|
Advantage (cryptography)
In cryptography, an adversary's advantage is a measure of how successfully it can attack a cryptographic algorithm, by distinguishing it from an idealized version of that type of algorithm. Note that in this context, the "Adversary (cryptography), adversary" is itself an algorithm and not a person. A cryptographic algorithm is considered secure if no adversary has a non-negligible function, negligible advantage, subject to specified bounds on the adversary's computational resources (see concrete security). "Negligible" usually means "within Big O notation, O(2−p)" where p is a security parameter associated with the algorithm. For example, p might be the number of bits in a block cipher's key (cryptography), key. Description of concept Let F be an oracle machine, oracle for the function being studied, and let G be an oracle for an idealized function of that type. The adversary A is a probabilistic algorithm, given F or G as input, and which outputs 1 or 0. A's job is to di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptography
Cryptography, or cryptology (from "hidden, secret"; and ''graphein'', "to write", or ''-logy, -logia'', "study", respectively), is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of Adversary (cryptography), adversarial behavior. More generally, cryptography is about constructing and analyzing Communication protocol, protocols that prevent third parties or the public from reading private messages. Modern cryptography exists at the intersection of the disciplines of mathematics, computer science, information security, electrical engineering, digital signal processing, physics, and others. Core concepts related to information security (confidentiality, data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation) are also central to cryptography. Practical applications of cryptography include electronic commerce, Smart card#EMV, chip-based payment cards, digital currencies, password, computer passwords, and military communications. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factorial
In mathematics, the factorial of a non-negative denoted is the Product (mathematics), product of all positive integers less than or equal The factorial also equals the product of n with the next smaller factorial: \begin n! &= n \times (n-1) \times (n-2) \times (n-3) \times \cdots \times 3 \times 2 \times 1 \\ &= n\times(n-1)!\\ \end For example, 5! = 5\times 4! = 5 \times 4 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1 = 120. The value of 0! is 1, according to the convention for an empty product. Factorials have been discovered in several ancient cultures, notably in Indian mathematics in the canonical works of Jain literature, and by Jewish mystics in the Talmudic book ''Sefer Yetzirah''. The factorial operation is encountered in many areas of mathematics, notably in combinatorics, where its most basic use counts the possible distinct sequences – the permutations – of n distinct objects: there In mathematical analysis, factorials are used in power series for the ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phillip Rogaway
Phillip Rogaway (also referred to as Phil Rogaway) is an American cryptographer and former professor of computer science at the University of California, Davis. He graduated from Beverly Hills High School, and later earned a BA in computer science from UC Berkeley and completed his PhD in cryptography at MIT, in the Theory of Computation group. He has taught at UC Davis since 1994. He was awarded the Paris Kanellakis Award in 2009 and the first Levchin Prize for Real World Cryptography in 2016. Rogaway received an NSF CAREER award in 1996, which the NSA had attempted to prevent by influencing the NSF. He has been interviewed in multiple media outlets regarding his stance on the ethical obligations that cryptographers and computer scientists have to serve to the public good, specifically in the areas of internet privacy and digital surveillance. Rogaway's papers cover topics including: * CMAC * Concrete security * DES and DES-X * Format-preserving encryption * OCB mode * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key-recovery Advantage
A key-recovery attack is an adversary's attempt to recover the cryptographic key of an encryption scheme. Normally this means that the attacker has a pair, or more than one pair, of plaintext message and the corresponding ciphertext. Goldwasser, S. and Bellare, M.br>"Lecture Notes on Cryptography". Summer course on cryptography, MIT, 1996-2001 Historically, cryptanalysis of block ciphers has focused on key-recovery, but security against these sorts of attacks is a very weak guarantee since it may not be necessary to recover the key to obtain partial information about the message or decrypt message entirely. Modern cryptography uses more robust notions of security. Recently, indistinguishability under adaptive chosen-ciphertext attack (IND-CCA2 security) has become the "golden standard" of security. The most obvious key-recovery attack is the exhaustive key-search attack. But modern ciphers often have a key space of size 2^ or greater, making such attacks infeasible with current te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudorandom-function Advantage
In cryptography, the pseudorandom-function advantage (PRF advantage) of an algorithm on a pseudorandom function family is a measure of how effectively the algorithm can distinguish between a member of the family and a random oracle In cryptography, a random oracle is an oracle (a theoretical black box) that responds to every ''unique query'' with a (truly) random response chosen uniformly from its output domain. If a query is repeated, it responds the same way every tim .... Consequently, the maximum pseudorandom advantage attainable by any algorithm with a fixed amount of computational resources is a measure of how well such a function family emulates a random oracle. Say that an adversary algorithm has access to an oracle that will apply a function to inputs that are sent to it. The algorithm sends the oracle a number of queries before deciding whether the oracle is a random oracle or simply an instance of the pseudorandom function family. Say also that there is a 50% chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
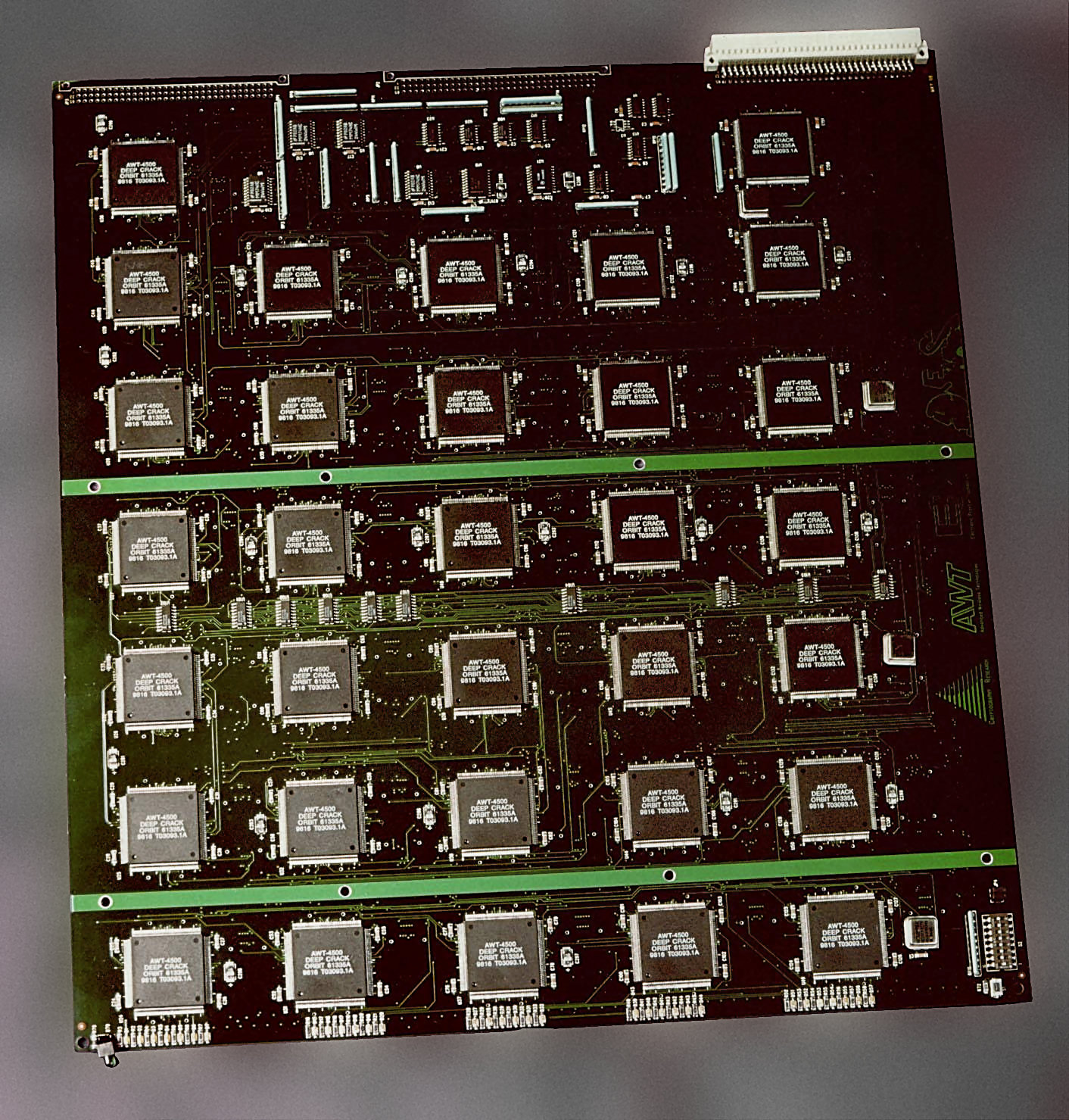
Brute Force Attack
In cryptography, a brute-force attack or exhaustive key search is a cryptanalytic attack that consists of an attacker submitting many possible Key (cryptography), keys or passwords with the hope of eventually guessing correctly. This strategy can theoretically be used to break any form of encryption that is not information-theoretically secure. However, in a properly designed cryptosystem the chance of successfully guessing the key is negligible. When Password cracking, cracking passwords, this method is very fast when used to check all short passwords, but for longer passwords other methods such as the dictionary attack are used because a brute-force search takes too long. Longer passwords, passphrases and keys have more possible values, making them exponentially more difficult to crack than shorter ones due to diversity of characters. Brute-force attacks can be made less effective by Obfuscation (software), obfuscating the data to be encoded making it more difficult for an att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brute-force Search
In computer science, brute-force search or exhaustive search, also known as generate and test, is a very general problem-solving technique and algorithmic paradigm that consists of Iteration#Computing, systematically checking all possible candidates for whether or not each candidate satisfies the problem's statement. A brute-force algorithm that finds the divisors of a natural number ''n'' would enumerate all integers from 1 to n, and check whether each of them divides ''n'' without remainder. A brute-force approach for the eight queens puzzle would examine all possible arrangements of 8 pieces on the 64-square chessboard and for each arrangement, check whether each (queen) piece can attack any other. While a brute-force search is simple to implement and will always find a solution if it exists, implementation costs are proportional to the number of candidate solutionswhich in many practical problems tends to grow very quickly as the size of the problem increases (#Combinatorial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Complexity Theory
In theoretical computer science and mathematics, computational complexity theory focuses on classifying computational problems according to their resource usage, and explores the relationships between these classifications. A computational problem is a task solved by a computer. A computation problem is solvable by mechanical application of mathematical steps, such as an algorithm. A problem is regarded as inherently difficult if its solution requires significant resources, whatever the algorithm used. The theory formalizes this intuition, by introducing mathematical models of computation to study these problems and quantifying their computational complexity, i.e., the amount of resources needed to solve them, such as time and storage. Other measures of complexity are also used, such as the amount of communication (used in communication complexity), the number of logic gate, gates in a circuit (used in circuit complexity) and the number of processors (used in parallel computing). O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chosen-ciphertext Attack
A chosen-ciphertext attack (CCA) is an attack model for cryptanalysis where the cryptanalyst can gather information by obtaining the decryptions of chosen ciphertexts. From these pieces of information the adversary can attempt to recover the secret key used for decryption. For formal definitions of security against chosen-ciphertext attacks, see for example: Michael Luby and Mihir Bellare et al. Introduction A number of otherwise secure schemes can be defeated under chosen-ciphertext attack. For example, the El Gamal cryptosystem is semantically secure under chosen-plaintext attack, but this semantic security can be trivially defeated under a chosen-ciphertext attack. Early versions of RSA padding used in the SSL protocol were vulnerable to a sophisticated adaptive chosen-ciphertext attack which revealed SSL session keys. Chosen-ciphertext attacks have implications for some self-synchronizing stream ciphers as well. Designers of tamper-resistant cryptographic smart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chosen-plaintext Attack
A chosen-plaintext attack (CPA) is an attack model for cryptanalysis which presumes that the attacker can obtain the ciphertexts for arbitrary plaintexts.Ross Anderson, ''Security Engineering: A Guide to Building Dependable Distributed Systems''. The first edition (2001): http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/~rja14/book.html The goal of the attack is to gain information that reduces the security of the encryption scheme. Modern ciphers aim to provide semantic security, also known as ''ciphertext indistinguishability under chosen-plaintext attack'', and they are therefore, by design, generally immune to chosen-plaintext attacks if correctly implemented. Introduction In a chosen-plaintext attack the adversary can (possibly adaptively) ask for the ciphertexts of arbitrary plaintext messages. This is formalized by allowing the adversary to interact with an encryption oracle, viewed as a black box. The attacker’s goal is to reveal all or a part of the secret encryption key. It may seem infe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Oracle
In cryptography, a random oracle is an oracle (a theoretical black box) that responds to every ''unique query'' with a (truly) random response chosen uniformly from its output domain. If a query is repeated, it responds the same way every time that query is submitted. Stated differently, a random oracle is a mathematical function chosen uniformly at random, that is, a function mapping each possible query to a (fixed) random response from its output domain. Random oracles first appeared in the context of complexity theory, in which they were used to argue that complexity class separations may face relativization barriers, with the most prominent case being the P vs NP problem, two classes shown in 1981 to be distinct relative to a random oracle almost surely. They made their way into cryptography by the publication of Mihir Bellare and Phillip Rogaway in 1993, which introduced them as a formal cryptographic model to be used in reduction proofs. They are typically used when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |