|
Adaptive Beamformer
An adaptive beamformer is a system that performs adaptive spatial signal processing with an array of transmitters or receivers. The signals are combined in a manner which increases the signal strength to/from a chosen direction. Signals to/from other directions are combined in a benign or destructive manner, resulting in degradation of the signal to/from the undesired direction. This technique is used in both radio frequency and acoustic arrays, and provides for directional sensitivity without physically moving an array of receivers or transmitters. Motivation/Applications Adaptive beamforming was initially developed in the 1960s for the military applications of sonar and radar. There exist several modern applications for beamforming, one of the most visible applications being commercial wireless networks such as LTE. Initial applications of adaptive beamforming were largely focused in radar and electronic countermeasures to mitigate the effect of signal jamming in the military doma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as audio signal processing, sound, image processing, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, Data storage, digital storage efficiency, correcting distorted signals, subjective video quality and to also detect or pinpoint components of interest in a measured signal. History According to Alan V. Oppenheim and Ronald W. Schafer, the principles of signal processing can be found in the classical numerical analysis techniques of the 17th century. They further state that the digital refinement of these techniques can be found in the digital control systems of the 1940s and 1950s. In 1948, Claude Shannon wrote the influential paper "A Mathematical Theory of Communication" which was published in the Bell System Technical Journal. The paper laid the groundwork for later development of information c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
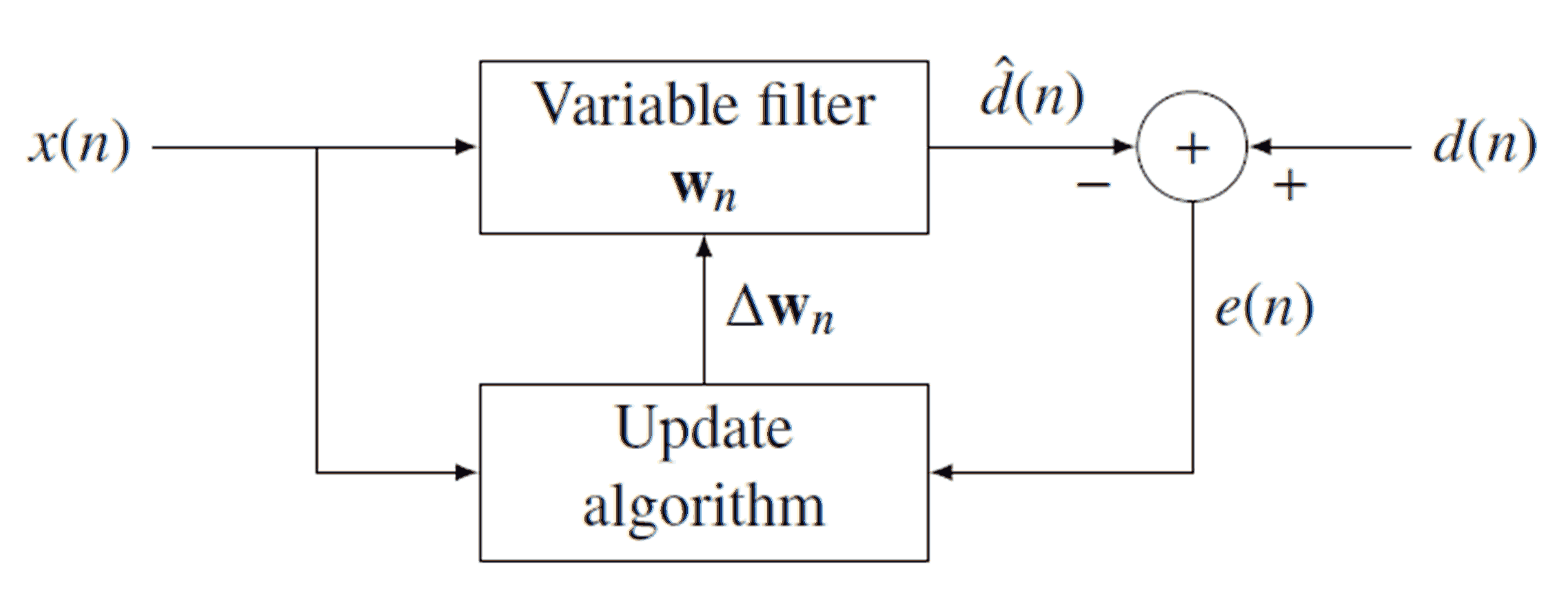
Least Mean Squares Filter
Least mean squares (LMS) algorithms are a class of adaptive filter used to mimic a desired filter by finding the filter coefficients that relate to producing the least mean square of the error signal (difference between the desired and the actual signal). It is a stochastic gradient descent method in that the filter is only adapted based on the error at the current time. It was invented in 1960 by Stanford University professor Bernard Widrow and his first Ph.D. student, Ted Hoff. Problem formulation Relationship to the Wiener filter The realization of the causal Wiener filter looks a lot like the solution to the least squares estimate, except in the signal processing domain. The least squares solution, for input matrix \mathbf and output vector \boldsymbol y is : \boldsymbol = (\mathbf ^\mathbf\mathbf)^\mathbf^\boldsymbol y . The FIR least mean squares filter is related to the Wiener filter, but minimizing the error criterion of the former does not rely on cross-corr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tx Rx Array
TX, T-X, or Tx may refer to: * Texas, abbreviated as TX Companies Consumer product companies * Tianxiang TX, a Chinese brand of drones and UAVs by Tianxiang Aerospace Science and Technology Co. * TX Watch Company, a former watch company by the Timex Group Media and telecommunication companies * TX Digital Illusions, a former American video game developer * TX Group, a Swiss media company * TX Network, a Japanese television network Transportation companies * Air Caraïbes (IATA airline designator TX) Electronics and machines * Canon TX, a 35mm single-lens reflex camera * Palm TX, a personal digital assistant * Sony Xperia TX, a smartphone Media * Fenix TX, a pop punk band from Houston, Texas, formerly known as Riverfenix ** ''Fenix TX'', the band's first album after their name change * T-X (Terminatrix), the antagonist in the movie ''Terminator 3: Rise of the Machines'' Science and technology Astronomy * TX Camelopardalis, a star in the Camelopardalis constellation * TX Piscium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIMO
In radio, multiple-input and multiple-output, or MIMO (), is a method for multiplying the capacity of a radio link using multiple transmission and receiving antennas to exploit multipath propagation. MIMO has become an essential element of wireless communication standards including IEEE 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4), IEEE 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5), HSPA+ (3G), WiMAX, and Long Term Evolution (LTE). More recently, MIMO has been applied to power-line communication for three-wire installations as part of the ITU G.hn standard and of the HomePlug AV2 specification. At one time, in wireless the term "MIMO" referred to the use of multiple antennas at the transmitter and the receiver. In modern usage, "MIMO" specifically refers to a class of techniques for sending and receiving more than one data signal simultaneously over the same radio channel by exploiting multipath propagation. Additionally, modern MIMO usage often refers to multiple data signals sent to different receivers (with one or more receiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smart Antennas
Smart antennas (also known as adaptive array antennas, digital antenna arrays, multiple antennas and, recently, MIMO) are antenna arrays with smart signal processing algorithms used to identify spatial signal signatures such as the direction of arrival (DOA) of the signal, and use them to calculate beamforming vectors which are used to track and locate the antenna beam on the mobile/target. Smart antennas should not be confused with reconfigurable antennas, which have similar capabilities but are single element antennas and not antenna arrays. Smart antenna techniques are used notably in acoustic signal processing, track and scan radar, radio astronomy and radio telescopes, and mostly in cellular systems like W-CDMA, UMTS, and LTE. Smart antennas have many functions: DOA estimation, beamforming, interference nulling, and constant modulus preservation.. Direction of arrival (DOA) estimation The smart antenna system estimates the direction of arrival of the signal, using techniqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constant Modulus
Constant or The Constant may refer to: Mathematics * Constant (mathematics), a non-varying value * Mathematical constant, a special number that arises naturally in mathematics, such as or Other concepts * Control variable or scientific constant, in experimentation the unchanging or constant variable * Physical constant, a physical quantity generally believed to be universal and unchanging * Constant (computer programming), a value that, unlike a variable, cannot be reassociated with a different value * Logical constant, a symbol in symbolic logic that has the same meaning in all models, such as the symbol "=" for "equals" People * Constant (given name) * Constant (surname) * John, Elector of Saxony (1468–1532), known as John the Constant * Constant Nieuwenhuys (1920-2005), better known as Constant Places * Constant, Barbados, a populated place Arts and entertainment * "The Constant", a 2008 episode of the television show ''Lost'' * ''The Constant'' (Story of the Year alb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjugate Gradient Method
In mathematics, the conjugate gradient method is an algorithm for the numerical solution of particular systems of linear equations, namely those whose matrix is positive-definite. The conjugate gradient method is often implemented as an iterative algorithm, applicable to sparse systems that are too large to be handled by a direct implementation or other direct methods such as the Cholesky decomposition. Large sparse systems often arise when numerically solving partial differential equations or optimization problems. The conjugate gradient method can also be used to solve unconstrained optimization problems such as energy minimization. It is commonly attributed to Magnus Hestenes and Eduard Stiefel, who programmed it on the Z4, and extensively researched it. The biconjugate gradient method provides a generalization to non-symmetric matrices. Various nonlinear conjugate gradient methods seek minima of nonlinear optimization problems. Description of the problem addressed by co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recursive Least Squares Filter
Recursive least squares (RLS) is an adaptive filter algorithm that recursively finds the coefficients that minimize a weighted linear least squares cost function relating to the input signals. This approach is in contrast to other algorithms such as the least mean squares (LMS) that aim to reduce the mean square error. In the derivation of the RLS, the input signals are considered deterministic, while for the LMS and similar algorithms they are considered stochastic. Compared to most of its competitors, the RLS exhibits extremely fast convergence. However, this benefit comes at the cost of high computational complexity. Motivation RLS was discovered by Gauss but lay unused or ignored until 1950 when Plackett rediscovered the original work of Gauss from 1821. In general, the RLS can be used to solve any problem that can be solved by adaptive filters. For example, suppose that a signal d(n) is transmitted over an echoey, noisy channel that causes it to be received as :x(n)=\sum_^q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sample Matrix Inversion
Sample matrix inversion (or direct matrix inversion) is an algorithm that estimates weights of an array (adaptive filter) by replacing the correlation matrix R with its estimate. Using K N-dimensional samples X_1, X_2,\dots,X_K, an unbiased estimate of R_, the N \times N correlation matrix of the array signals, may be obtained by means of a simple averaging scheme: :\hat_ = \frac \sum\limits_^K X_k X^H_k, where H is the conjugate transpose In mathematics, the conjugate transpose, also known as the Hermitian transpose, of an m \times n complex matrix \boldsymbol is an n \times m matrix obtained by transposing \boldsymbol and applying complex conjugate on each entry (the complex con .... The expression of the theoretically optimal weights requires the inverse of R_, and the inverse of the estimates matrix is then used for finding estimated optimal weights. References * * {{cite book , first1=S. , last1=Haykin , year=2002 , title=Adaptive Filter Theory , url=https://archive.org/de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal-to-noise Ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power, often expressed in decibels. A ratio higher than 1:1 (greater than 0 dB) indicates more signal than noise. SNR, bandwidth, and channel capacity of a communication channel are connected by the Shannon–Hartley theorem. Definition Signal-to-noise ratio is defined as the ratio of the power of a signal (meaningful input) to the power of background noise (meaningless or unwanted input): : \mathrm = \frac, where is average power. Both signal and noise power must be measured at the same or equivalent points in a system, and within the same system bandwidth. Depending on whether the signal is a constant () or a random variable (), the signal-to-noise ratio for random noise becomes: : \mathrm = \frac where E refers to the expected value, i.e. in this case ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LTE (telecommunication)
In telecommunications, long-term evolution (LTE) is a standard for wireless broadband communication for mobile devices and data terminals, based on the GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSPA standards. It improves on those standards' capacity and speed by using a different radio interface and core network improvements. LTE is the upgrade path for carriers with both GSM/UMTS networks and CDMA2000 networks. Because LTE frequencies and bands differ from country to country, only multi-band phones can use LTE in all countries where it is supported. The standard is developed by the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) and is specified in its Release 8 document series, with minor enhancements described in Release 9. LTE is also called 3.95G and has been marketed as "4G LTE" and "Advanced 4G"; but it does not meet the technical criteria of a 4G wireless service, as specified in the 3GPP Release 8 and 9 document series for LTE Advanced. The requirements were set forth by the ITU-R organisation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna Gain Pattern
Antenna ( antennas or antennae) may refer to: Science and engineering * Antenna (radio), also known as an aerial, a transducer designed to transmit or receive electromagnetic (e.g., TV or radio) waves * Antennae Galaxies, the name of two colliding galaxies NGC 4038 and NGC 4039 Biology * Antenna (biology), one of one or more pairs of appendages used for sensing in arthropods * ''Antenna'' (journal), the journal of the Royal Entomological Society Media Broadcasting * ANT1, a Greek-language terrestrial channel * Antena Internațional, a Romanian television channel * Antena 1 (Romania), a Romanian television channel * Antena 2 (Romania), a Romanian television channel * Antena 3 (Romania), a Romanian television channel * Antena 3 (Spain), a Spanish terrestrial television channel * Antenna TV, a U.S. television channel established in 2011 by Tribune Broadcasting * RDP Antena 1, Portuguese public radio station * RDP Antena 2, Portuguese public radio station * RDP Antena 3, Portugues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |