|
Stagonolepis
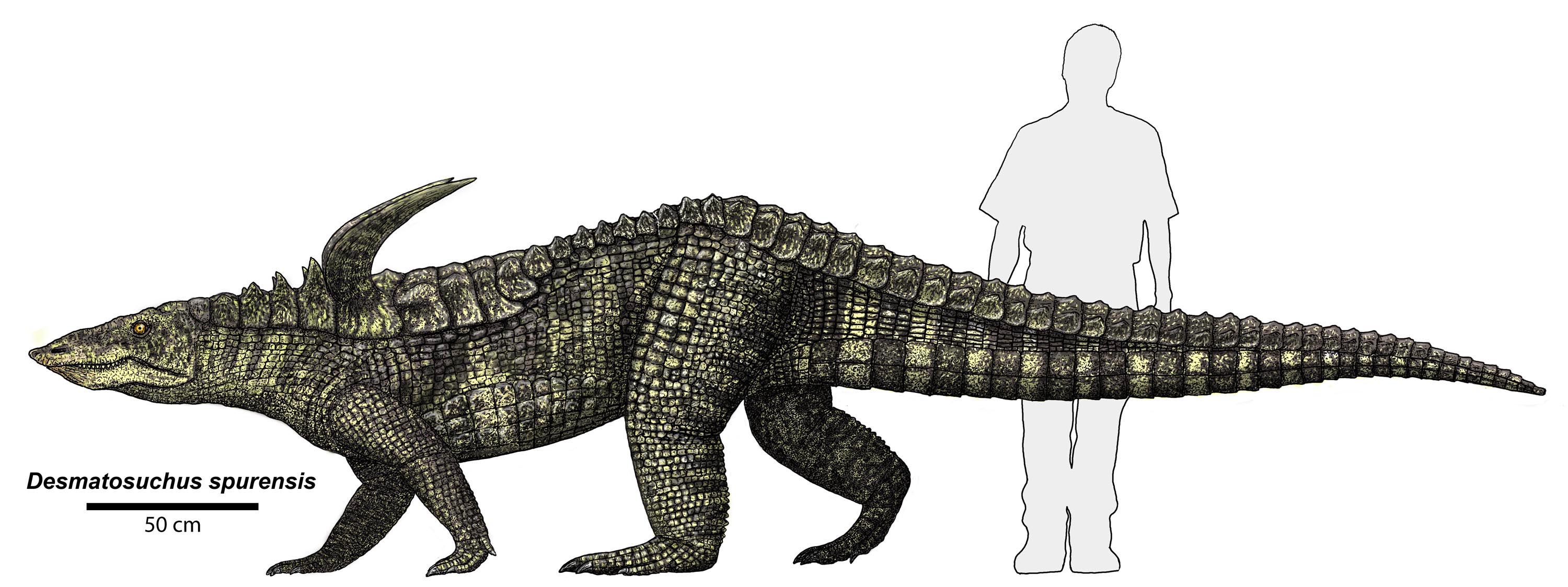
''Stagonolepis'' is an extinct genus of stagonolepidid aetosaur known from the Late Triassic (Carnian stage) Hassberge Formation of Germany, the Drawno Beds of Poland, and the Lossiemouth Sandstone of Scotland. Supposed fossils from North and South America have been placed into their own genera, ''Calyptosuchus'' and ''Aetosauroides'', respectively. Description ''Stagonolepis robertsoni'' was about long. It was a quadrupedal animal covered in thick armoured scales that ran down the length of its body. A slow-moving browser, it would have used this heavy body armour to repel attacks from contemporary thecodont carnivores. ''Stagonolepis'' had a very small head for its size; it was only , accounting for less than 10% of the total body length. It had no teeth in the front of its jaws, but instead had a beak-like tip that arched upwards. This would have allowed it to uproot plants in a similar manner to a modern pig. The peg-like teeth at the back of its mouth would have bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stagonolepidid
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria (; from Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetosaur
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria (; from Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stagonolepis
''Stagonolepis'' is an extinct genus of stagonolepidid aetosaur known from the Late Triassic (Carnian stage) Hassberge Formation of Germany, the Drawno Beds of Poland, and the Lossiemouth Sandstone of Scotland. Supposed fossils from North and South America have been placed into their own genera, ''Calyptosuchus'' and ''Aetosauroides'', respectively. Description ''Stagonolepis robertsoni'' was about long. It was a quadrupedal animal covered in thick armoured scales that ran down the length of its body. A slow-moving browser, it would have used this heavy body armour to repel attacks from contemporary thecodont carnivores. ''Stagonolepis'' had a very small head for its size; it was only , accounting for less than 10% of the total body length. It had no teeth in the front of its jaws, but instead had a beak-like tip that arched upwards. This would have allowed it to uproot plants in a similar manner to a modern pig. The peg-like teeth at the back of its mouth would have bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetosauroides
''Aetosauroides'' (meaning "'' Aetosaurus''-like") is an extinct genus of aetosaur from the Late Triassic of South America. It is one of four aetosaurs known from South America, the others being '' Neoaetosauroides'', '' Chilenosuchus'' and '' Aetobarbakinoides''. Three species have been named: the type species ''A. scagliai'', ''A. subsulcatus'' and ''A. inhamandensis''. Fossils have been found in the Cancha de Bochas Member of the Ischigualasto Formation in the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina and the Santa Maria Formation in the Paraná Basin in southeastern Brazil. The strata date to the late Carnian and early Norian stages, making ''Aetosauroides'' one of the oldest aetosaurs. Description Most individuals of ''Aetosauroides'' measured around in length, with one large individual reaching (with histology suggesting an age of 23 years). Sexual maturity was probably reached at in length, although these individuals were not yet fully grown. Sexua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calyptosuchus
''Calyptosuchus'' (meaning "covered crocodile") is an extinct genus of aetosaur from the Late Triassic of North America. Like other aetosaurs, it was heavily armored and had a pig-like snout used to uproot plants. Description ''Calyptosuchus'' was estimated to have been four metres long, or possibly larger, with a maximum carapace width of almost seventy centimetres. The osteoderms were not entirely fused. Each row of the osteoderms corresponded to one vertebra, and comprised four dorsal osteoderms. Two small squarish osteoderms formed the outside of the row (about 10 by 10 cm), and two much broader osteoderms (approximately 20 by 10 cm) formed the inside of the row and covered most of the back. Each of the lateral osteoderms have a raised boss towards the centre at the posterior end of the osteoderm, and are almost bent around the side of the creature, with a dorsal flange along the back contacting the paramedian (dorsal) osteoderms and a lateral flange running a lit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lossiemouth Sandstone
The Lossiemouth Sandstone is a Middle to Late Triassic (Ladinian to Norian) age geological formation. It is exposed on the south side of the Moray Firth near Lossiemouth and near Golspie in Sutherland. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel et al., 2004, "Dinosaur distribution." pp.517-607 Fossil content See also * List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations ** List of stratigraphic units with indeterminate dinosaur fossils * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Scotland * Ischigualasto Formation, contemporaneous fossiliferous formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin, Argentina * Candelária Formation, contemporaneous fossiliferous formation of the Paraná Basin in southeastern Brazil * Molteno Formation The Molteno Formation is a geological formation found in several localities in Lesotho and South Africa. It lies mainly south of Maseru, near Burgersdorp, Aliwal North, Dordrecht, Molteno, and Elliot. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycad
Cycads are seed plants that typically have a stout and woody (ligneous) trunk with a crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and (usually) pinnate leaves. The species are dioecious, that is, individual plants of a species are either male or female. Cycads vary in size from having trunks only a few centimeters to several meters tall. They typically grow very slowly and live very long. Because of their superficial resemblance, they are sometimes mistaken for palms or ferns, but they are not closely related to either group. Cycads are gymnosperms (naked-seeded), meaning their unfertilized seeds are open to the air to be directly fertilized by pollination, as contrasted with angiosperms, which have enclosed seeds with more complex fertilization arrangements. Cycads have very specialized pollinators, usually a specific species of beetle. Both male and female cycads bear cones (strobili), somewhat similar to conifer cones. Cycads have been reported to fix nitrogen in association ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes except the lycopods, and differ from mosses and other bryophytes by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissues that conduct water and nutrients and in having life cycles in which the branched sporophyte is the dominant phase. Ferns have complex leaves called megaphylls, that are more complex than the microphylls of clubmosses. Most ferns are leptosporangiate ferns. They produce coiled fiddleheads that uncoil and expand into fronds. The group includes about 10,560 known extant species. Ferns are defined here in the broad sense, being all of the Polypodiopsida, comprising both the leptosporangiate ( Polypodiidae) and eusporangiate ferns, the latter group including horsetails, whisk ferns, marattioid ferns, and ophioglossoid fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horsetail
''Equisetum'' (; horsetail, snake grass, puzzlegrass) is the only living genus in Equisetaceae, a family of ferns, which reproduce by spores rather than seeds. ''Equisetum'' is a " living fossil", the only living genus of the entire subclass Equisetidae, which for over 100 million years was much more diverse and dominated the understorey of late Paleozoic forests. Some equisetids were large trees reaching to tall. The genus ''Calamites'' of the family Calamitaceae, for example, is abundant in coal deposits from the Carboniferous period. The pattern of spacing of nodes in horsetails, wherein those toward the apex of the shoot are increasingly close together, is said to have inspired John Napier to invent logarithms. Modern horsetails first appeared during the Jurassic period. A superficially similar but entirely unrelated flowering plant genus, mare's tail (''Hippuris''), is occasionally referred to as "horsetail", and adding to confusion, the name "mare's tail" is so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion of a single continent called Americas, America. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent generally includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territory, dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one administrative division, internal territory: French Guiana. In addition, the ABC islands (Leeward Antilles), ABC islands of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Ascension Island (dependency of Saint Helena, Asce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restorations Of Stagonolepis Robertsoni, After Skeletal By Hartman, 2016
Restoration is the act of restoring something to its original state and may refer to: * Conservation and restoration of cultural heritage ** Audio restoration ** Film restoration ** Image restoration ** Textile restoration *Restoration ecology **Environmental restoration Film and television * ''The Restoration'' (1909 film), a film by D.W. Griffith starring Mary Pickford * ''The Restoration'' (1910 film), an American silent short drama produced by the Thanhouser Company *The Restoration (2020 film), a Peruvian comedy film * ''Restoration'' (1995 film), a film by Michael Hoffman starring Robert Downey Jr * ''Restoration'' (2011 film), an Israeli film by Yossi Madmoni * ''Restoration'' (2016 film), an Australian science fiction thriller by Stuart Willis * ''Restoration'' (TV series), a BBC TV series * "Restoration" (''Arrow''), an episode of ''Arrow'' History * Kenmu Restoration (1333) in Japan * Portuguese Restoration War (1640–1668) * Stuart Restoration (1660) in Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fish, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)


