|
Agamid
Agamidae is a family of over 300 species of iguanian lizards indigenous to Africa, Asia, Australia, and a few in Southern Europe. Many species are commonly called dragons or dragon lizards. Overview Phylogenetically, they may be sister to the Iguanidae, and have a similar appearance. Agamids usually have well-developed, strong legs. Their tails cannot be shed and regenerated like those of geckos (and several other families such as skinks), though a certain amount of regeneration is observed in some. Many agamid species are capable of limited change of their colours to regulate their body temperature. In some species, males are more brightly coloured than females, and colours play a part in signaling and reproductive behaviours. Although agamids generally inhabit warm environments, ranging from hot deserts to tropical rainforests, at least one species, the mountain dragon, is found in cooler regions. They are particularly diverse in Australia. This group of lizards includes som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lizard - E
Lizards are a widespread group of Squamata, squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia although some lizards are more closely related to these two excluded groups than they are to other lizards. Lizards range in size from chameleons and geckos a few centimeters long to the 3-meter-long Komodo dragon. Most lizards are quadrupedal, running with a strong side-to-side motion. Some lineages (known as "legless lizards"), have secondarily lost their legs, and have long snake-like bodies. Some such as the forest-dwelling ''Draco (genus), Draco'' lizards are able to glide. They are often Territory (animal), territorial, the males fighting off other males and signalling, often with bright colours, to attract mates and to intimidate rivals. Lizards are mainly carnivorous, often being sit-and-wait predators; many smaller species eat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iguania
Iguania is an infraorder of squamate reptiles that includes iguanas, chameleons, agamids, and New World lizards like anoles and phrynosomatids. Using morphological features as a guide to evolutionary relationships, the Iguania are believed to form the sister group to the remainder of the Squamata, which comprise nearly 11,000 named species, roughly 2000 of which are iguanians. However, molecular information has placed Iguania well within the Squamata as sister taxa to the Anguimorpha and closely related to snakes. The order has been under debate and revisions after being classified by Charles Lewis Camp in 1923 due to difficulties finding adequate synapomorphic morphological characteristics. Most Iguanias are arboreal but there are several terrestrial groups. They usually have primitive fleshy, non-prehensile tongues, although the tongue is highly modified in chameleons. The group has a fossil record that extends back to the Early Jurassic (the oldest known member is '' B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia although some lizards are more closely related to these two excluded groups than they are to other lizards. Lizards range in size from chameleons and geckos a few centimeters long to the 3-meter-long Komodo dragon. Most lizards are quadrupedal, running with a strong side-to-side motion. Some lineages (known as "legless lizards"), have secondarily lost their legs, and have long snake-like bodies. Some such as the forest-dwelling ''Draco'' lizards are able to glide. They are often territorial, the males fighting off other males and signalling, often with bright colours, to attract mates and to intimidate rivals. Lizards are mainly carnivorous, often being sit-and-wait predators; many smaller species eat insects, while the Komodo eats mammals a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chameleon
Chameleons or chamaeleons (family Chamaeleonidae) are a distinctive and highly specialized clade of Old World lizards with 202 species described as of June 2015. The members of this family are best known for their distinct range of colors, being capable of shifting to different hues and degrees of brightness. The large number of species in the family exhibit considerable variability in their capacity to change color. For some, it is more of a shift of brightness (shades of brown); for others, a plethora of color-combinations (reds, yellows, greens, blues) can be seen. Chameleons are distinguished by their zygodactylous feet, their prehensile tail, their laterally compressed bodies, their head casques, their projectile tongues, their swaying gait, and crests or horns on their brow and snout. Chameleons' eyes are independently mobile, and because of this there are two separate, individual images that the brain is analyzing of the chameleon’s environment. When hunting prey, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Dragon
''Rankinia'' is a genus of small agamid reptiles. As currently delineated, it is monotypic, containing only ''Rankinia diemensis'' (Gray, 1841), also known as the mountain heath dragon or mountain dragon. It is endemic to Australia. Distribution and habitat It occurs in the uplands of New South Wales and Victoria, as well as in Tasmania, where it is the only native agamid. Mountain dragons are found in dry woodlands and heaths with access to open areas for sunning themselves. They are oviparous and feed on ants and other small invertebrates.Cogger, H.G. (1979). ''Reptiles and Amphibians of Australia''. Reed: Sydney. They do not climb very high, relying instead on camouflage to evade predators. Description Their overall colour is grey to reddish brown, with two rows of lighter-coloured paravertebral stripes or blotches running down their backs. These stripes are deeply scalloped, so they appear like two series of blotches. They can have cream-coloured bellies. Individuals can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mwanza Flat-headed Rock Agama
The Mwanza flat-headed rock agama (''Agama mwanzae'') or the Spider-Man agama, because of its coloration, is a lizard reptile in the family Agamidae, found in Tanzania, Rwanda, and Kenya. It lives in semideserts and can often be seen in the heat of the day basking on rocks or kopjes. The male's head, neck, and shoulders are bright red or violet, while the body is dark blue. The female is mostly brown and is difficult to distinguish from female agamas of other species. This lizard is often confused with the red-headed rock agama (''Agama agama''). Males preferably have around five breeding partners and are highly territorial. Once a male has won over a female, the lizard will perform exotic head bobs and head swinging to court her. The species has become a fashionable pet due to the male's coloration, which resembles the comic-book superhero Spider-Man Spider-Man is a superhero appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. Created by writer-editor Stan Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Water Dragon
The Chinese water dragon (''Physignathus cocincinus'') is a species of agamid lizard native to China and mainland Southeast Asia. It is also known as the Asian water dragon, Thai water dragon, and green water dragon. The genus name is Greek for "inflated jaw". Description Chinese water dragons can grow up to 36" (0.9m) in total length, including tail, and can live from 10 to 15 years. Coloration ranges from dark to light green, or sometimes purple with an orange stomach. Diagonal stripes of green or turquoise are found on the body, while the tail is banded from the middle to the end with green and white. Their undersides range from white, off white, very pale green, or pale yellow. But their throats are considered to be more attractive, which can be quite colorful (blue and purple, or peach), some with a single color, some with stripes. Adult males have larger, more triangular heads than females, and develop larger crests on the head, neck and tail, and are larger in general. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uromastyx
''Uromastyx'' is a genus of African and Asian agamid lizards, the member species of which are commonly called spiny-tailed lizards, uromastyces, mastigures, or dabb lizards. Lizards in the genus ''Uromastyx'' are primarily herbivorous, but occasionally eat insects and other small animals, especially young lizards. They spend most of their waking hours basking in the sun, hiding in underground chambers at daytime, or when danger appears. They tend to establish themselves in hilly, rocky areas with good shelter and accessible vegetation. Taxonomy The generic name (''Uromastyx'') is derived from the Ancient Greek words ''ourá'' (οὐρά) meaning "tail" and ''-mastix'' (μάστιξ) meaning "whip" or "scourge", after the thick-spiked tail characteristic of all ''Uromastyx'' species. Species The following species are in the genus ''Uromastyx''.. www.reptile-database.org. Three additional species were formerly placed in this genus, but have been moved to their own genu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
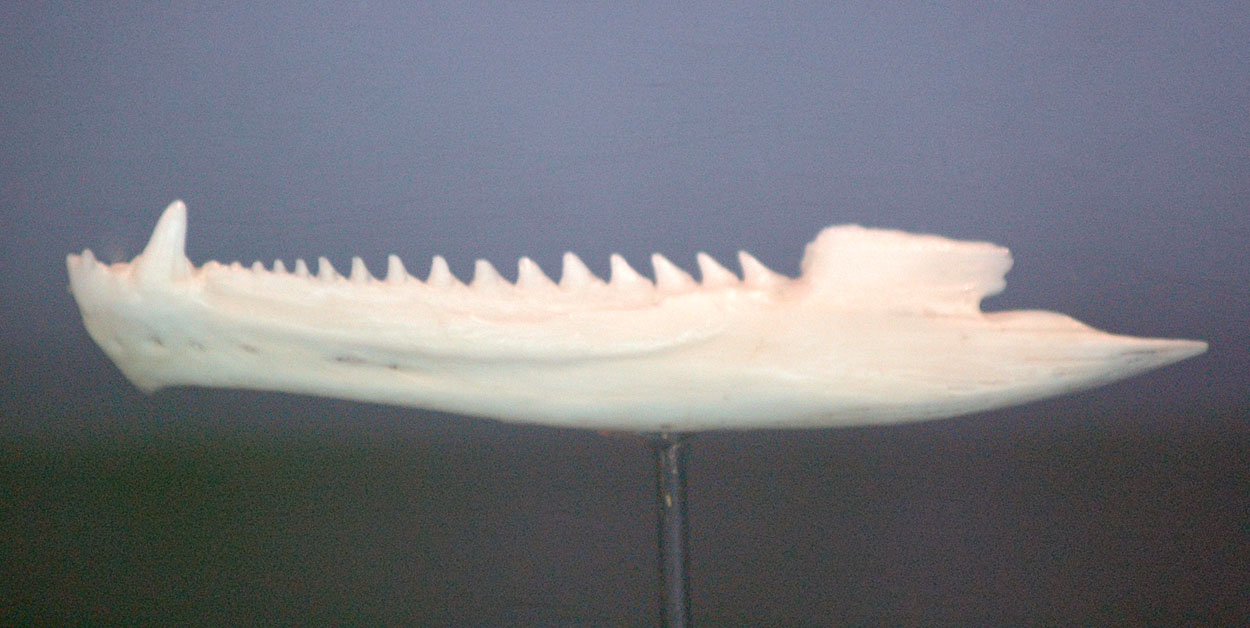
Acrodont
Acrodonty (from Greek ''akros'' 'highest' + ''dont'' 'tooth') is an anatomical placement of the teeth at the summit of the alveolar ridge of the jaw, without sockets, characteristic of bony fish. Functionally, acrodont tooth implantation may be related to strong bite force. Acrodonty in the Animal Kingdom Squamata: Within squamate reptiles, acrodont tooth implantation is best known in Acrodonta and some species of amphisbaenians, though some snakes are also referred to as being acrodont. Acrodonta is unique in that the name of the clade is based upon this trait. Most other squamate reptiles have pleurodont dentition, though some snakes are occasionally described as having acrodont dentition. Rhynchocephalia: Acrodont tooth implantation is common within Rhynchocephalia, including ''Sphenodon''. Amphibia: Acrodont tooth implantation also present in some frogs and the temnospondyl ''Microposaurus ''Microposaurus'' (meaning "small eyed lizard"; from Greek , "small" + , "face" o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleurodont
Pleurodont is a form of tooth implantation common in reptiles of the order Squamata, as well as in at least one temnospondyl. The labial (cheek) side of pleurodont teeth are fused (ankylosed) to the inner surface of the jaw bones which host them. The lingual (tongue) side of pleurodont teeth are not attached to bone, and instead are typically held in place by connective ligaments. This contrasts with thecodont Thecodontia (meaning 'socket-teeth'), now considered an obsolete taxonomic grouping, was formerly used to describe a diverse "order" of early archosaurian reptiles that first appeared in the latest Permian period and flourished until the end of th ... implantation, in which the teeth are set in sockets and surrounded by bone on all sides. References External links Tooth Implantation at palaeos.comOral Cavity of Reptiles - Anatomy and Physiology Dentition types Reptile anatomy {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuatara
Tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') are reptiles endemic to New Zealand. Despite their close resemblance to lizards, they are part of a distinct lineage, the order Rhynchocephalia. The name ''tuatara'' is derived from the Māori language and means "peaks on the back". The single extant species of tuatara is the only surviving member of its order. Rhynchocephalians originated during the Triassic (~250 million years ago), reached worldwide distribution and peak diversity during the Jurassic and, with the exception of tuatara, were extinct by 60 million years ago. Their closest living relatives are squamates (lizards and snakes). For this reason, tuatara are of interest in the study of the evolution of lizards and snakes, and for the reconstruction of the appearance and habits of the earliest diapsids, a group of amniote tetrapods that also includes dinosaurs (including birds) and crocodilians. Tuatara are greenish brown and grey, and measure up to from head to tail-tip and wei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)