|
Adolf-Heinz Beckerle
Adolf-Heinz Beckerle (4 February 1902 – 3 April 1976) was a German politician, SA officer and diplomat who played a significant role in the Holocaust in Bulgaria. ''Völkisch'' Activist Beckerle was born in Frankfurt am Main, the son of a post office official. Beckerle was educated at the elementary school and at the ''Realgymnasium'' (the type of high school that prepares one for university in Germany) in Frankfurt from 1908 to 1921. In March 1921, he passed the ''Abitur'' (university entrance exam). From 1921 to 1927, he attended the University of Frankfurt, where he graduated with a degree in economics in 1927. While at university, he joined a fraternity, the Coburger Convent. In 1921–1922, he served in the ''Reichswehr'' as a reserve officer. As a student, he also became active in several ''völkisch'' groups on campus, joining the Viking League in 1922. On 29 August 1922, he joined the NSDAP, but dropped out shortly afterwards. Beckerle broke off his studies several tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brackets
A bracket is either of two tall fore- or back-facing punctuation marks commonly used to isolate a segment of text or data from its surroundings. Typically deployed in symmetric pairs, an individual bracket may be identified as a 'left' or 'right' bracket or, alternatively, an "opening bracket" or "closing bracket", respectively, depending on the Writing system#Directionality, directionality of the context. Specific forms of the mark include parentheses (also called "rounded brackets"), square brackets, curly brackets (also called 'braces'), and angle brackets (also called 'chevrons'), as well as various less common pairs of symbols. As well as signifying the overall class of punctuation, the word "bracket" is commonly used to refer to a specific form of bracket, which varies from region to region. In most English-speaking countries, an unqualified word "bracket" refers to the parenthesis (round bracket); in the United States, the square bracket. Glossary of mathematical sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freikorps
(, "Free Corps" or "Volunteer Corps") were irregular German and other European military volunteer units, or paramilitary, that existed from the 18th to the early 20th centuries. They effectively fought as mercenary or private armies, regardless of their own nationality. In German-speaking countries, the first so-called ("free regiments", Freie Regimenter) were formed in the 18th century from native volunteers, enemy renegades, and deserters. These, sometimes exotically equipped, units served as infantry and cavalry (or, more rarely, as artillery); sometimes in just company strength and sometimes in formations of up to several thousand strong. There were also various mixed formations or legions. The Prussian included infantry, jäger, dragoons and hussars. The French '' Volontaires de Saxe'' combined uhlans and dragoons. In the aftermath of World War I and during the German Revolution of 1918–19, consisting largely of World War I veterans were raised as paramilitar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanns Ludin
Hanns Elard Ludin (10 June 1905, in Freiburg – 9 December 1947, in Bratislava) was a German diplomat. Born in Freiburg to Friedrich and Johanna Ludin, Ludin began his Nazi affiliation in 1930 by joining the party, and was arrested for his political activities the same year. Imprisoned until 1931, he joined the SA on his release. Ludin was lucky to survive the "Night of the Long Knives" in 1934 when Hitler purged much of the left-wing of the Nazi party. Ludin restored his reputation by joining the Foreign Office and became Ambassador to the Slovak Republic in 1941, replacing Manfred von Killinger. Ludin's activities included convincing the Slovak government to comply with deportations for slave labor and providing diplomatic cover to such activities. In 1943, he was promoted to ''SA-ObergruppenfГјhrer''. Ludin was arrested after the war and extradited to Czechoslovakia, where he was tried with '' SS-ObergruppenfГјhrer'' Hermann HГ¶fle (not to be confused with '' SS-St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dietrich Von Jagow
Dietrich () is an ancient German name meaning "Ruler of the People.” Also "keeper of the keys" or a "lockpick" either the tool or the profession. Given name * Dietrich, Count of Oldenburg (c. 1398 – 1440) * Thierry of Alsace (german: Dietrich, link=no; 1099–1168), Count of Flanders * Dietrich of Ringelheim (9th century), Saxon count and father of St Matilda * Dietrich Bonhoeffer (1906–1945), German Lutheran pastor and theologian * Wilhelm Dietrich von Buddenbrock (1672–1757), Prussian field marshal and cavalry leader * Dieterich Buxtehude (c. 1637/39–1707), Danish-German composer and organist * Dietrich von Choltitz (1894–1966), German General and last commander of Nazi-occupied Paris in 1944 * Dietrich Eckart (1868–1923), German politician * Dietrich Enns (born 1991), American baseball player * Dietrich Fischer-Dieskau (1925–2012), German baritone singer * Dietrich von Hildebrand (1889–1977), German Catholic philosopher and theologian * Dietrich Hollinderbä ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siegfried Kasche
Siegfried Kasche (18 June 1903 – 7 June 1947) was an ambassador of the German Reich to the Independent State of Croatia and ''Obergruppenführer'' of the ''Sturmabteilung'' (SA), a paramilitary wing of the Nazi Party. Kasche was the proposed ruler of the Reichskommissariat Moskowien, but the Reichskommissariat failed to materialize. He was hanged for war crimes in Yugoslavia on 7 June 1947. Early life Kasche was born in Strausberg. After attending cadet school in Potsdam and the Lichterfelde military academy, he spent 1919-20 in the ''Freikorps'' in Berlin and the Baltic states. He joined the Sturmabteilung in 1925 and the Nazi Party in 1926. He was also a leader of the SA in Pommerania. From 1928-31, Kasche was deputy Gauleiter in Ostmark, and in September 1930 was elected to the Reichstag. In 1934, Kasche was promoted to ''SA-Obergruppenführer'', a rank equal to a lieutenant general in the Wehrmacht. Kasche was one of the few SA general officers to survive the Night of the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manfred Freiherr Von Killinger
Manfred Freiherr von Killinger (July 14, 1886 – September 2, 1944) was a German naval officer, ''Freikorps'' leader, military writer and Nazism, Nazi politician. A veteran of World War I and member of the ''Marinebrigade Ehrhardt'' during the German Revolution, he took part in the military intervention against the Bavarian Soviet Republic. After the ''Freikorps'' was disbanded, the Antisemitism, antisemitic Killinger was active in the ''Germanenorden'' and ''Organisation Consul'', masterminding the murder of Matthias Erzberger. He was subsequently a Nazi Party representative in the Reichstag (German Empire), Reichstag and a leader of the ''Sturmabteilung'', before serving as Saxony's List of Ministers-President of Saxony, Minister-President and playing a part in implementing Nazi policies at a local level. Purged during the Night of the Long Knives, he was able to recover his status, and served as Nazi Germany's Consul (representative), Consul in San Francisco between 1936 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joachim Von Ribbentrop
Ulrich Friedrich Wilhelm Joachim von Ribbentrop (; 30 April 1893 – 16 October 1946) was a German politician and diplomat who served as Minister of Foreign Affairs of Nazi Germany from 1938 to 1945. Ribbentrop first came to Adolf Hitler's notice as a well-travelled businessman with more knowledge of the outside world than most senior Nazis and as a perceived authority on foreign affairs. He offered his house Schloss Fuschl for the secret meetings in January 1933 that resulted in Hitler's appointment as Chancellor of Germany. He became a close confidant of Hitler, to the disgust of some party members, who thought him superficial and lacking in talent. He was appointed ambassador to the Court of St James's, the royal court of the United Kingdom, in 1936 and then Foreign Minister of Germany in February 1938. Before World War II, he played a key role in brokering the Pact of Steel (an alliance with Fascist Italy) and the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact (the Nazi–Soviet non-aggr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Antonescu
Ion Antonescu (; ; – 1 June 1946) was a Romanian military officer and marshal who presided over two successive wartime dictatorships as Prime Minister and ''Conducător'' during most of World War II. A Romanian Army career officer who made his name during the 1907 peasants' revolt and the World War I Romanian Campaign, the antisemitic Antonescu sympathized with the far-right and fascist National Christian and Iron Guard groups for much of the interwar period. He was a military attaché to France and later Chief of the General Staff, briefly serving as Defense Minister in the National Christian cabinet of Octavian Goga as well as the subsequent First Cristea cabinet, in which he also served as Air and Marine Minister. During the late 1930s, his political stance brought him into conflict with King Carol II and led to his detainment. Antonescu nevertheless rose to political prominence during the political crisis of 1940, and established the National Legionary State, an unea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horia Sima
Horia Sima (3 July 1906 – 25 May 1993) was a Romanian fascist politician, best known as the second and last leader of the fascist paramilitary movement known as the Iron Guard (also known as the Legion of the Archangel Michael). Sima was also the vice president of the council of ministers and de facto co-leader in Ion Antonescu's National Legionary State. Sima had previously served briefly as State Secretary of Education under Gheorghe TДѓtДѓrescu in 1940, and as a short-lived Minister of Religion and Arts in the government of Ion Gigurtu. In January 1941, Sima initiated and led the Legionnaires' Rebellion against ConducДѓtor Ion Antonescu and the Romanian Army, for which he was sentenced to death, as well as the Bucharest pogrom, the largest and most violent pogrom against Jews in the history of Muntenia. Following the rebellion, Sima escaped to Germany, and later to Spain, where he lived until his death. In 1946, the Romanian People's Tribunals again sentenced Sima to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legionnaires' Rebellion And Bucharest Pogrom
Between 21 and 23 January 1941, a rebellion of the Iron Guard paramilitary organization, whose members were known as Legionnaires, occurred in Bucharest, National Legionary State, Romania. As their privileges were being gradually removed by the ''Conducător'' Ion Antonescu, the Legionnaires revolted. During the rebellion and subsequent pogrom, the Iron Guard killed 125 Jews, and 30 soldiers died in the confrontation with the rebels. Following this, the Iron Guard movement was banned and 9,000 of its members were imprisoned. For details of the Pogrom itself, see volume I, pp. 363–400. Background Following World War I Romania gained many new territories, thus becoming "Greater Romania". However, the international recognition of the formal union with these territories came with the condition of granting civil rights to ethnic minorities in those regions. The new territories, especially Bessarabia and Bukovina, included large numbers of Jews, whose presence stood out because of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
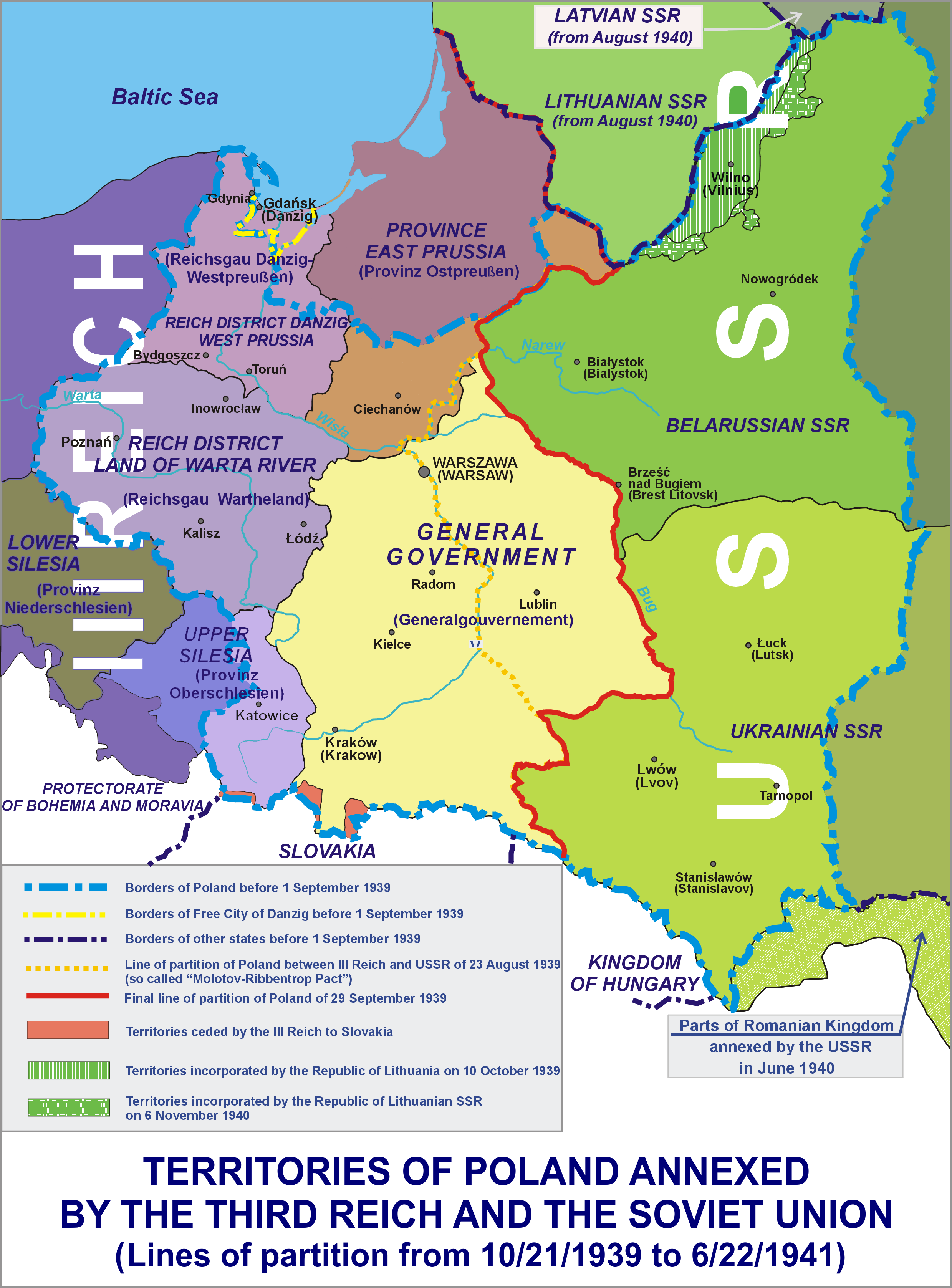
German-occupied Poland
German-occupied Poland during World War II consisted of two major parts with different types of administration. The Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany following the invasion of Poland at the beginning of World War II—nearly a quarter of the entire territory of the Second Polish Republic—were placed directly under the German civil administration. The official term used by the Nazi authorities for these areas was the "incorporated Eastern territories" (german: Eingegliederte Ostgebiete). They planned for a complete Germanization of the annexed territories, considering them part of ''lebensraum''. The rest of Nazi-occupied Poland was renamed as the General Government district ().Polish Ministry of Foreign Affairs, "German Occupation of Poland" (Washington, D.C.: Dale Street Books, 2014), pp. 12-16. See also *Occupation of Poland (1939–1945) The occupation of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union during World War II (1939–1945) began with the German-Soviet in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ЕЃГіdЕє
ЕЃГіdЕє, also rendered in English as Lodz, is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of ЕЃГіdЕє Voivodeship, and is located approximately south-west of Warsaw. The city's coat of arms is an example of canting arms, canting, as it depicts a boat ( in Polish language, Polish), which alludes to the city's name. As of 2022, ЕЃГіdЕє has a population of 670,642 making it the country's List of cities and towns in Poland, fourth largest city. ЕЃГіdЕє was once a small settlement that first appeared in 14th-century records. It was granted city rights, town rights in 1423 by Polish King WЕ‚adysЕ‚aw II JagieЕ‚Е‚o and it remained a private town of the Kuyavian bishops and clergy until the late 18th century. In the Second Partition of Poland in 1793, ЕЃГіdЕє was annexed to Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia before becoming part of the Napoleonic Duchy of Warsaw; the city joined Congress Poland, a Russian Empire, Russian client state, at the 1815 Congress of Vien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |