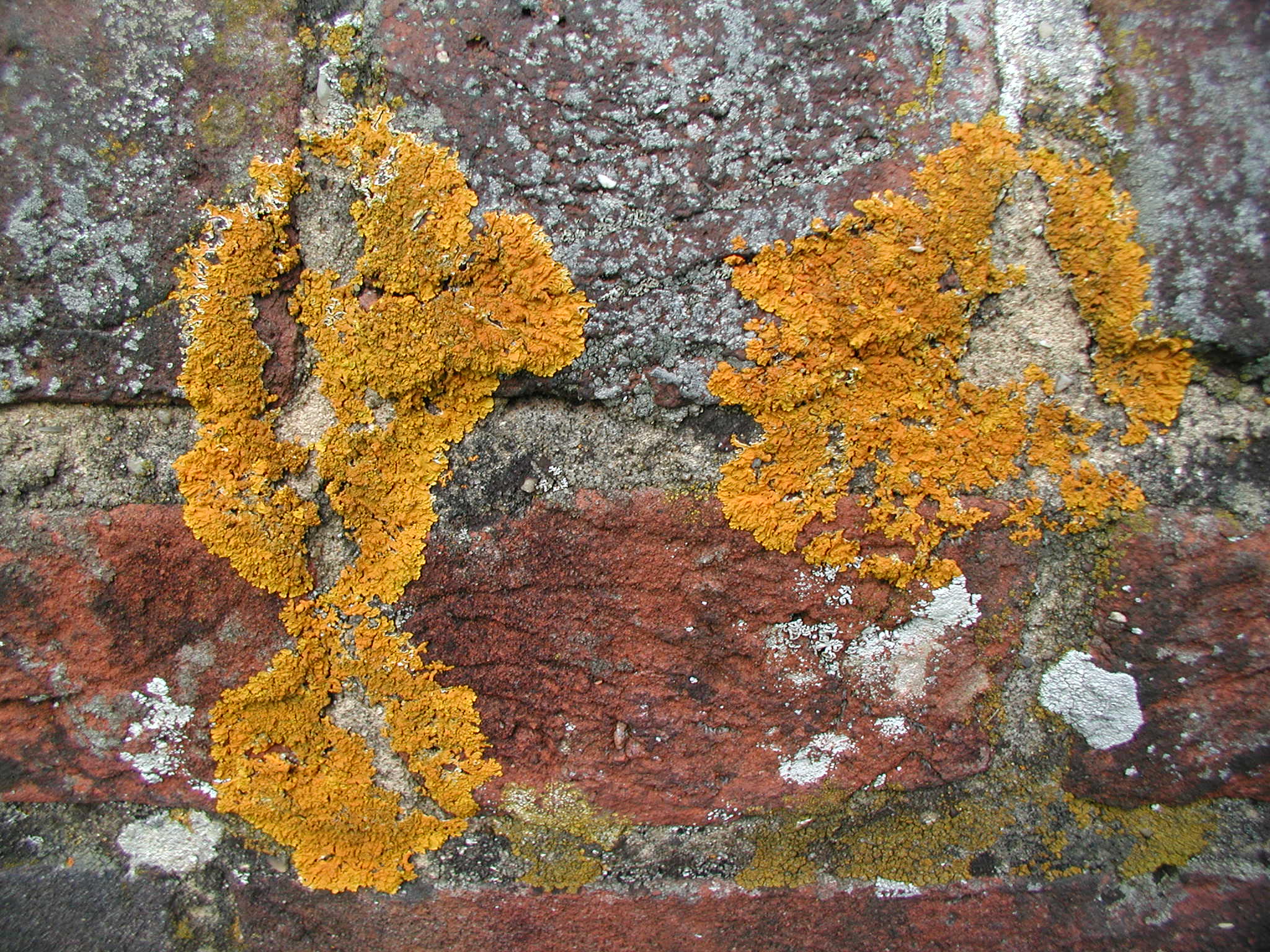|
Adelolecia
''Adelolecia'' is a genus of crustose lichens in the family Lecanoraceae. The genus was circumscribed by Hannes Hertel and Josef Hafellner in 1984. The genus was formerly classified in the family Ramalinaceae, but molecular phylogenetic Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to ... analysis showed it to belong to the Lecanoraceae. Species *'' Adelolecia kolaensis'' *'' Adelolecia pilati'' *'' Adelolecia rhododendrina'' *'' Adelolecia sonorae'' References Lecanoraceae Lichen genera Lecanorales genera Taxa described in 1984 Taxa named by Josef Hafellner Taxa named by Hannes Hertel {{Lecanorales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelolecia Pilati
''Adelolecia'' is a genus of crustose lichens in the family Lecanoraceae. The genus was circumscribed by Hannes Hertel and Josef Hafellner in 1984. The genus was formerly classified in the family Ramalinaceae, but molecular phylogenetic Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to ... analysis showed it to belong to the Lecanoraceae. Species *'' Adelolecia kolaensis'' *'' Adelolecia pilati'' *'' Adelolecia rhododendrina'' *'' Adelolecia sonorae'' References Lecanoraceae Lichen genera Lecanorales genera Taxa described in 1984 Taxa named by Josef Hafellner Taxa named by Hannes Hertel {{Lecanorales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelolecia Rhododendrina
''Adelolecia'' is a genus of crustose lichens in the family Lecanoraceae. The genus was circumscribed by Hannes Hertel and Josef Hafellner in 1984. The genus was formerly classified in the family Ramalinaceae, but molecular phylogenetic analysis showed it to belong to the Lecanoraceae. Species *'' Adelolecia kolaensis'' *''Adelolecia pilati ''Adelolecia'' is a genus of crustose lichens in the family Lecanoraceae. The genus was circumscribed by Hannes Hertel and Josef Hafellner in 1984. The genus was formerly classified in the family Ramalinaceae, but molecular phylogenetic Molecu ...'' *'' Adelolecia rhododendrina'' *'' Adelolecia sonorae'' References Lecanoraceae Lichen genera Lecanorales genera Taxa described in 1984 Taxa named by Josef Hafellner Taxa named by Hannes Hertel {{Lecanorales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelolecia Sonorae
''Adelolecia'' is a genus of crustose lichens in the family Lecanoraceae. The genus was circumscribed by Hannes Hertel and Josef Hafellner in 1984. The genus was formerly classified in the family Ramalinaceae, but molecular phylogenetic analysis showed it to belong to the Lecanoraceae. Species *'' Adelolecia kolaensis'' *''Adelolecia pilati'' *''Adelolecia rhododendrina ''Adelolecia'' is a genus of crustose lichens in the family Lecanoraceae. The genus was circumscribed by Hannes Hertel and Josef Hafellner in 1984. The genus was formerly classified in the family Ramalinaceae, but molecular phylogenetic analysis ...'' *'' Adelolecia sonorae'' References Lecanoraceae Lichen genera Lecanorales genera Taxa described in 1984 Taxa named by Josef Hafellner Taxa named by Hannes Hertel {{Lecanorales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelolecia Kolaensis
''Adelolecia kolaensis'' is a species of crustose lichen belonging to the family Lecanoraceae The Lecanoraceae are a family of lichenized fungi in the order Lecanorales. Species of this family have a widespread distribution. Taxonomy Lecanoraceae was circumscribed by German lichenologist Gustav Wilhelm Körber in 1855. Genera According .... It is native to Europe and Northern America. References Lichens described in 1863 Lichen species Fungi of Europe Fungi of North America Taxa named by William Nylander (botanist) {{Lecanorales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lecanoraceae
The Lecanoraceae are a family of lichenized fungi in the order Lecanorales. Species of this family have a widespread distribution. Taxonomy Lecanoraceae was circumscribed by German lichenologist Gustav Wilhelm Körber in 1855. Genera According to a 2017 estimate, Lecanoraceae contains 791 species distributed amongst 25 genera. *''Adelolecia'' – 4 spp. *'' Ameliella'' – 2 spp. *''Bryodina'' – 2 spp. *''Bryonora'' – 11 spp. *'' Cladidium'' – 2 spp. *'' Claurouxia'' – 1 sp. *'' Clauzadeana'' – 1 sp. *'' Edrudia'' – 1 sp. *'' Frutidella'' – 3 sp. *'' Huea'' – 25 spp. *''Japewiella'' – 7 spp. *''Lecanora'' – 550 spp. *''Lecidella'' – 80 spp. *'' Miriquidica'' – 25 spp. *''Myriolecis'' – 34 spp. *'' Myrionora'' – 2 spp. *''Palicella'' – 3 spp. *'' Polyozosia'' – 42 spp. *'' Protoparmeliopsis'' – 39 spp. *'' Psorinia'' – 2 spp. *''Pulvinora'' – 2 spp. *''Punctonora'' – 1 sp. *''Pyrrhospora'' – 8 spp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramalinaceae
The Ramalinaceae are a family of lichenized fungi in the order Lecanorales. The family name is synonymous with the name ''Bacidiaceae''. Species of this family have a widespread distribution. Genera *''Aciculopsora'' *''Adelolecia'' *'' Arthrosporum'' *''Bacidia'' *'' Bacidina'' *'' Bacidiopsora'' *'' Badimia'' *''Bibbya'' *'' Biatora'' *''Bilimbia'' *'' Catinaria'' *'' Cenozosia'' *'' Cliostomum'' *'' Compsocladium'' *''Coppinsidea'' *'' Crocynia'' *'' Echidnocymbium'' *'' Frutidella'' *'' Heppsora'' *'' Herteliana'' *'' Japewia'' *''Jarmania'' *''Krogia'' *''Lecania'' *'' Lopezaria'' *'' Lueckingia'' *'' Myelorrhiza'' *'' Phyllopsora'' *'' Physcidia'' *''Ramalina'' *'' Ramalinopsis'' *'' Rolfidium'' *'' Schadonia'' *''Scutula'' *'' Stirtoniella'' *'' Thamnolecania'' *'' Tibellia'' *''Toninia'' *'' Toniniopsis'' *'' Triclinum'' – synonymous with ''Squamacidia'' Brako *''Vermilacinia ''Vermilacinia'', a genus of lichenized fungi in the family Ramalinaceae, is a yellow-gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hafellner
Josef Hafellner (1951– ) is an Austrian mycologist and lichenologist. He was awarded the Acharius Medal in 2016 for his lifetime contributions to lichenology. Before his retirement, he was a professor at the Karl-Franzens-Universität in Graz. Hafellner started developing an interest in lichens while he was a student at this institution, studying under Josef Poelt. He earned a master's degree in 1975 and a PhD in 1978, defending a doctoral thesis about the genus '' Karschia''. In 2003, Hafellner received his habilitation. By this time, he had studied with French lichenologist André Bellemère (1927–2014) at Saint-Cloud, where he learned techniques of transmission electron microscopy and how their application in studying asci could be used in lichen systematics. His 1984 work ''Studien in Richtung einer natürlicheren Gliederung der Sammelfamilien Lecanoraceae und Lecideaceae'' has been described as "probably the single most influential publication in lichen systematics in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustose Lichen
Crustose lichens are lichens that form a crust which strongly adheres to the Substrate (biology), substrate (soil, rock, tree bark, etc.), making separation from the substrate impossible without destruction. The basic structure of crustose lichens consists of a cortex (botany), cortex layer, an algal layer, and a medulla. The upper cortex layer is differentiated and is usually pigmented. The algal layer lies beneath the cortex. The medulla fastens the lichen to the substrate and is made up of Fungus, fungal hyphae. The surface of crustose lichens is characterized by branching cracks that periodically close in response to climatic variations such as alternate wetting and drying regimes. Subtypes * Powdery – considered as the simplest subtype due to the absence of an organized thallus. :The thallus appears powdery. :E.g. Genera ''Lepraria'', ''Vezdaea'' * Endolithic – grows inside the rock, usually in interstitial spaces between mineral grains. The :upper cortex is usually d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumscription (taxonomy)
In biological taxonomy, circumscription is the content of a taxon, that is, the delimitation of which subordinate taxa are parts of that taxon. If we determine that species X, Y, and Z belong in Genus A, and species T, U, V, and W belong in Genus B, those are our circumscriptions of those two genera. Another systematist might determine that T, U, V, W, X, Y, and Z all belong in genus A. Agreement on circumscriptions is not governed by the Codes of Zoological or Botanical Nomenclature, and must be reached by scientific consensus. A goal of biological taxonomy is to achieve a stable circumscription for every taxon. This goal conflicts, at times, with the goal of achieving a natural classification that reflects the evolutionary history of divergence of groups of organisms. Balancing these two goals is a work in progress, and the circumscriptions of many taxa that had been regarded as stable for decades are in upheaval in the light of rapid developments in molecular phylogenetics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josef Hafellner
Josef Hafellner (1951– ) is an Austrian mycologist and lichenologist. He was awarded the Acharius Medal in 2016 for his lifetime contributions to lichenology. Before his retirement, he was a professor at the Karl-Franzens-Universität in Graz. Hafellner started developing an interest in lichens while he was a student at this institution, studying under Josef Poelt. He earned a master's degree in 1975 and a PhD in 1978, defending a doctoral thesis about the genus '' Karschia''. In 2003, Hafellner received his habilitation. By this time, he had studied with French lichenologist André Bellemère (1927–2014) at Saint-Cloud, where he learned techniques of transmission electron microscopy and how their application in studying asci could be used in lichen systematics. His 1984 work ''Studien in Richtung einer natürlicheren Gliederung der Sammelfamilien Lecanoraceae und Lecideaceae'' has been described as "probably the single most influential publication in lichen systematics in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Phylogenetic
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to determine the processes by which diversity among species has been achieved. The result of a molecular phylogenetic analysis is expressed in a phylogenetic tree. Molecular phylogenetics is one aspect of molecular systematics, a broader term that also includes the use of molecular data in taxonomy and biogeography. Molecular phylogenetics and molecular evolution correlate. Molecular evolution is the process of selective changes (mutations) at a molecular level (genes, proteins, etc.) throughout various branches in the tree of life (evolution). Molecular phylogenetics makes inferences of the evolutionary relationships that arise due to molecular evolution and results in the construction of a phylogenetic tree. History The theoretical framew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |