|
Acroeimeria Pintoi
''Acroeimeria'' is a genus of parasites that contains those species which initially develop immediately beneath the brush-border of the intestinal epithelium, but the meronts and gamonts of which are early on extruded to form a layer on the surface of the gut mucosa. Morphologically they are similar to the ''Eimeria'' to which they are closely related. The genus was described in 1989 by Paperna and Landsberg. General features The defining feature of this genus is their development, after becoming enclosed by extensions of the host cell membrane, within the resulting parasitophorous 'sack' which bulges out above the surface of the intestinal mucosa. This pattern of development is not known to occur in birds or mammals but is common in fish. The endogenous development of the parasite is intra-cytoplasmic, within the epithelial cells of the ileum. The parasites lie above (closer to the lumen) the host cell nucleus. Below the parasitophorous vacuole, the host cytoplasm expands as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meront
Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organism is typified by a ''cellular variety'' with a distinct morphology and biochemistry. Not all apicomplexa develop all the following cellular varieties and division methods. This presentation is intended as an outline of a hypothetical generalised apicomplexan organism. Methods of asexual replication Apicomplexans (sporozoans) replicate via ways of multiple fission (also known as schizogony). These ways include , and , although the latter is sometimes referred to as schizogony, despite its general meaning. Merogony is an asexually reproductive process of apicomplexa. After infecting a host cell, a trophozoite ( see glossary below) increases in size while repeatedly replicating its nucleus and other organelles. During this process, the org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ameiva Ameiva
''Ameiva ameiva'', also known as the giant ameiva, green ameiva, South American ground lizard, or Amazon racerunner, is a species of lizard in the family Teiidae found in Central, South America, and some Caribbean Islands. Geographic range It is widespread in Central America and South America, including: Panama, Brazil, Colombia, Surinam, French Guiana, Guyana, Venezuela, Bolivia, Ecuador, Peru, Argentina, and Paraguay. It is also found on the Caribbean islands of Trinidad and Tobago, Grenada, the Grenadines, Barbados, Margarita, Swan Island, and Isla de la Providencia. Reptile-database.reptarium.cz It was also once present on Saint Vincent but has since been |
Cnemidophorus Lemniscatus
The rainbow whiptail (''Cnemidophorus lemniscatus'') is a species of lizard found in Central America, the Caribbean, and northern South America. It has also been introduced in Florida and has established populations there. A rainbow whiptail grows up to approximately 12 inches (30.5 cm). Both sexually reproducing and parthenogenetic populations are known. Cnemidophorus lemniscatus (01).JPG, Tayrona National Natural Park, Colombia Rainbow Ameiva.jpg, Tayrona National Natural Park, Colombia Cnemidophorus lemniscatus blue.JPG, Blue specimen in Providencia Island Isla de Providencia, historically Old Providence, and generally known as Providencia, is a mountainous Caribbean island that is part of the Colombian department of Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina and the municipality o ..., Colombia Rainbow whiptail (Cnemidophorus lemniscatus) - Parque Nacional Natural Tayrona 05.jpg, Rainbow whiptail at Tayrona Natural Park. Rainbow whiptail (Cnemidophor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stieda Body
The Stieda body is an organelle located at the polar region of the sporocyst of some coccidia visible with electron microscopy. It appears as a knob like structure and is a plug occluding a hole in the sporocyst. The breakdown of this body allows excystation of the sporozoite Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organism is ...s. References Apicomplexa {{Microbiology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporozoite
Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organism is typified by a ''cellular variety'' with a distinct morphology and biochemistry. Not all apicomplexa develop all the following cellular varieties and division methods. This presentation is intended as an outline of a hypothetical generalised apicomplexan organism. Methods of asexual replication Apicomplexans (sporozoans) replicate via ways of multiple fission (also known as schizogony). These ways include , and , although the latter is sometimes referred to as schizogony, despite its general meaning. Merogony is an asexually reproductive process of apicomplexa. After infecting a host cell, a trophozoite ( see glossary below) increases in size while repeatedly replicating its nucleus and other organelles. During this process, the org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apicomplexa Lifecycle Stages
Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organism is typified by a ''cellular variety'' with a distinct morphology and biochemistry. Not all apicomplexa develop all the following cellular varieties and division methods. This presentation is intended as an outline of a hypothetical generalised apicomplexan organism. Methods of asexual replication Apicomplexans (sporozoans) replicate via ways of multiple fission (also known as schizogony). These ways include , and , although the latter is sometimes referred to as schizogony, despite its general meaning. Merogony is an asexually reproductive process of apicomplexa. After infecting a host cell, a trophozoite ( see glossary below) increases in size while repeatedly replicating its nucleus and other organelles. During this process, the orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
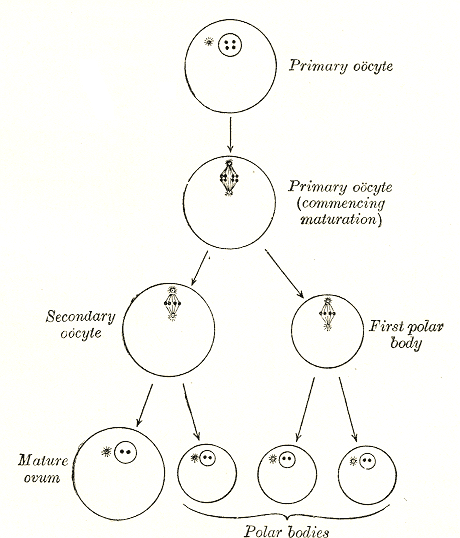
Oocyte
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell (PGC), which then undergoes mitosis, forming oogonia. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Formation The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of ovulation. Characteristics Cytoplasm Oocytes are rich in cytoplasm, which contains yolk granules to nourish the cell early in development. Nucleus During the primary oocyte stage of oogenesis, the nucleus is called a germinal vesicle. The only normal human type of secondary oocyte has t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
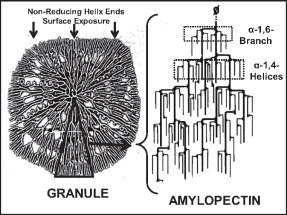
Amylopectin
Amylopectin is a water-insoluble polysaccharide and highly branched polymer of α-glucose units found in plants. It is one of the two components of starch, the other being amylose. Plants store starch within specialized organelles called amyloplasts. To generate energy, the plant hydrolyzes the starch, releasing the glucose subunits. Humans and other animals that eat plant foods also use amylase, an enzyme that assists in breaking down amylopectin, to initiate the hydrolyzation of starch. Starch is made of about 70–80% amylopectin by weight, though it varies depending on the source. For example, it ranges from lower percent content in long-grain rice, amylomaize, and russet potatoes to 100% in glutinous rice, waxy potato starch, and waxy corn. Amylopectin is highly branched, being formed of 2,000 to 200,000 glucose units. Its inner chains are formed of 20–24 glucose subunits. Dissolved amylopectin starch has a lower tendency of retrogradation (a partial recrystallization a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleolus
The nucleolus (, plural: nucleoli ) is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis, which is the synthesis of ribosomes. The nucleolus also participates in the formation of signal recognition particles and plays a role in the cell's response to stress. Nucleoli are made of proteins, DNA and RNA, and form around specific chromosomal regions called nucleolar organizing regions. Malfunction of nucleoli can be the cause of several human conditions called "nucleolopathies" and the nucleolus is being investigated as a target for cancer chemotherapy. History The nucleolus was identified by bright-field microscopy during the 1830s. Little was known about the function of the nucleolus until 1964, when a study of nucleoli by John Gurdon and Donald Brown in the African clawed frog ''Xenopus laevis'' generated increasing interest in the function and detailed structure of the nucleolus. They found that 25% of the frog e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |