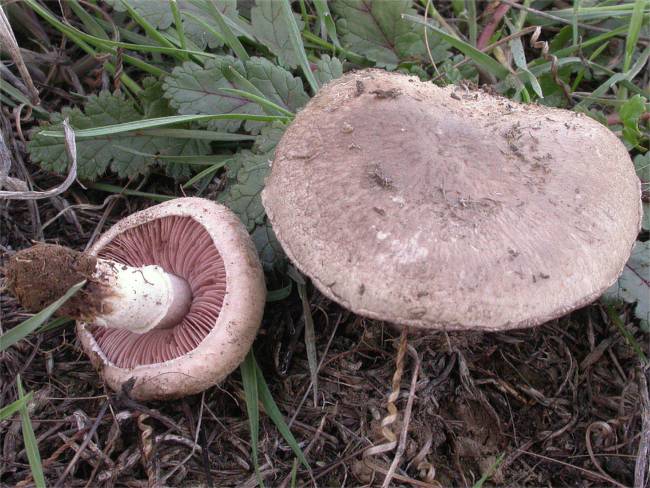
Agaricus Hondensis
''Agaricus hondensis'', commonly known as the felt-ringed agaricus, is a species of fungus in the family Agaricaceae. The species was officially described in 1912 by mycologist William Alphonso Murrill, along with three other ''Agaricus'' species that have since been placed in synonymy with ''A. hondensis''. Found in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, ''A. hondensis'' fruits in the fall under conifers or in mixed forests. The fungus produces fruit bodies (mushrooms) with white to gray-brown caps up to in diameter covered with pale pinkish-brown scales that darken in age. The tightly-packed gills on the cap underside are initially white before becoming pinkish, lilac-gray, and finally brownish as the spores mature. The stout stipe is bulbous and has a thick, white, felt-like ring. The mushroom is poisonous, and causes severe gastrointestinal upset if consumed. It has an unpleasant odor similar to phenol or creosote, and develops a soapy-metallic taste w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Sequence
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery. Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, DNA Genographic Projects and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. Comparing healthy and mutated DNA sequences can diagnose different diseases including various cancers, characterize antibody repertoire, and can be used to guide patient treatment. Having a quick way to sequence DNA allows for faster and more individualized medical care to be administered, and for more organisms to be identified and cataloged. The rapid speed of sequencing attained with modern D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Agaricus Species
''Agaricus'' is a genus of mushrooms containing both edible and poisonous species, with over 400 members worldwide and possibly again as many disputed or newly-discovered species. The genus includes the common ("button") mushroom (''Agaricus bisporus'') and the field mushroom ('' A. campestris''), the dominant cultivated mushrooms of the West. Members of ''Agaricus'' are characterized by having a fleshy cap or pileus, from the underside of which grow a number of radiating plates or gills, on which are produced the naked spores. They are distinguished from other members of their family, Agaricaceae, by their chocolate-brown spores. Members of ''Agaricus'' also have a stem or stipe, which elevates it above the object on which the mushroom grows, or substrate, and a partial veil, which protects the developing gills and later forms a ring or annulus on the stalk. The genus contains the most widely consumed and best-known mushroom today, '' A. bisporus'', with '' A. arvensis'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricus
''Agaricus'' is a genus of mushrooms containing both edible and poisonous species, with over 400 members worldwide and possibly again as many disputed or newly-discovered species. The genus includes the common ("button") mushroom (''Agaricus bisporus'') and the field mushroom ('' A. campestris''), the dominant cultivated mushrooms of the West. Members of ''Agaricus'' are characterized by having a fleshy cap or pileus, from the underside of which grow a number of radiating plates or gills, on which are produced the naked spores. They are distinguished from other members of their family, Agaricaceae, by their chocolate-brown spores. Members of ''Agaricus'' also have a stem or stipe, which elevates it above the object on which the mushroom grows, or substrate, and a partial veil, which protects the developing gills and later forms a ring or annulus on the stalk. The genus contains the most widely consumed and best-known mushroom today, '' A. bisporus'', with '' A. arvensis'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Described In 2001
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fungi' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |