|
Adrian Bejan
Adrian Bejan is an American professor who has made contributions to modern thermodynamics and developed his constructal law. He is J. A. Jones Distinguished Professor of Mechanical Engineering at Duke University and author of the books Design in Nature, ''The Physics of Life'' '', Freedom and Evolution'' and Time And Beauty: Why Time Flies And Beauty Never Dies Early life and education Bejan was born in Galaţi, a city on the Danube in Romania. His mother, Marioara Bejan (1914–1998), was a pharmacist. His father, Dr. Anghel Bejan (1910–1976), was a veterinarian. Bejan showed an early talent in drawing, and his parents enrolled him in art school. He also excelled in basketball, which earned him a position on the Romanian national basketball team. At age 19 Bejan won a scholarship to the United States and entered Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge, Massachusetts. In 1972 he was awarded BS and MS degrees as a member of the Honors Course in Mechanical Engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franklin Institute
The Franklin Institute is a science museum and the center of science education and research in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It is named after the American scientist and statesman Benjamin Franklin. It houses the Benjamin Franklin National Memorial. Founded in 1824, the Franklin Institute is one of the oldest centers of science education and development in the United States. Its chief astronomer is Derrick Pitts. History On February 5, 1824, Samuel Vaughan Merrick and William H. Keating founded the Franklin Institute of the State of Pennsylvania for the Promotion of the Mechanic Arts. Begun in 1825, the institute was an important force in the professionalization of American science and technology through the nineteenth century, beginning with early investigations into steam engines and water power. In addition to conducting scientific inquiry, it fostered research and education by running schools, publishing the influential ''Journal of The Franklin Institute'', sponsoring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Harry Potter Gold Medal
James is a common English language surname and given name: *James (name), the typically masculine first name James * James (surname), various people with the last name James James or James City may also refer to: People * King James (other), various kings named James * Saint James (other) * James (musician) * James, brother of Jesus Places Canada * James Bay, a large body of water * James, Ontario United Kingdom * James College, a college of the University of York United States * James, Georgia, an unincorporated community * James, Iowa, an unincorporated community * James City, North Carolina * James City County, Virginia ** James City (Virginia Company) ** James City Shire * James City, Pennsylvania * St. James City, Florida Arts, entertainment, and media * ''James'' (2005 film), a Bollywood film * ''James'' (2008 film), an Irish short film * ''James'' (2022 film), an Indian Kannada-language film * James the Red Engine, a character in ''Thomas the Tank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exergy
In thermodynamics, the exergy of a system is the maximum useful work possible during a process that brings the system into equilibrium with a heat reservoir, reaching maximum entropy. When the surroundings are the reservoir, exergy is the potential of a system to cause a change as it achieves equilibrium with its environment. Exergy is the energy that is available to be used. After the system and surroundings reach equilibrium, the exergy is zero. Determining exergy was also the first goal of thermodynamics. The term "exergy" was coined in 1956 by Zoran Rant (1904–1972) by using the Greek '' ex'' and ''ergon'' meaning "from work", but the concept had been earlier developed by J Willard Gibbs (the namesake of Gibbs free energy) in 1873. Energy is neither created nor destroyed during a process. Energy changes from one form to another (''see First Law of Thermodynamics''). In contrast, exergy is always destroyed when a process is irreversible, for example loss of heat to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreversibility
In science, a process that is not reversible is called irreversible. This concept arises frequently in thermodynamics. All complex natural processes are irreversible, although a phase transition at the coexistence temperature (e.g. melting of ice cubes in water) is well approximated as reversible. In thermodynamics, a change in the thermodynamic state of a system and all of its surroundings cannot be precisely restored to its initial state by infinitesimal changes in some property of the system without expenditure of energy. A system that undergoes an irreversible process may still be capable of returning to its initial state. Because entropy is a state function, the change in entropy of the system is the same whether the process is reversible or irreversible. However, the impossibility occurs in restoring the environment to its own initial conditions. An irreversible process increases the total entropy of the system and its surroundings. The second law of thermodynamics can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
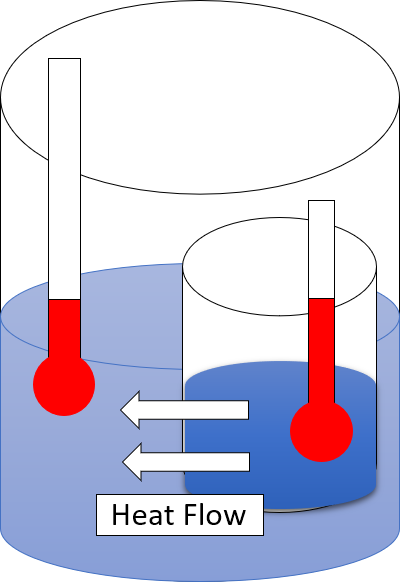
Second Law Of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on universal experience concerning heat and energy interconversions. One simple statement of the law is that heat always moves from hotter objects to colder objects (or "downhill"), unless energy in some form is supplied to reverse the direction of heat flow. Another definition is: "Not all heat energy can be converted into work in a cyclic process."Young, H. D; Freedman, R. A. (2004). ''University Physics'', 11th edition. Pearson. p. 764. The second law of thermodynamics in other versions establishes the concept of entropy as a physical property of a thermodynamic system. It can be used to predict whether processes are forbidden despite obeying the requirement of conservation of energy as expressed in the first law of thermodynamics and provides necessary criteria for spontaneous processes. The second law may be formulated by the observation that the entropy of isolated systems left to spontaneous evolution cannot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang-Lin Tien
Chang-lin Tien (; July 24, 1935 – October 29, 2002) was a Chinese-American professor of mechanical engineering and university administrator. He was the seventh chancellor of the University of California, Berkeley (1990–1997), and in that capacity was the first person of Asian descent to head a major research university in the United States. Biography Early years Born in Huangpi, Hubei, China, Tien and his family fled to Taiwan in 1949 at the end of the Chinese Civil War. He earned a BS in mechanical engineering from the National Taiwan University in 1955 and went on to a fellowship at the University of Louisville in 1956, where he received an MME in heat transfer in 1957. He then earned his MA and PhD degrees in mechanical engineering from Princeton University in 1959. Career Tien joined UC Berkeley faculty as an assistant professor of mechanical engineering in 1959, and three years later, at the age of 26, became the youngest professor ever to be honored with UC Berke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miller Research Fellows
The Miller Research Fellows program is the central program of the Adolph C. and Mary Sprague Miller Institute for Basic Research in Science on the University of California Berkeley campus. The program constitutes the support of Research Fellows - a group of the world’s most brilliant young scientists. Each year, eight to ten Miller Research Fellows are chosen from hundreds of nominations in all areas of science based on the promise of their scientific research. The Fellowships are three-year appointments, during which the young scientists launch their careers, being mentored by Berkeley’s faculty and making use of the facilities at the university. A few Fellows stay on as new Berkeley faculty. Most move on to contribute to faculty positions at other reputed institutions around the world. Other comparable programs are the Harvard Junior Fellows and the Junior Fellowship Program at the University of Cambridge. To date, there have been over 500 Miller Fellows from all areas of sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge, Massachusetts
Cambridge ( ) is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. As part of the Greater Boston, Boston metropolitan area, the cities population of the 2020 United States Census, 2020 U.S. census was 118,403, making it the fourth most populous city in the state, behind Boston, Massachusetts, Boston, Worcester, Massachusetts, Worcester, and Springfield, Massachusetts, Springfield. It is one of two de jure county seats of Middlesex County, although the county's executive government was abolished in 1997. Situated directly north of Boston, across the Charles River, it was named in honor of the University of Cambridge in England, once also an important center of the Puritan theology embraced by the town's founders. Harvard University, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Lesley University, and Hult International Business School are in Cambridge, as was Radcliffe College before it merged with Harvard. Kendall Square in Cambridge has been called "the most innovati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian National Basketball Team
The Romania men's national basketball team ( ro, Echipa națională de baschet a României) represents Romania in international basketball competition. The team is administered by the Romanian Basketball Federation (FRB). Romania has qualified for the EuroBasket 18 times throughout their history. Their best tournament results occurred in 1957 and 1967 respectively, where they finished fifth. The national team has also appeared at the Olympic Games once, in 1952. However, Romania has yet to clinch qualification for their first trip to the FIBA World Cup. History EuroBasket 1935 At the first European Championship in Geneva, the Romania national team finished in last place in the then ten team tournament. Losing all three of their matches; 42-9 to Switzerland, 66-23 to France, and 24-17 to Hungary. EuroBasket 1947 Romania returned to the European championship twelve years later in Prague, for the EuroBasket 1947. Romania finished with a record of 1-2 after the preliminary round, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , passing through or bordering Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria, Moldova, and Ukraine before draining into the Black Sea. Its drainage basin extends into nine more countries. The largest cities on the river are Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade and Bratislava, all of which are the capitals of their respective countries; the Danube passes through four capital cities, more than any other river in the world. Five more capital cities lie in the Danube's basin: Bucharest, Sofia, Zagreb, Ljubljana and Sarajevo. The fourth-largest city in its basin is Munich, the capital of Bavaria, standing on the Isar River. The Danube is the second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through much of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, and maintain mechanical systems. It is one of the oldest and broadest of the engineering branches. Mechanical engineering requires an understanding of core areas including mechanics, dynamics, thermodynamics, materials science, structural analysis, and electricity. In addition to these core principles, mechanical engineers use tools such as computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and product lifecycle management to design and analyze manufacturing plants, industrial equipment and machinery, heating and cooling systems, transport systems, aircraft, watercraft, robotics, medical devices, weapons, and others. Mechanical engineering emerged as a field during the Industrial Revolution in Europe in the 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distinguished Professor
Distinguished Professor is an academic title given to some top tenured professors in a university, school, or department. Some distinguished professors may have endowed chairs. In the United States Often specific to one institution, titles such as "president's professor", "university professor", "distinguished professor", "distinguished research professor", "distinguished teaching professor", "distinguished university professor", or "regents professor" are granted to a small percentage of the top tenured faculty who are regarded as particularly important in their respective fields of research. Some institutions grant more university-specific, formal titles such as M.I.T.'s " Institute Professor", Yale University's "Sterling Professor Sterling Professor, the highest academic rank at Yale University, is awarded to a tenured faculty member considered the best in his or her field. It is akin to the rank of university professor at other universities. The appointment, made by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |