|
Adamantane Dication
Adamantane is an organic compound with a formula C10H16 or, more descriptively, (CH)4(CH2)6. Adamantane molecules can be described as the fusion of three cyclohexane rings. The molecule is both rigid and virtually stress-free. Adamantane is the most stable isomer of C10H16. The spatial arrangement of carbon atoms in the adamantane molecule is the same as in the diamond crystal. This similarity led to the name ''adamantane'', which is derived from the Greek ''adamantinos'' (relating to steel or diamond). It is a white solid with a camphor-like odor. It is the simplest diamondoid. The discovery of adamantane in petroleum in 1933 launched a new field of chemistry dedicated to the synthesis and properties of polyhedral organic compounds. Adamantane derivatives have found practical application as drugs, polymeric materials, and thermally stable lubricants. History and synthesis In 1924, H. Decker suggested the existence of adamantane, which he called decaterpene. The first attempted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society (professional association) in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Royal Institute of Chemistry, the Faraday Society, and the Society for Analytical Chemistry with a new Royal Charter and the dual role of learned society and professional body. At its inception, the Society had a combined membership of 34,000 in the UK and a further 8,000 abroad. The headquarters of the Society are at Burlington House, Piccadilly, London. It also has offices in Thomas Graham House in Cambridge (named after Thomas Graham (chemist), Thomas Graham, the first president of the Chemical Society) where ''RSC Publishing'' is based. The Society has offices in the United States, on the campuses of The University of Pennsylvania and Drexel University, at the University City Science Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in both Beijing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diethyl Malonate
Diethyl malonate, also known as DEM, is the diethyl ester of malonic acid. It occurs naturally in grapes and strawberries as a colourless liquid with an apple-like odour, and is used in perfumes. It is also used to synthesize other compounds such as barbiturates, artificial flavourings, vitamin B1, and vitamin B6. Structure and properties Malonic acid is a rather simple dicarboxylic acid, with two the carboxyl groups close together. In forming diethyl malonate from malonic acid, the hydroxyl group (−OH) on both of the carboxyl groups is replaced by an ethoxy group (−OEt; −OCH2CH3). The methylene group (−CH2−) in the middle of the malonic part of the diethyl malonate molecule is neighboured by two carbonyl groups (−C(=O)−). The hydrogen atoms on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group in a molecule is significantly more acidic than hydrogen atoms on a carbon adjacent to alkyl groups (up to 30 orders of magnitude). (This is known as the α position with re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
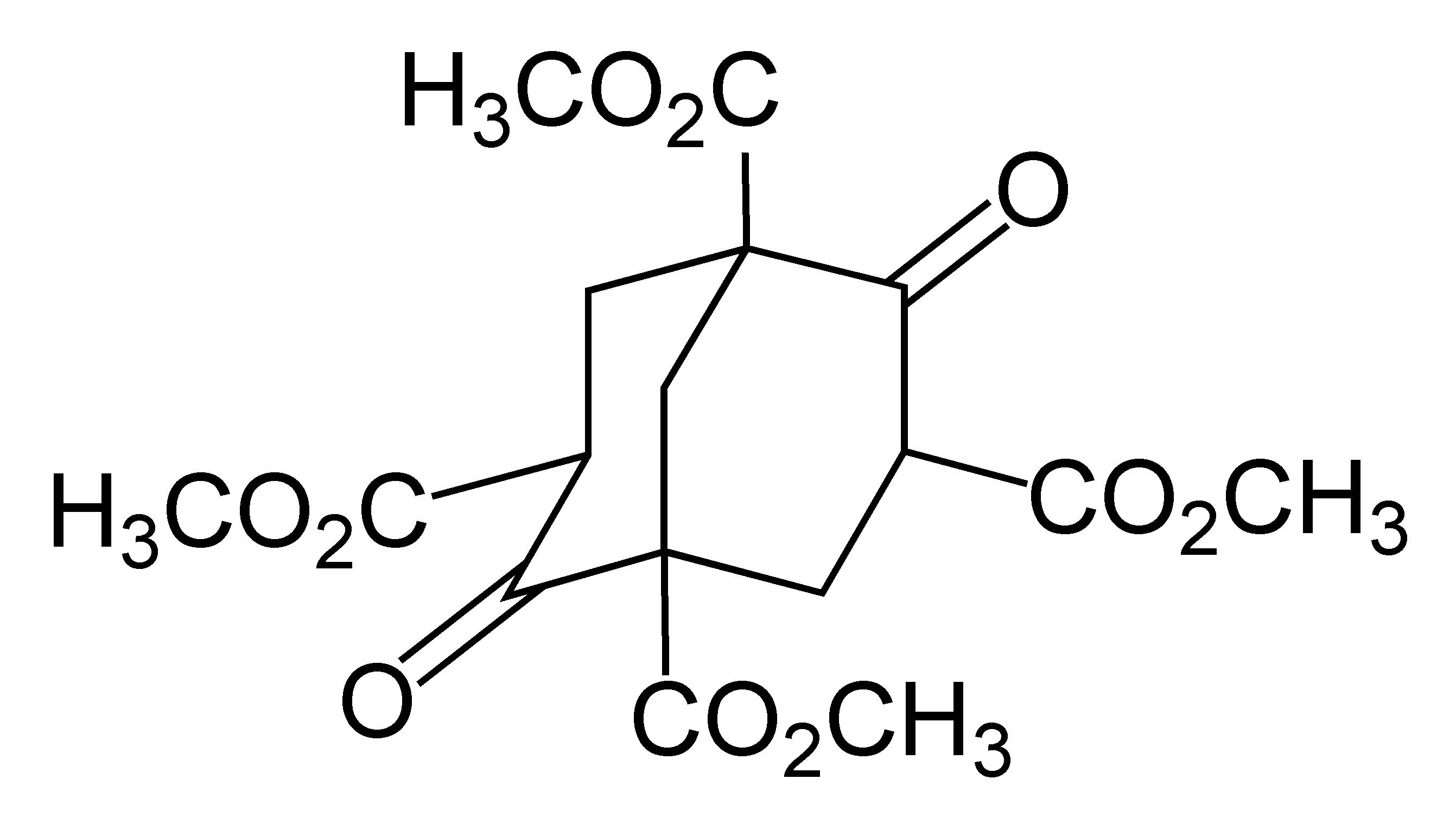
Adamantane Synthesis
Adamantane is an organic compound with a formula C10H16 or, more descriptively, (CH)4(CH2)6. Adamantane molecules can be described as the fusion of three cyclohexane rings. The molecule is both rigid and virtually stress-free. Adamantane is the most stable isomer of C10H16. The spatial arrangement of carbon atoms in the adamantane molecule is the same as in the diamond crystal. This similarity led to the name ''adamantane'', which is derived from the Greek ''adamantinos'' (relating to steel or diamond). It is a white solid with a camphor-like odor. It is the simplest diamondoid. The discovery of adamantane in petroleum in 1933 launched a new field of chemistry dedicated to the synthesis and properties of polyhedral organic compounds. Adamantane derivatives have found practical application as drugs, polymeric materials, and thermally stable lubricants. History and synthesis In 1924, H. Decker suggested the existence of adamantane, which he called decaterpene. The first attempted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Chloride
Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It forms hexahydrate with the formula , containing six water molecules of hydration. Both are colourless crystals, but samples are often contaminated with iron(III) chloride, giving a yellow color. The anhydrous material is important commercially. It has a low melting and boiling point. It is mainly produced and consumed in the production of aluminium metal, but large amounts are also used in other areas of the chemical industry. The compound is often cited as a Lewis acid. It is an example of an inorganic compound that reversibly changes from a polymer to a monomer at mild temperature. Structure Anhydrous adopts three structures, depending on the temperature and the state (solid, liquid, gas). Solid has a sheet-like layered structure with cubic close-packed chloride ions. In this framework, the Al centres exhibit octahedral coordination geometry. In contrast, has a more mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis Acids And Bases
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any species that has a filled orbital containing an electron pair which is not involved in bonding but may form a dative bond with a Lewis acid to form a Lewis adduct. For example, NH3 is a Lewis base, because it can donate its lone pair of electrons. Trimethylborane (Me3B) is a Lewis acid as it is capable of accepting a lone pair. In a Lewis adduct, the Lewis acid and base share an electron pair furnished by the Lewis base, forming a dative bond. In the context of a specific chemical reaction between NH3 and Me3B, a lone pair from NH3 will form a dative bond with the empty orbital of Me3B to form an adduct NH3•BMe3. The terminology refers to the contributions of Gilbert N. Lewis. From p. 142: "We are inclined to think of substances as pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adams' Catalyst
Adams' catalyst, also known as platinum dioxide, is usually represented as platinum(IV) oxide hydrate, PtO2•H2O. It is a catalyst for hydrogenation and hydrogenolysis in organic synthesis. This dark brown powder is commercially available. The oxide itself is not an active catalyst, but it becomes active after exposure to hydrogen whereupon it converts to platinum black, which is responsible for reactions. Preparation Adams' catalyst is prepared from chloroplatinic acid H2PtCl6 or ammonium chloroplatinate, (NH4)2PtCl6, by fusion with sodium nitrate. The first published preparation was reported by V. Voorhees and Roger Adams. The procedure involves first preparing a platinum nitrate which is then heated to expel nitrogen oxides. :H2PtCl6 + 6 NaNO3 → Pt(NO3)4 + 6 NaCl (aq) + 2 HNO3 :Pt(NO3)4 → PtO2 + 4 NO2 + O2 The resulting brown cake is washed with water to free it from nitrates. The catalyst can either be used as is or dried and stored in a desiccator for later use. Platin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a Catalysis, catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to redox, reduce or Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, often an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces Double bond, double and Triple bond, triple bonds in hydrocarbons. Process Hydrogenation has three components, the Saturated and unsaturated compounds, unsaturated substrate, the hydrogen (or hydrogen source) and, invariably, a catalyst. The redox, reduction reaction is carried out at different temperatures and pressures depending upon the substrate and the activity of the catalyst. Related or competing reactions The same ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicyclopentadiene
Dicyclopentadiene, abbreviated DCPD, is a chemical compound with formula C10H12. At room temperature, it is a white brittle wax, although lower purity samples can be straw coloured liquids. The pure material smells somewhat of soy wax or camphor, with less pure samples possessing a stronger acrid odor. Its energy density is 10,975 Wh/l. Dicyclopentadiene is a co-produced in large quantities in the steam cracking of naphtha and gas oils to ethylene. The major use is in resins, particularly, unsaturated polyester resins. It is also used in inks, adhesives, and paints. The top seven suppliers worldwide together had an annual capacity in 2001 of 179 kilotonnes (395 million pounds). Synthesis and structure The spontaneous dimerization of cyclopentadiene at room temperature to form dicyclopentadiene proceeds to around 50% conversion over 24 hours and yields the ''endo'' isomer in better than 99:1 ratio as the kinetically favored product (about 150:1 ''endo'':''exo'' at 80 °C). How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Von Ragué Schleyer
Paul von Ragué Schleyer (February 27, 1930 – November 21, 2014) was an American physical organic chemist whose research is cited with great frequency. A 1997 survey indicated that Dr. Schleyer was, at the time, the world's third most cited chemist, with over 1100 technical papers produced. He was Eugene Higgins Professor of Chemistry at Princeton University, Professor and co-director of the Institute for Organic Chemistry (Institut für organische Chemie) at the University of Erlangen–Nuremberg in Germany, and later Graham Perdue Professor of Chemistry at the University of Georgia in Athens, Georgia. He published twelve books in the fields of lithium chemistry, ab initio molecular orbital theory and carbonium ions. He was past president of the World Association of Theoretically Oriented Chemists, a fellow of the International Academy of Quantum Molecular Science and editor-in-chief of the ''Encyclopedia of Computational Chemistry''. Early life Born on February 27, 1930, in Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adamantane Synthesis By Prelog
Adamantane is an organic compound with a formula C10H16 or, more descriptively, (CH)4(CH2)6. Adamantane molecules can be described as the fusion of three cyclohexane rings. The molecule is both rigid and virtually stress-free. Adamantane is the most stable isomer of C10H16. The spatial arrangement of carbon atoms in the adamantane molecule is the same as in the diamond crystal. This similarity led to the name ''adamantane'', which is derived from the Greek ''adamantinos'' (relating to steel or diamond). It is a white solid with a camphor-like odor. It is the simplest diamondoid. The discovery of adamantane in petroleum in 1933 launched a new field of chemistry dedicated to the synthesis and properties of polyhedral organic compounds. Adamantane derivatives have found practical application as drugs, polymeric materials, and thermally stable lubricants. History and synthesis In 1924, H. Decker suggested the existence of adamantane, which he called decaterpene. The first attempted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
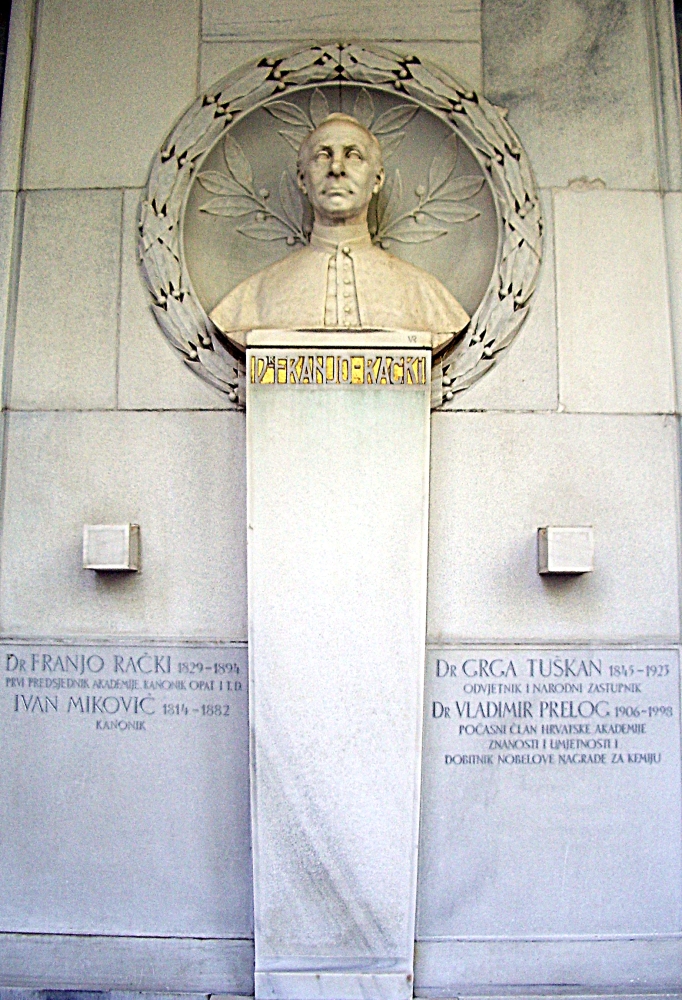
Vladimir Prelog
Vladimir Prelog (23 July 1906 – 7 January 1998) was a Croatian-Swiss organic chemist who received the 1975 Nobel Prize in chemistry for his research into the stereochemistry of organic molecules and reactions. Prelog was born and grew up in Sarajevo.Vladimir Prelog (1975Autobiography the Nobel Committee. He lived and worked in Prague, Zagreb and Zürich during his lifetime. Early life Prelog was born in Sarajevo, Condominium of Bosnia and Herzegovina, at that time within Austria-Hungary, to Croat parents who were working there. His father, Milan, a native of Zagreb, was a history professor at a gymnasium in Sarajevo and later at the University of Zagreb. As an 8-year-old boy, he stood near the place where the assassination of Franz Ferdinand occurred. Education Prelog attended elementary school in Sarajevo, but in 1915, as a child, Prelog moved to Zagreb (then part of the Austro-Hungary) with his parents. In Zagreb he graduated from elementary school. At first, he attended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |