|
Affinely Extended Real Number System
In mathematics, the extended real number system is obtained from the real number system \R by adding two elements denoted +\infty and -\infty that are respectively greater and lower than every real number. This allows for treating the potential infinities of infinitely increasing sequences and infinitely decreasing series as actual infinities. For example, the infinite sequence (1,2,\ldots) of the natural numbers increases ''infinitively'' and has no upper bound in the real number system (a potential infinity); in the extended real number line, the sequence has +\infty as its least upper bound and as its limit (an actual infinity). In calculus and mathematical analysis, the use of +\infty and -\infty as actual limits extends significantly the possible computations. It is the Dedekind–MacNeille completion of the real numbers. The extended real number system is denoted \overline, \infty,+\infty/math>, or \R\cup\left\. When the meaning is clear from context, the symbol +\inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Of A Function
In mathematics, the graph of a function f is the set of ordered pairs (x, y), where f(x) = y. In the common case where x and f(x) are real numbers, these pairs are Cartesian coordinates of points in a plane (geometry), plane and often form a Plane curve, curve. The graphical representation of the graph of a Function (mathematics), function is also known as a ''Plot (graphics), plot''. In the case of Bivariate function, functions of two variables – that is, functions whose Domain of a function, domain consists of pairs (x, y) –, the graph usually refers to the set of ordered triples (x, y, z) where f(x,y) = z. This is a subset of three-dimensional space; for a continuous real-valued function of two real variables, its graph forms a Surface (mathematics), surface, which can be visualized as a ''surface plot (graphics), surface plot''. In science, engineering, technology, finance, and other areas, graphs are tools used for many purposes. In the simplest case one variable is p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supremum
In mathematics, the infimum (abbreviated inf; : infima) of a subset S of a partially ordered set P is the greatest element in P that is less than or equal to each element of S, if such an element exists. If the infimum of S exists, it is unique, and if ''b'' is a lower bound of S, then ''b'' is less than or equal to the infimum of S. Consequently, the term ''greatest lower bound'' (abbreviated as ) is also commonly used. The supremum (abbreviated sup; : suprema) of a subset S of a partially ordered set P is the least element in P that is greater than or equal to each element of S, if such an element exists. If the supremum of S exists, it is unique, and if ''b'' is an upper bound of S, then the supremum of S is less than or equal to ''b''. Consequently, the supremum is also referred to as the ''least upper bound'' (or ). The infimum is, in a precise sense, dual to the concept of a supremum. Infima and suprema of real numbers are common special cases that are important in analy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subset
In mathematics, a Set (mathematics), set ''A'' is a subset of a set ''B'' if all Element (mathematics), elements of ''A'' are also elements of ''B''; ''B'' is then a superset of ''A''. It is possible for ''A'' and ''B'' to be equal; if they are unequal, then ''A'' is a proper subset of ''B''. The relationship of one set being a subset of another is called inclusion (or sometimes containment). ''A'' is a subset of ''B'' may also be expressed as ''B'' includes (or contains) ''A'' or ''A'' is included (or contained) in ''B''. A ''k''-subset is a subset with ''k'' elements. When quantified, A \subseteq B is represented as \forall x \left(x \in A \Rightarrow x \in B\right). One can prove the statement A \subseteq B by applying a proof technique known as the element argument:Let sets ''A'' and ''B'' be given. To prove that A \subseteq B, # suppose that ''a'' is a particular but arbitrarily chosen element of A # show that ''a'' is an element of ''B''. The validity of this technique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compact Space
In mathematics, specifically general topology, compactness is a property that seeks to generalize the notion of a closed and bounded subset of Euclidean space. The idea is that a compact space has no "punctures" or "missing endpoints", i.e., it includes all ''limiting values'' of points. For example, the open interval (0,1) would not be compact because it excludes the limiting values of 0 and 1, whereas the closed interval ,1would be compact. Similarly, the space of rational numbers \mathbb is not compact, because it has infinitely many "punctures" corresponding to the irrational numbers, and the space of real numbers \mathbb is not compact either, because it excludes the two limiting values +\infty and -\infty. However, the ''extended'' real number line ''would'' be compact, since it contains both infinities. There are many ways to make this heuristic notion precise. These ways usually agree in a metric space, but may not be equivalent in other topological spaces. One suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Topology
In mathematics, an order topology is a specific topology that can be defined on any totally ordered set. It is a natural generalization of the topology of the real numbers to arbitrary totally ordered sets. If ''X'' is a totally ordered set, the order topology on ''X'' is generated by the subbase of "open rays" :\ :\ for all ''a, b'' in ''X''. Provided ''X'' has at least two elements, this is equivalent to saying that the open intervals :(a,b) = \ together with the above rays form a base for the order topology. The open sets in ''X'' are the sets that are a union of (possibly infinitely many) such open intervals and rays. A topological space ''X'' is called orderable or linearly orderable if there exists a total order on its elements such that the order topology induced by that order and the given topology on ''X'' coincide. The order topology makes ''X'' into a completely normal Hausdorff space. The standard topologies on R, Q, Z, and N are the order topologies. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Totally Ordered Set
In mathematics, a total order or linear order is a partial order in which any two elements are comparable. That is, a total order is a binary relation \leq on some set X, which satisfies the following for all a, b and c in X: # a \leq a ( reflexive). # If a \leq b and b \leq c then a \leq c ( transitive). # If a \leq b and b \leq a then a = b ( antisymmetric). # a \leq b or b \leq a ( strongly connected, formerly called totality). Requirements 1. to 3. just make up the definition of a partial order. Reflexivity (1.) already follows from strong connectedness (4.), but is required explicitly by many authors nevertheless, to indicate the kinship to partial orders. Total orders are sometimes also called simple, connex, or full orders. A set equipped with a total order is a totally ordered set; the terms simply ordered set, linearly ordered set, toset and loset are also used. The term ''chain'' is sometimes defined as a synonym of ''totally ordered set'', but generally refers to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominated Convergence Theorem
In measure theory, Lebesgue's dominated convergence theorem gives a mild sufficient condition under which limits and integrals of a sequence of functions can be interchanged. More technically it says that if a sequence of functions is bounded in absolute value by an integrable function and is almost everywhere pointwise convergent to a function then the sequence converges in L_1 to its pointwise limit, and in particular the integral of the limit is the limit of the integrals. Its power and utility are two of the primary theoretical advantages of Lebesgue integration over Riemann integration. In addition to its frequent appearance in mathematical analysis and partial differential equations, it is widely used in probability theory, since it gives a sufficient condition for the convergence of expected values of random variables. Statement Lebesgue's dominated convergence theorem. Let (f_n) be a sequence of complex-valued measurable functions on a measure space . Suppose that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotone Convergence Theorem
In the mathematical field of real analysis, the monotone convergence theorem is any of a number of related theorems proving the good convergence behaviour of monotonic sequences, i.e. sequences that are non- increasing, or non- decreasing. In its simplest form, it says that a non-decreasing bounded-above sequence of real numbers a_1 \le a_2 \le a_3 \le ...\le K converges to its smallest upper bound, its supremum. Likewise, a non-increasing bounded-below sequence converges to its largest lower bound, its infimum. In particular, infinite sums of non-negative numbers converge to the supremum of the partial sums if and only if the partial sums are bounded. For sums of non-negative increasing sequences 0 \le a_ \le a_ \le \cdots , it says that taking the sum and the supremum can be interchanged. In more advanced mathematics the monotone convergence theorem usually refers to a fundamental result in measure theory due to Lebesgue and Beppo Levi that says that for sequences of non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
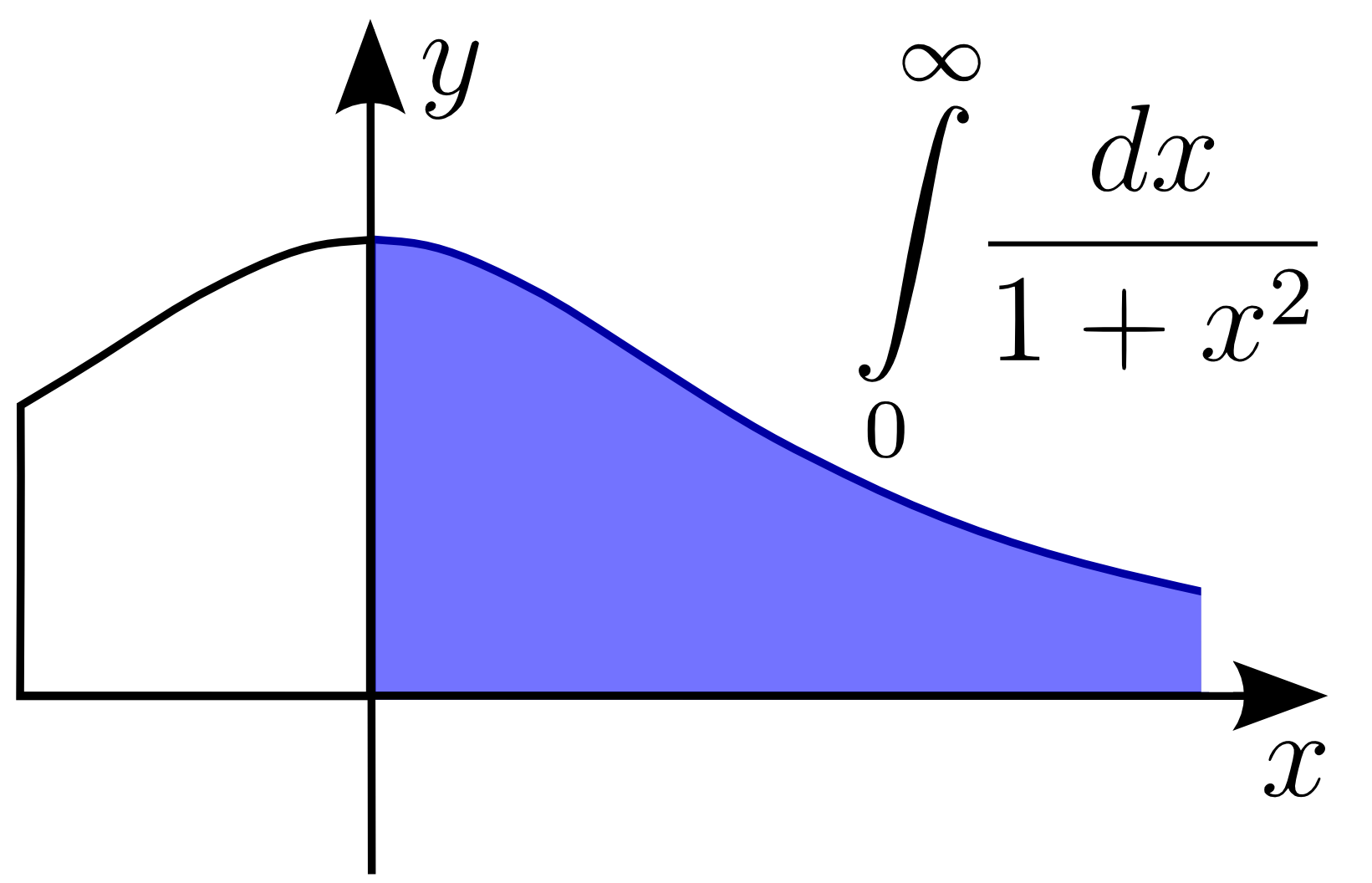
Improper Integral
In mathematical analysis, an improper integral is an extension of the notion of a definite integral to cases that violate the usual assumptions for that kind of integral. In the context of Riemann integrals (or, equivalently, Darboux integrals), this typically involves unboundedness, either of the set over which the integral is taken or of the integrand (the function being integrated), or both. It may also involve bounded but not closed sets or bounded but not continuous functions. While an improper integral is typically written symbolically just like a standard definite integral, it actually represents a limit of a definite integral or a sum of such limits; thus improper integrals are said to converge or diverge. If a regular definite integral (which may retronymically be called a proper integral) is worked out as if it is improper, the same answer will result. In the simplest case of a real-valued function of a single variable integrated in the sense of Riemann (or Darbou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interval (mathematics)
In mathematics, a real interval is the set of all real numbers lying between two fixed endpoints with no "gaps". Each endpoint is either a real number or positive or negative infinity, indicating the interval extends without a bound. A real interval can contain neither endpoint, either endpoint, or both endpoints, excluding any endpoint which is infinite. For example, the set of real numbers consisting of , , and all numbers in between is an interval, denoted and called the unit interval; the set of all positive real numbers is an interval, denoted ; the set of all real numbers is an interval, denoted ; and any single real number is an interval, denoted . Intervals are ubiquitous in mathematical analysis. For example, they occur implicitly in the epsilon-delta definition of continuity; the intermediate value theorem asserts that the image of an interval by a continuous function is an interval; integrals of real functions are defined over an interval; etc. Interval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measure (mathematics)
In mathematics, the concept of a measure is a generalization and formalization of geometrical measures (length, area, volume) and other common notions, such as magnitude, mass, and probability of events. These seemingly distinct concepts have many similarities and can often be treated together in a single mathematical context. Measures are foundational in probability theory, integration theory, and can be generalized to assume negative values, as with electrical charge. Far-reaching generalizations (such as spectral measures and projection-valued measures) of measure are widely used in quantum physics and physics in general. The intuition behind this concept dates back to Ancient Greece, when Archimedes tried to calculate the area of a circle. But it was not until the late 19th and early 20th centuries that measure theory became a branch of mathematics. The foundations of modern measure theory were laid in the works of Émile Borel, Henri Lebesgue, Nikolai Luzin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |