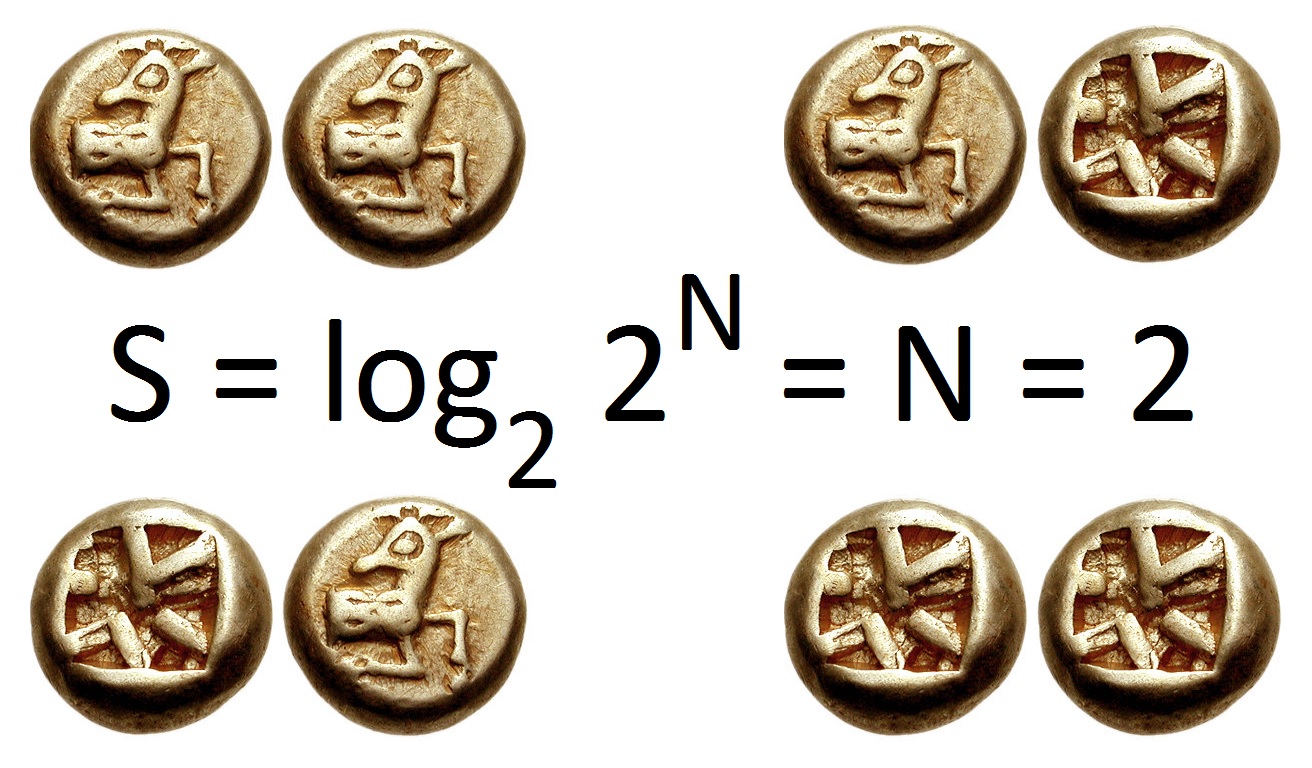|
Adaptability
Adaptability ( "fit to, adjust") is a feature of a system or of a process. This word has been put to use as a specialised term in different disciplines and in business operations. Word definitions of adaptability as a specialised term differ little from dictionary definitions. According to Andresen and Gronau adaptability in the field of organizational management can in general be seen as an ability to change something or oneself to fit to occurring changes. In ecology, adaptability has been described as the ability to cope with unexpected disturbances in the environment. With respect to business and manufacturing systems and processes, adaptability has come to be seen increasingly as an important factor for their efficiency and economic success. In contrast, adaptability and efficiency are held to be in opposition to each other in biological and ecological systems, requiring a trade-off, since both are important factors in the success of such systems. To determine the adaptabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Mckeown
Max McKeown (born in London) is an English writer, consultant, and researcher specialising in innovation Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or service (economics), services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a n ... strategy, leadership and culture. He has written six influential books and conducts research with Warwick Business School (Young, 2008). He is a fellow of the RSA. He served on the advisory board for the Rollins Center for eBusiness. He earned his master's degree in Business Administration and PhD from the Warwick Business School under the supervision of Professor David Wilson and Professor Sotirios Paroutis, who was in turn supervised by Andrew Pettigrew. McKeown is an advocate of innovation culture. He also argues that failure can be positive for progress if it is viewed as part of learning (Chynoweth, 2010). He makes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy (information Theory)
In information theory, the entropy of a random variable quantifies the average level of uncertainty or information associated with the variable's potential states or possible outcomes. This measures the expected amount of information needed to describe the state of the variable, considering the distribution of probabilities across all potential states. Given a discrete random variable X, which may be any member x within the set \mathcal and is distributed according to p\colon \mathcal\to[0, 1], the entropy is \Eta(X) := -\sum_ p(x) \log p(x), where \Sigma denotes the sum over the variable's possible values. The choice of base for \log, the logarithm, varies for different applications. Base 2 gives the unit of bits (or "shannon (unit), shannons"), while base Euler's number, ''e'' gives "natural units" nat (unit), nat, and base 10 gives units of "dits", "bans", or "Hartley (unit), hartleys". An equivalent definition of entropy is the expected value of the self-information of a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manufacturing Execution Systems
Manufacturing execution systems (MES) are computerized systems used in manufacturing to track and document the transformation of raw materials to finished goods. MES provides information that helps manufacturing decision-makers understand how current conditions on the plant floor can be optimized to improve production output. MES works as real-time monitoring system to enable the control of multiple elements of the production process (e.g. inputs, personnel, machines and support services). MES may operate across multiple function areas, for example management of product definitions across the product life-cycle, resource scheduling, order execution and dispatch, production analysis and downtime management for overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), product quality, or materials track and trace. MES creates the "as-built" record, capturing the data, processes and outcomes of the manufacturing process. This can be especially important in regulated industries, such as food and bev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and is expressed in its functioning. Systems are the subjects of study of systems theory and other systems sciences. Systems have several common properties and characteristics, including structure, function(s), behavior and interconnectivity. Etymology The term ''system'' comes from the Latin word ''systēma'', in turn from Greek language, Greek ''systēma'': "whole concept made of several parts or members, system", literary "composition"."σύστημα" , Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek–English Lexicon'', on Pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer System
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to automatically carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as ''programs'', which enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. The term computer system may refer to a nominally complete computer that includes the hardware, operating system, software, and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation; or to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of industrial and consumer products use computers as control systems, including simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls, and factory devices like industrial robots. Computers are at the core of general-purpose devices such as personal computers and mobile devices such as smartphones. Computers power the Internet, which links billions of compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive System
An adaptive system is a set of interacting or interdependent entities, real or abstract, forming an integrated whole that together are able to respond to environmental changes or changes in the interacting parts, in a way analogous to either continuous physiological homeostasis or evolutionary adaptation in biology. Feedback loops represent a key feature of adaptive systems, such as ecosystems and individual organisms; or in the human world, communities, organizations, and families. Adaptive systems can be organized into a hierarchy. Artificial adaptive systems include robots with control systems that utilize negative feedback to maintain desired states. The law of adaptation The law of adaptation may be stated informally as: Formally, the law can be defined as follows: Given a system S, we say that a physical event E is a stimulus for the system S if and only if the probability P(S \rightarrow S', E) that the system suffers a change or be perturbed (in its elements or i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open System (systems Theory)
An open system is a system that has external interactions. Such interactions can take the form of information, energy, or material transfers into or out of the system boundary, depending on the discipline which defines the concept. An open system is contrasted with the concept of an isolated system which exchanges neither energy, matter, nor information with its environment. An open system is also known as a flow system. The concept of an open system was formalized within a framework that enabled one to interrelate the theory of the organism, thermodynamics, and evolutionary theory. This concept was expanded upon with the advent of information theory and subsequently systems theory. Today the concept has its applications in the natural and social sciences. In the natural sciences an open system is one whose border is permeable to both energy and mass. By contrast, a closed system is permeable to energy but not to matter. The definition of an open system assumes that there a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Resilience
In ecology, resilience is the capacity of an ecosystem to respond to a perturbation or Disturbance (ecology), disturbance by resisting damage and subsequently recovering. Such perturbations and disturbances can include stochastic events such as fires, flooding, windstorms, insect population explosions, and human activities such as deforestation, fracking of the ground for oil extraction, pesticide sprayed in soil, and the Introduced species, introduction of exotic plant or animal species. Disturbances of sufficient Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude or duration can profoundly affect an ecosystem and may force an ecosystem to reach a Ecological threshold, threshold beyond which a different regime of processes and structures predominates. When such thresholds are associated with a critical or bifurcation theory, bifurcation point, these regime shifts may also be referred to as critical transitions. Human activities that adversely affect ecological resilience such as loss of biodiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Terms
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or buying and selling products (such as goods and services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for profit." A business entity is not necessarily separate from the owner and the creditors can hold the owner liable for debts the business has acquired except for limited liability company. The taxation system for businesses is different from that of the corporates. A business structure does not allow for corporate tax rates. The proprietor is personally taxed on all income from the business. A distinction is made in law and public offices between the term business and a company (such as a corporation or cooperative). Colloquially, the terms are used interchangeably. Corporations are distinct from sole proprietors and partnerships. Corporations are separate and unique legal entities from their shareholders; as such they provide limited liability for their owners and members. Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Theories
Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world. The field is broad and includes foundations in ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |