|
Ada Regulon
In DNA repair, the Ada regulon is a set of genes whose expression is essential to adaptive response (also known as "Ada response", hence the name), which is triggered in prokaryotic cells by exposure to sub-lethal doses of alkylating agents. This allows the cells to tolerate the effects of such agents, which are otherwise toxic and mutagenic. The Ada response includes the expression of four genes: ''ada, alkA, alkB, and aidB''. The product of ''ada'' gene, the Ada protein, is an activator of transcription of all four genes. DNA bases damaged by alkylation are removed by distinct strategies. Alkylating agents The alkylating agents from a group of mutagens and carcinogens that modify DNA by alkylation. Alkyl base lesions can arrest replication, interrupt transcription, or signal the activation of cell cycle checkpoints or apoptosis. In mammals, they could be involved in carcinogenesis, neurodegenerative disease and aging. The alkylating agents can introduce methyl or et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs). This can eventually lead to malign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Ligase
DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, () that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms (such as DNA ligase IV) may specifically repair double-strand breaks (i.e. a break in both complementary strands of DNA). Single-strand breaks are repaired by DNA ligase using the complementary strand of the double helix as a template, with DNA ligase creating the final phosphodiester bond to fully repair the DNA. DNA ligase is used in both DNA repair and DNA replication (see '' Mammalian ligases''). In addition, DNA ligase has extensive use in molecular biology laboratories for recombinant DNA experiments (see '' Research applications''). Purified DNA ligase is used in gene cloning to join DNA molecules together to form recombinant DNA. Enzymatic mechanism The mechanism of DNA ligase is to form two covalent p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutagenesis
Mutagenesis () is a process by which the genetic information of an organism is changed by the production of a mutation. It may occur spontaneously in nature, or as a result of exposure to mutagens. It can also be achieved experimentally using laboratory procedures. A mutagen is a mutation-causing agent, be it chemical or physical, which results in an increased rate of mutations in an organism's genetic code. In nature mutagenesis can lead to cancer and various heritable diseases, and it is also a driving force of evolution. Mutagenesis as a science was developed based on work done by Hermann Muller, Charlotte Auerbach and J. M. Robson in the first half of the 20th century. History DNA may be modified, either naturally or artificially, by a number of physical, chemical and biological agents, resulting in mutations. Hermann Muller found that "high temperatures" have the ability to mutate genes in the early 1920s, and in 1927, demonstrated a causal link to mutation upon experimen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stationary Phase (biology)
250px, Growth is shown as ''L'' = log(numbers) where numbers is the number of colony forming units per ml, versus ''T'' (time.) Bacterial growth is proliferation of bacterium into two daughter cells, in a process called binary fission. Providing no event occurs, the resulting daughter cells are genetically identical to the original cell. Hence, bacterial growth occurs. Both daughter cells from the division do not necessarily survive. However, if the surviving number exceeds unity on average, the bacterial population undergoes exponential growth. The measurement of an exponential bacterial growth curve in batch culture was traditionally a part of the training of all microbiologists; the basic means requires bacterial enumeration (cell counting) by direct and individual (microscopic, flow cytometry), direct and bulk (biomass), indirect and individual (colony counting), or indirect and bulk (most probable number, turbidity, nutrient uptake) methods. Models reconcile theory with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
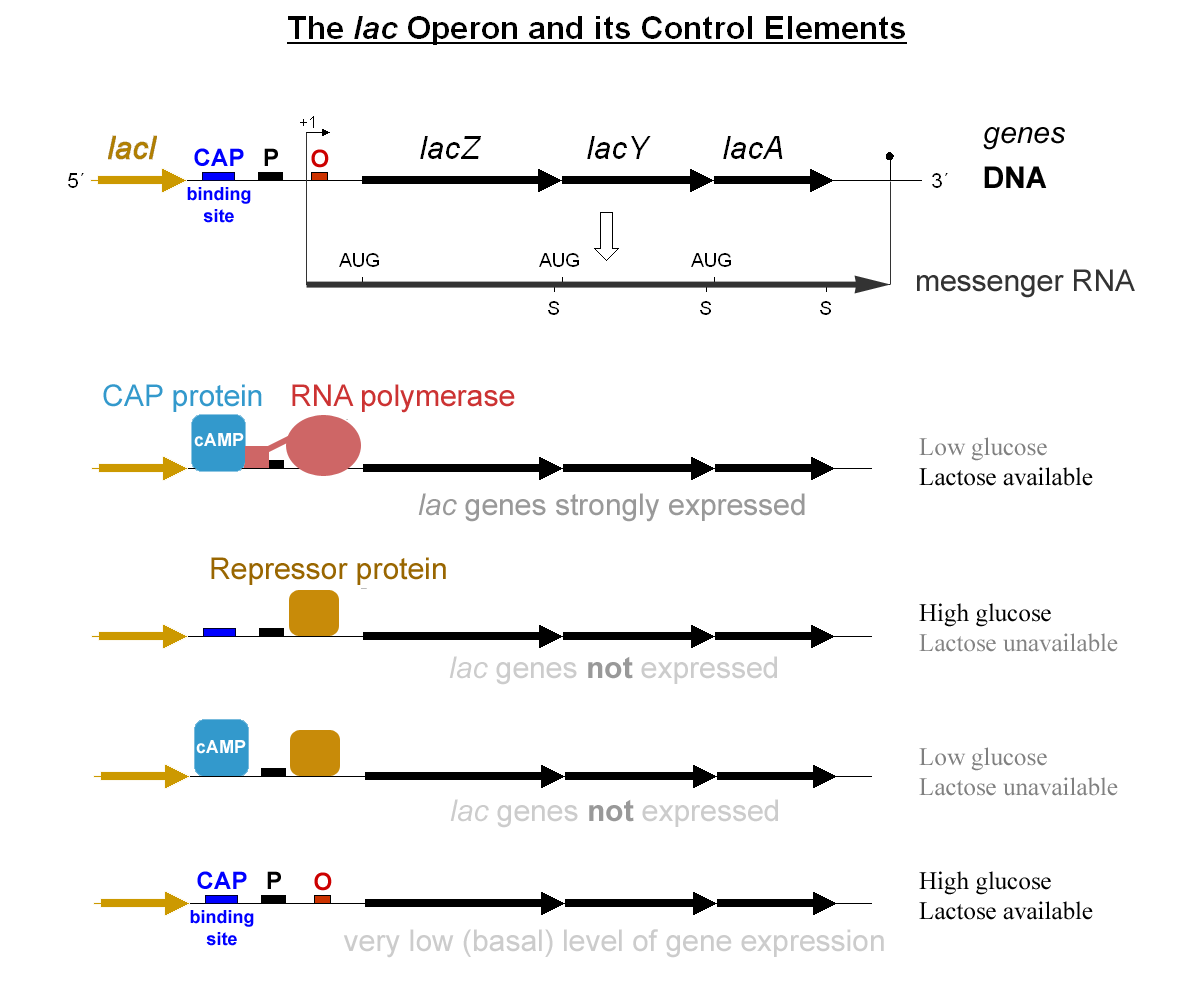
Regulon
In molecular genetics, a regulon is a group of genes that are regulated as a unit, generally controlled by the same regulatory gene that expresses a protein acting as a repressor or activator. This terminology is generally, although not exclusively, used in reference to prokaryotes, whose genomes are often organized into operons; the genes contained within a regulon are usually organized into more than one operon at disparate locations on the chromosome. Applied to eukaryotes, the term refers to any group of non-contiguous genes controlled by the same regulatory gene. A modulon is a set of regulons or operons that are collectively regulated in response to changes in overall conditions or stresses, but may be under the control of different or overlapping regulatory molecules. The term stimulon is sometimes used to refer to the set of genes whose expression responds to specific environmental stimuli. Examples Commonly studied regulons in bacteria are those involved in response to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometimes the symbol Cyz is used. The deprotonated form can generally be described by the symbol Cym as well. The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. In this case, the symbol Cyx is sometimes used. When used as a food additive, it has the E number E920. Cysteine is encoded by the codons UGU and UGC. The sulfur-containing amino acids cysteine and methionine are more easily oxidized than the other amino acids. Structure Like other amino acids (not as a residue of a protein), cysteine exists as a zwitterion. Cysteine has chirality in the older / notation based on homology to - and -glyceraldehyde. In the newer ''R''/''S'' system of design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activator (genetics)
A transcriptional activator is a protein (transcription factor) that increases transcription of a gene or set of genes. Activators are considered to have ''positive'' control over gene expression, as they function to promote gene transcription and, in some cases, are required for the transcription of genes to occur. Most activators are DNA-binding proteins that bind to enhancers or promoter-proximal elements. The DNA site bound by the activator is referred to as an "activator-binding site". The part of the activator that makes protein–protein interactions with the general transcription machinery is referred to as an "activating region" or "activation domain". Most activators function by binding sequence-specifically to a regulatory DNA site located near a promoter and making protein–protein interactions with the general transcription machinery ( RNA polymerase and general transcription factors), thereby facilitating the binding of the general transcription machinery to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Response (Ada) Regulatory Network
Adaptation, in biology, is the process or trait by which organisms or population better match their environment Adaptation may also refer to: Arts * Adaptation (arts), a transfer of a work of art from one medium to another ** Film adaptation, a story from another work, adapted into a film ** Literary adaptation, a story from a literary source, adapted into another work ** ** Theatrical adaptation, a story from another work, adapted into a play * ''Adaptation'' (film), a 2002 film by Spike Jonze * "Adaptation" (''The Walking Dead''), a television episode *''Adaptation'', a 2012 novel by Malinda Lo Biology and medicine * Adaptation (eye), the eye's adjustment to light ** Chromatic adaptation, visual systems' adjustments to changes in illumination for preservation of colors ** Prism adaptation, sensory-motor adjustments after the visual field has been artificially shifted * Cellular adaptation, changes by cells/tissues in response to changed microenvironments * High-altitude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavins
Flavins (from Latin ''flavus'', "yellow") are organic compounds, like their base, pteridine. They are formed by the tricyclic heterocycle isoalloxazine. The biochemical source is the vitamin riboflavin. The flavin moiety is often attached with an adenosine diphosphate to form flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), and, in other circumstances, is found as flavin mononucleotide (or FMN), a phosphorylated form of riboflavin. It is in one or the other of these forms that flavin is present as a prosthetic group in flavoproteins. The flavin group is capable of undergoing oxidation-reduction reactions, and can accept either one electron in a two-step process or two electrons at once. Reduction is made with the addition of hydrogen atoms to specific nitrogen atoms on the isoalloxazine ring system: In aqueous solution, flavins are yellow-coloured when oxidized, taking a red colour in the semi-reduced anionic state or blue in the neutral (semiquinone) state, and colourless when totally re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are harmless, but some serotypes ( EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains do not cause disease in humans and are part of the normal microbiota of the gut; such strains are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7-Methylguanine
7-Methylguanine is a modified purine nucleobase. It is a methylated version of guanine. The 7-methylguanine nucleoside is called 7-methylguanosine 7-Methylguanosine (m7G) is a modified purine nucleoside. It is a methylated version of guanosine and when found in human urine, it may be a biomarker of some types of cancer. In the RNAs, 7-methylguanosine have been used to study and examin .... However, the free 7-methylguanine base is not involved in the synthesis of nucleotides and not incorporated directly into nucleic acids. 7-Methylguanine is a natural inhibitor of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) and tRNA guanine transglycosylase (TGT) - and thus may exert anticancer activity. For example, it was demonstrated that 7-methylguanine could accelerate apoptotic death of BRCA1-deficient breast cancer cells induced by cisplatin and doxorubicin. References Nucleobases Purines {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Regulatory_Network.png)