|
Aetosaurinae
Aetosaurinae is one of the two main clades of aetosaurs, the other being Desmatosuchia. It is a stem-based taxon defined as all aetosaurs more closely related to ''Aetosaurus'' than ''Desmatosuchus''. Aetosaurinae currently comprises ''Aetosaurus,'' similar forms such as '' Coahomasuchus'' and '' Stenomyti'', and the widespread and successful aetosaur clade Typothoracinae. Previous usage Aetosaurinae was originally named in 2000, as a subfamily solely including ''Aetosaurus'', which was assumed to be the earliest-diverging aetosaur. In 2007, it was extended to include the subfamily Typothoracinae as well as various basal aetosaurs which were not clearly within Desmatosuchinae. These proposed non-typothoracine aetosaurines included ''Coahomasuchus'', ''Neoaetosauroides'', ''Aetosauroides'', ''Stagonolepis robertsoni,'' and ''"Stagonolepis"'' (''Calyptosuchus'') ''wellesi''. As a subfamily containing practically all non-desmatosuchine aetosaurs, Aetosaurinae was poorly-supported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetosaur
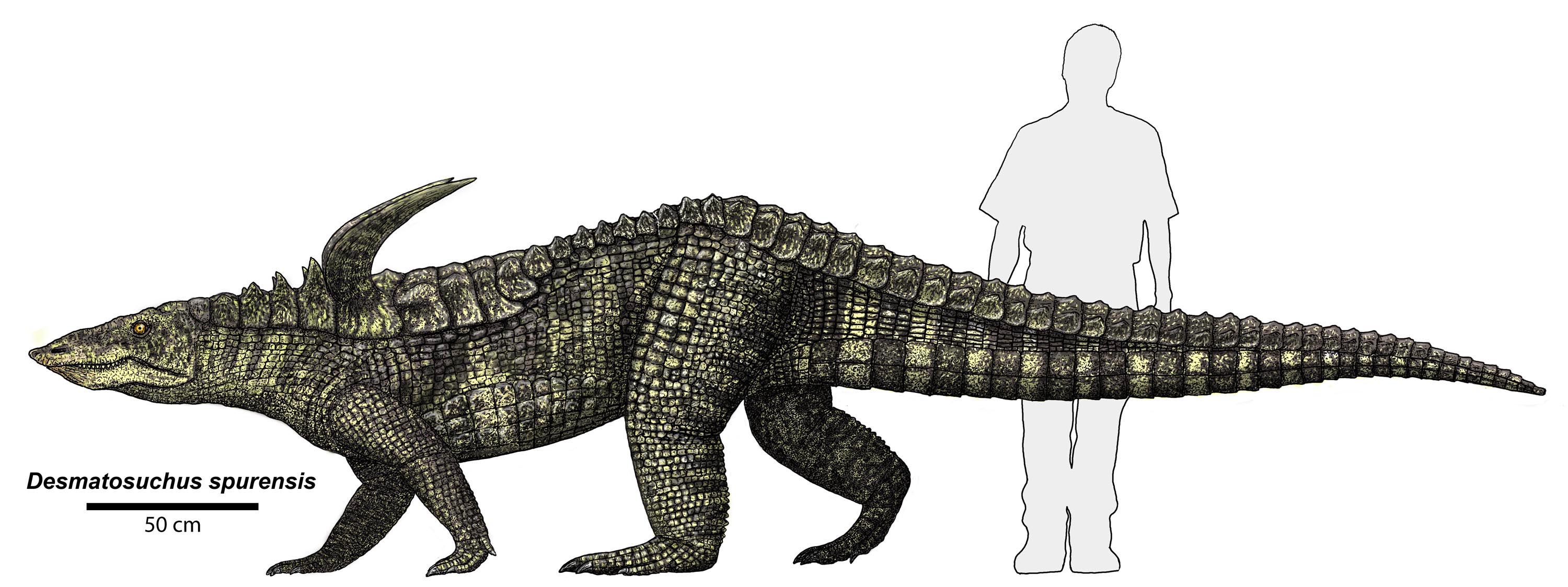
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria (; from Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmatosuchia
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria (; from Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typothoracinae
Typothoracinae is a clade of aetosaurs within the subfamily Aetosaurinae. It was originally defined as a stem-based taxon including all aetosaurs closer to ''Typothorax'' than to ''Stagonolepis'' or ''Desmatosuchus''. This definition was later expanded to specifically exclude ''Aetosaurus''; as of 2016, Typothoracinae is defined as the least inclusive clade containing ''Typothorax'' and ''Paratypothorax'', but not ''Aetosaurus,'' ''Stagonolepis'', or ''Desmatosuchus''. The clade was first named in 2007 under the spelling Typothoracisinae, after its namesake ''Typothorax''. However, this spelling was based on incorrect taxonomic nomenclature, and the clade's name was corrected to Typothoracinae in 2016. Typothoracines can be distinguished by their wide bodies. The transverse processes of the dorsal (trunk) vertebrae are reinforced and elongated, more than twice the width of the centrum. Their neural spines, on the other hand, are short. The overlying carapace A carapace is a Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typothoracine
Typothoracinae is a clade of aetosaurs within the subfamily Aetosaurinae. It was originally defined as a stem-based taxon including all aetosaurs closer to ''Typothorax'' than to ''Stagonolepis'' or ''Desmatosuchus''. This definition was later expanded to specifically exclude ''Aetosaurus''; as of 2016, Typothoracinae is defined as the least inclusive clade containing ''Typothorax'' and ''Paratypothorax'', but not ''Aetosaurus,'' ''Stagonolepis'', or ''Desmatosuchus''. The clade was first named in 2007 under the spelling Typothoracisinae, after its namesake ''Typothorax''. However, this spelling was based on incorrect taxonomic nomenclature, and the clade's name was corrected to Typothoracinae in 2016. Typothoracines can be distinguished by their wide bodies. The transverse processes of the dorsal (trunk) vertebrae are reinforced and elongated, more than twice the width of the centrum. Their neural spines, on the other hand, are short. The overlying carapace A carapace is a Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coahomasuchus
''Coahomasuchus'' is an extinct genus of aetosaurine aetosaur. Remains of the genus have been found from deposits in Texas and North Carolina that date to the Otischalkian faunachron (lower late Carnian) of the Late Triassic. It was small for an aetosaur, being less than long. The dorsal plates are distinctively flat and unflexed, and have a faint sub-parallel to radial ornamentation. The genus lacked spines or keels on these plates, features seen in many other aetosaurs. ''Coahomasuchus'' was very similar in appearance to the closely related ''Aetosaurus''. Two species of ''Coahomasuchus'' are known. ''C. kahleorum'', the type species, was named by Heckert and Lucas in 1999; it is known from the Colorado City Formation of the Dockum Group. ''C. chathamensis'', a second species named by Heckert ''et al.'' in 2017, is from the Pekin Formation of the Newark Supergroup. The holotype of the latter species contains parts of the skull, which is rare among aetosaurs. ''C. chathamensis' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to have evolved in their most recent common ancestor. ) In cladistics, synapomorphy implies homology. Examples of apomorphy are the presence of erect gait, fur, the evolution of three middle ear bones, and mammary glands in mammals but not in other vertebrate animals such as amphibians or reptiles, which have retained their ancestral traits of a sprawling gait and lack of fur. Thus, these derived traits are also synapomorphies of mammals in general as they are not shared by other vertebrate animals. Etymology The word —coined by German entomologist Willi Hennig—is derived from the Ancient Greek words (''sún''), meaning "with, together"; (''apó''), meaning "away from"; and (''morphḗ''), meaning "shape, form". Clade analysis T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoderm
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinct amphibians), various groups of dinosaurs (most notably ankylosaurs and stegosaurians), phytosaurs, aetosaurs, placodonts, and hupehsuchians (marine reptiles with possible ichthyosaur affinities). Osteoderms are uncommon in mammals, although they have occurred in many xenarthrans (armadillos and the extinct glyptodonts and mylodontid and scelidotheriid ground sloths). The heavy, bony osteoderms have evolved independently in many different lineages. The armadillo osteoderm is believed to develop in subcutaneous dermal tissues. These varied structures should be thought of as anatomical analogues, not homologues, and do not necessarily indicate monophyly. The structures are however derived from scutes, common to all classes of amniotes and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In contrast, a monophyletic group (a clade) includes a common ancestor and ''all'' of its descendants. The terms are commonly used in phylogenetics (a subfield of biology) and in the tree model of historical linguistics. Paraphyletic groups are identified by a combination of Synapomorphy and apomorphy, synapomorphies and symplesiomorphy, symplesiomorphies. If many subgroups are missing from the named group, it is said to be polyparaphyletic. The term was coined by Willi Hennig to apply to well-known taxa like Reptilia (reptiles) which, as commonly named and traditionally defined, is paraphyletic with respect to mammals and birds. Reptilia contains the last common ancestor of reptiles a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to have evolved in their most recent common ancestor. ) In cladistics, synapomorphy implies homology. Examples of apomorphy are the presence of erect gait, fur, the evolution of three middle ear bones, and mammary glands in mammals but not in other vertebrate animals such as amphibians or reptiles, which have retained their ancestral traits of a sprawling gait and lack of fur. Thus, these derived traits are also synapomorphies of mammals in general as they are not shared by other vertebrate animals. Etymology The word —coined by German entomologist Willi Hennig—is derived from the Ancient Greek words (''sún''), meaning "with, together"; (''apó''), meaning "away from"; and (''morphḗ''), meaning "shape, form". Clade analysis T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Taxon
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa. Examples Just as the term ''monotypic'' is used to describe a taxon including only one subdivision, the contained taxon can also be referred to as monotypic within the higher-level taxon, e.g. a genus monotypic within a family. Some examples of monotypic groups are: Plants * In the order Amborellales, there is only one family, Amborellaceae and there is only one genus, '' Amborella'', and in this genus there is only one species, namely ''Amborella trichopoda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series (stratigraphy), series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Geologic time scale, Ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Namoh, Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful sandstone'')'', t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stagonolepis
''Stagonolepis'' is an extinct genus of stagonolepidid aetosaur known from the Late Triassic (Carnian stage) Hassberge Formation of Germany, the Drawno Beds of Poland, and the Lossiemouth Sandstone of Scotland. Supposed fossils from North and South America have been placed into their own genera, ''Calyptosuchus'' and ''Aetosauroides'', respectively. Description ''Stagonolepis robertsoni'' was about long. It was a quadrupedal animal covered in thick armoured scales that ran down the length of its body. A slow-moving browser, it would have used this heavy body armour to repel attacks from contemporary thecodont carnivores. ''Stagonolepis'' had a very small head for its size; it was only , accounting for less than 10% of the total body length. It had no teeth in the front of its jaws, but instead had a beak-like tip that arched upwards. This would have allowed it to uproot plants in a similar manner to a modern pig. The peg-like teeth at the back of its mouth would have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |