|
Acteonellidae
Acteonellidae is an extinct family of gastropods in the informal group Lower Heterobranchia (according to the taxonomy of the Gastropoda by Bouchet & Rocroi, 2005). Taxonomy * Acteonellinae ** '' Acteonella'' d'Orbigny, 1843 - type genus In biological taxonomy, the type genus is the genus which defines a biological family and the root of the family name. Zoological nomenclature According to the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, "The name-bearing type of a nominal f ... ** '' Trochactaeon'' Meek, 1863 * Cylindrobullininae Wenz, 1938 * Itieriinae Cossmann, 1896 References External links Gastropod families {{paleo-gastropod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acteonellidae
Acteonellidae is an extinct family of gastropods in the informal group Lower Heterobranchia (according to the taxonomy of the Gastropoda by Bouchet & Rocroi, 2005). Taxonomy * Acteonellinae ** '' Acteonella'' d'Orbigny, 1843 - type genus In biological taxonomy, the type genus is the genus which defines a biological family and the root of the family name. Zoological nomenclature According to the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, "The name-bearing type of a nominal f ... ** '' Trochactaeon'' Meek, 1863 * Cylindrobullininae Wenz, 1938 * Itieriinae Cossmann, 1896 References External links Gastropod families {{paleo-gastropod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acteonella
''Acteonella'' is a genus of extinct sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the extinct family Acteonellidae. The genus is known from the Cretaceous The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ... period. Species Species within the genus ''Acteonella'' include: * '' Actaeonella borneensis'' Sohl and Kollmann, 1985 * '' Actaeonella briggsi'' Sohl and Kollmann, 1985 * '' Actaeonella browni'' Sohl and Kollmann, 1985 * '' Actaeonella coquiensis'' Sohl and Kollmann, 1985 * '' Actaeonella cubensis'' Sohl and Kollmann, 1985 * '' Actaeonella delgadoi'' Choffat, 1901 * '' Actaeonella jicarensis'' Sohl and Kollmann, 1985 * '' Actaeonella lucianoi'' Maury, 1930 * '' Actaeonella marchmontensis'' Sohl and Kollmann, 1985 * '' Actaeonella oviformis'' Gabb, 1869 * '' Actaeonella pecosens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
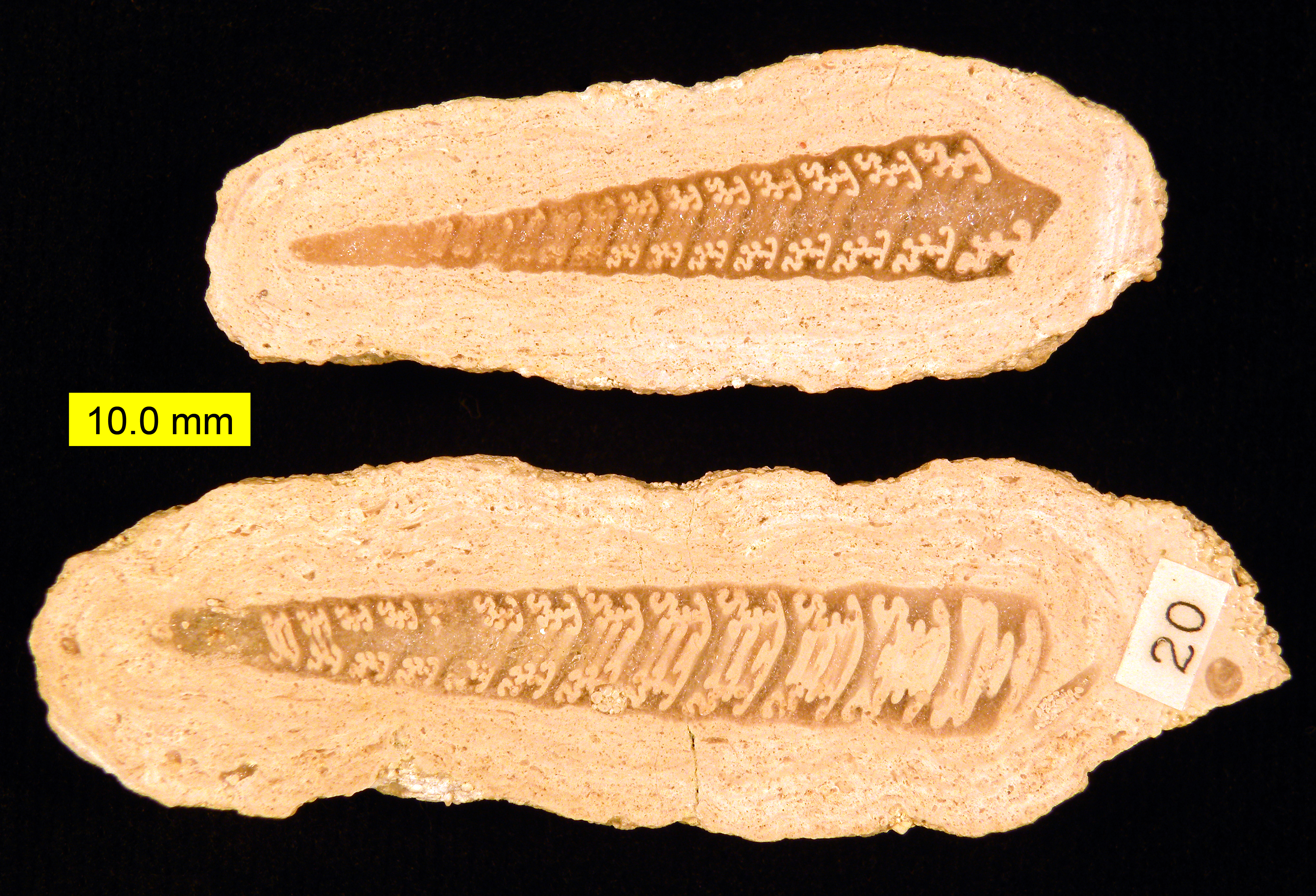
Trochactaeon Conicus
''Trochactaeon'' is an extinct genus of fossil sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Acteonellidae. The genus was named in 1863. The genus ''Trochactaeon'' is known from the Early to the Late Cretaceous The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ... epochs. Species Species in the genus ''Trochactaeon'' include: * '' Trochactaeon conicus'' - late Cretaceous * '' Trochactaeon crisimensis'' Choffat, 1966 References Acteonellidae Early Cretaceous genus first appearances Late Cretaceous genus extinctions {{paleo-gastropod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trochactaeon
''Trochactaeon'' is an extinct genus of fossil sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Acteonellidae. The genus was named in 1863. The genus ''Trochactaeon'' is known from the Early to the Late Cretaceous epochs. Species Species in the genus ''Trochactaeon'' include: * ''Trochactaeon conicus ''Trochactaeon'' is an extinct genus of fossil sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Acteonellidae. The genus was named in 1863. The genus ''Trochactaeon'' is known from the Early to the Late Cretaceous The Late Cretaceous (100 ...'' - late Cretaceous * '' Trochactaeon crisimensis'' Choffat, 1966 References Acteonellidae Early Cretaceous genus first appearances Late Cretaceous genus extinctions {{paleo-gastropod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acteonoidea
Acteonoidea is a superfamily of sea snails, or bubble snails, marine gastropod mollusks. Taxonomy In the taxonomy of Bouchet & Rocroi (2005), the superfamily Acteonoidea has been included into the informal group "Lower Heterobranchia" (Heterostropha ''sensu'' Ponder & Warén, 1988), also known as the Allogastropoda. Only one of analyses by Jörger et al. (2010) indicates the Acteonoidea sister to Nudipleura. This clade that had resulted repeatedly in molecular studies with still limited "lower heterobranch" taxon sampling, either in a derived position or as a basal offshoot within Euthyneura. A recent molecular phylogeny on Acteonoidea suggest a common origin with lower heterobranch Rissoelloidea and a sister group relationship to Nudipleura.Gbbeler K. & Klussmann-Kolb A. (2010). "The phylogeny of the Acteonoidea (Gastropoda): molecular systematics and first detailed morphological study of ''Rictaxis punctocaelatus'' (Carpenter, 1864)". ''Journal of Molluscan Studies'' 76(4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy Of The Gastropoda (Bouchet & Rocroi, 2005)
The taxonomy of the Gastropoda as it was revised in 2005 by Philippe Bouchet and Jean-Pierre Rocroi is a system for the scientific classification of gastropod mollusks. (Gastropods are a taxonomic class of animals which consists of snails and slugs of every kind, from the land, from freshwater, and from saltwater.) The paper setting out this taxonomy was published in the journal ''Malacologia''. The system encompasses both living and extinct groups, as well as some fossils whose classification as gastropods is uncertain. The Bouchet & Rocroi system was the first complete gastropod taxonomy that primarily employed the concept of clades, and was derived from research on molecular phylogenetics; in this context a clade is a "natural grouping" of organisms based upon a statistical cluster analysis. In contrast, most of the previous overall taxonomic schemes for gastropods relied on morphological features to classify these animals, and used taxon ranks such as order, superorder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusca
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The gastropod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropoda
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, and land snails and slugs. The class Gastropoda contains a vast total of named species, second only to the insects in overall number. The fossil history of this class goes back to the Late Cambrian. , 721 families of gastropods are known, of which 245 are extinct and appear only in the fossil record, while 476 are currently extant with or without a fossil record. Gastropoda (previously known as univalves and sometimes spelled "Gasteropoda") are a major part of the phylum Mollusca, and are the most highly diversified class in the phylum, with 65,000 to 80,000 living snail and slug species. The anatomy, behavior, feeding, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterobranchia
Heterobranchia, the ''heterobranchs'' (meaning "different-gilled snails"), is a taxonomic clade of snails and slugs, which includes marine, aquatic and terrestrial gastropod mollusks. Heterobranchia is one of the main clades of gastropods. Currently Heterobranchia comprises three informal groups: the lower heterobranchs, the opisthobranchs and the pulmonates.Bouchet P. & Rocroi J.-P. (Ed.); Frýda J., Hausdorf B., Ponder W., Valdes A. & Warén A. 2005. ''Classification and nomenclator of gastropod families''. Malacologia: International Journal of Malacology, 47(1-2). ConchBooks: Hackenheim, Germany. . . 397 pp. http://www.vliz.be/Vmdcdata/imis2/ref.php?refid=78278 Diversity The three subdivisions of this large clade are quite diverse: * The Lower Heterobranchia includes shelled marine and freshwater species. * Opisthobranchia are almost all marine species, some shelled and some not. The internal organs of the opisthobranchs have undergone detorsion (unwinding of the visc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Heterobranchia
Lower Heterobranchia, also known as the Allogastropoda, is a group of rather specialized, highly evolved sea slugs and sea snails, ( marine gastropod mollusks) within the subclass Heterobranchia. WoRMS (2020). "Lower Heterobranchia". Accessed at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1054700 on 2020-05-16 Although the great majority of Lower Heterobranchs are indeed marine, a few have succeeded in making the transition to freshwater. Description The shell shapes in this group are typically those that are seen in the sundial, pyramid, rissoella and orbitestellid families of snails. Taxonomy 2005 taxonomy In the taxonomy of the Gastropoda by Bouchet & Rocroi, 2005, the Lower Heterobranchia is an Informal Group. Superfamilies within the Lower Heterobranchia include: *Unassigned to a superfamily (orbitestellid-shells) ** Family Cimidae ** † Family Dolomitellidae ** † Family Heterosubulitidae ** † Family Kuskokwimiidae ** † Family Misurinellid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |